
Fong T. Leong, PhD, MRCP
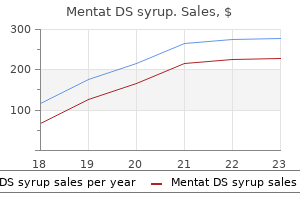
Mentat DS syrup dosages: 100 ml
Mentat DS syrup packs: 1 bottles, 2 bottles, 3 bottles, 4 bottles, 5 bottles, 6 bottles, 7 bottles, 8 bottles, 9 bottles, 10 bottles

Careful analysis of the anatomical and physiological abnormalities is of utmost importance medications interactions buy mentat ds syrup 100 ml with visa. Both the anatomy of the valve area and its function during inspiration and expiration should therefore be carefully examined and measured. Septal Surgery When obstruction at the valve area is caused by a deviation, convexity, or thickening of the cartilaginous septum, we will try to restore normal function by septal surgery. Dealing with a septal deviation or a convexity in area 2 is described and illustrated in detail in Chapter 5, page 187. For instance, a septal convexity in area 2 may be combined with hypertrophy of the head of the lower turbinate. A narrow, prominent pyramid may coincide with atrophy of the triangular cartilage. An excellent overview of the various types of pathology of the valve area was presented by Kern (1978). Inferior Turbinate Surgery When hypertrophy of the head of the inferior turbinate is the cause of obstruction of the valve area, the logical treatment is submucous reduction of the turbinate head (anterior turbinoplasty). Generally, we would first investigate the effect of topical corticosteroids before definitely deciding to perform turbinate reduction by submucosal surgery. Triangular Cartilage Surgery Modifying the inferior margin of the triangular cartilage to improve valvular function is a delicate and risky type of surgery. First of all, the structural basis for the functional disturbance of the valve must be correctly diagnosed. Subsequently, the abnormality must be both anatomically and physiologically corrected in a technically flawless way. Otherwise, the result will be disappointing and the situation may even be worsened. Some methods are said to be effective in almost all cases, for example a spreader graft or a valve plasty. In fact, we object to the propagation of a standard method to correct valve area pathology. If the valve area is narrowed by a septal deviation or convexity, we will correct the septum. If the obstruction is due to a narrow, high valve area, we may let down the pyramid. The caudal part of the triangular cartilage is exposed by careful subcutaneous dissection (on the lateral side of the valve) and submucoperichondrial dissection (on the medial side of the valve). This is best performed with delicate anatomical forceps (Adson-Brown) and pointed, slightly curved scissors.
Therefore medicine woman strain mentat ds syrup 100 ml purchase without prescription, various surgeons have tried to develop less aggressive ways to reduce a dorsal hump. Two techniques that leave the bony pyramid intact have been suggested: the pushdown technique, and let-down after resection of wedges at the base of the bony pyramid. A vertical and a horizontal basal strip are resected from the septum, osteotomies are performed, and the nasal bones are infractured and pushed down. In this way the dorsum is kept intact; however, only small humps can be corrected. Besides, the effect of a push-down is often annihilated in the healing phase (Barelli 1975). The anterior (ventral) margins of the septum and the two medial margins of the triangular cartilages are trimmed as required. An open roof can be prevented by: (1) preserving the mucoperiosteum of the undersurface of the bony pyramid; (2) closing the bony dorsum by bringing the lateral walls together after osteotomies; and (3) inserting crushed septal cartilage under the skin in the area of the hump removal. Some surgeons prefer to reimplant part of the removed hump to cover the open roof. However, we find it difficult to avoid asymmetries and irregularities with this option. These complications can be avoided by: not overstretching the skin while undermining; closing an open roof; leaving a smooth dorsum; and inserting some crushed cartilage or connective tissue to reinforce the skin at the end of the operation. Let-Down (After Resection of Wedges at the Base of the Bony Pyramid) To overcome the shortcomings of the push-down technique, let-down after bilateral wedge resection was suggested (Huizing 1975). In our opinion, the let-down technique is the method of choice to reduce a limited or moderate hump, especially humps that are associated with a prominent, narrow pyramid. Saddling and a saddle nose are generally accepted terms for a more or less severe depression of the bony and/or cartilaginous pyramid. It is seen after severe trauma and infection (septal abscess), but may also be a congenital anomaly or a sequela of a specific disease. Sagging is the common term for a limited depression of the cartilaginous pyramid, which may arise after trauma and septal surgery. Saddling and sagging of the nasal pyramid usually cause both aesthetic and functional complaints. The functional complaints that may be related to saddling and sagging vary considerably. Actually, it would be more correct to call it a technical failure instead of a complication. The bony and cartilaginous dorsa were lowered too much, especially in the region of the K area.
Being honest Most patients accept that something may go wrong during their treatment treatment 32 buy cheap mentat ds syrup 100 ml, especially in surgery. Documentation Make a careful and honest documentation of your considerations and steps, preferably handwritten. Remaining in contact with your patient It is of utmost importance to stay in contact with the patient if treatment has been taken over by another colleague or another hospital. In our experience, patients often do not sue the doctor because of the complication itself but because they are left to deal with it alone. A septal perforation following septal surgery is indeed principally the result of a technical failure. However, this complication can occur even in the hands of the most experienced and careful surgeon. Prevention Some suggestions on reducing the chances of claims and lawsuits have already been presented. Briefly, prevention of medicolegal problems in nasal surgery may be condensed into the following ten questions ("The List of Ten", Huizing 2001): 1. Was the patient duly informed about the diagnosis, the treatment proposal, risks, and alternatives The terms most frequently used by courts are: "careful," "reproachful," "negligent," "average capable," "standard," and "state of the art. By closing the incisions, the tissues are adjusted and fixed in their new positions. Endonasal mucosal and skin incisions are generally closed with resorbable materials. A great advantage of using resorbable sutures endonasally is that no sutures have to be removed from the inside of the nose during the first postoperative days. External skin incisions are closed with nonresorbable monofilament synthetic materials. These are also used to close special incisions in the nasal vestibule, such as infracartilaginous incisions. Fixation of plates or grafts of cartilage to rebuild the septum or other structures is usually done with slowly resorbable materials. By closing the incisions, the tissues are adjusted and fixed in their new positions, postoperative bleeding is prevented, and scarring and stenosis is avoided. Internal dressings serve three purposes: (1) to keep the septum in the midline and prevent septal hematoma; (2) to support the nasal bones, cartilaginous pyramid, and lobular cartilages in their new position; and (3) to limit risk of postoperative bleeding. Currently, the use of internal dressings has diminished, especially in patients in whom no pyramid surgery has been performed.
These nutrients are used for the storage and release of energy medicine woman buy cheap mentat ds syrup 100 ml on line, as well as for growth and for repairing any damage to themselves. Cells can reproduce themselves, not by means of sexual reproduction but by asexual reproduction, in which they first of all develop double the number of organelles and then divide, with the same number and types of organelle and structure present in each half. Cells react to things that irritate or stimulate them; for example, in response to threats from chemicals and viruses. This cell membrane is a semipermeable biological membrane separating the interior of the cell from the outside environment, and protecting the cell from its surrounding environment. It is semipermeable because it allows only certain substances to pass through it for the benefit of the cell itself. For example, it is selectively permeable to certain ions and molecules (Alberts et al. Contained within the cell membrane are the cytoplasm and the organelles, which include amongst others such organelles as the lysosomes, mitochondria and the nucleus of the cell. In the bilayer of the cell membrane, all the heads of each phospholipid molecule are situated facing outwards on the outer and inner surfaces of the cell, whilst the tails point into the cell membrane; it is this central part of the cell membrane consisting of hydrophobic tails that makes the cell impermeable to water-soluble molecules (Nair, 2011). In addition to the phospholipid molecules, the cell membrane contains a variety of molecules, mainly proteins and lipids, and these are involved in many different cellular functions, such as communication and transport. The reversible attachment of proteins to cell membranes has been shown to regulate cell signalling, and these cell membrane proteins are also involved in many other important cellular events, such as acting as enzymes to catalyse cellular reactions through a variety of mechanisms (Cafiso, 2005). The cell Chapter 4 Fluid mosaic model According to the fluid mosaic model, biological membranes can be considered as a twodimensional liquid in which lipid and protein molecules diffuse more or less easily (Singer and Nicolson, 1972). Although the lipid bilayers forming the basis of the membranes do form twodimensional liquids by themselves, the plasma membrane also contains a large quantity of proteins, providing more structure. Examples of such structures are protein-to-protein complexes formed by the cytoskeleton. It allows the cells to attach to each other and form tissues by attaching to the cellular matrix. It is responsible for the transport of materials/substances needed for the functioning of the cell organelles. By means of its protein molecules, it receives signals from other cells or from the outside environment, which it then converts into messages for organelle response. In some of our cells, the membrane protein molecules group together to form enzymes. The cell membrane proteins help to transport very small molecules through the cell membranebut only if the very small molecules are moving from an area of high concentration of these molecules to one of low concentration. Some are receptors, enabling hormones and other substances, such as neurotransmitters, to play their roles. Finally, some of these proteins are glycoproteins playing an important role in cell-to-cell recognition; for example, the mucins found in the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts. These proteins in the cell membrane have many functions; for example:Having introduced the cell membrane, we can now explore some of its functions and roles in more detail.
Eye drops and contact lens wear Contact lens wear 142 It is generally not good practice to continue wearing contact lenses while having topical treatment for an eye condition symptoms nasal polyps generic mentat ds syrup 100 ml on line. This may not be such a problem Drugs commonly used for acute eye conditions for daily disposable contact lens wearers but should be avoided in extended wear lenses. The eye problem may well have been caused by contact lens wear in the first place and therefore part of the treatment would be avoiding contact lens wear for a period of three to four weeks or longer. It may also be worth bearing in mind that some systemic medications can affect the eye surface or tear quality. Gas permeable lenses are not affected by topical eye drops and there may be some cases where topical treatment is extensive and contact lens wear could be resumed when the eye is more comfortable, for example in iritis when treatment continues usually for four to six weeks. Take care when instilling fluorescein sodium dye, used for the detection of corneal abrasions or lesions, as a soft contact lens will stain bright yellow and cannot be salvaged. The formation and secretion of aqueous humour by the ciliary body is a complex process in which the enzyme carbonic anhydrase plays an important role. Acetazolamide is a member of a small group of drugs known as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Systemically it produces a slight diuresis and it is also used in the treatment of epilepsy. This is followed by oral doses of 250 mg, but no more than 1g total should be given over 24 hours (rarely, a consultant ophthalmologist may prescribe an additional dose if complete sight loss is threatened). It has many quite serious side effects, the commonest, including tingling of hands and face, nausea, confusion and sleepiness, being the least serious. Pilocarpine hydrochloride (2 and 4%) is a miotic, a parasympathomimetic drug which produces a small pupil thus pulling the trabecular meshwork open to facilitate aqueous drainage from the anterior chamber of the eye. It is not readily absorbed into the circulation of the eye until the intra-ocular pressure begins to fall. Antibiotics Antibiotics these are preparations that are prescribed to combat bacteria that are sensitive to their effects and are either bacteriostatic or bacteriocidal. Chloramphenicol is a bacteriostatic, broad spectrum antibiotic used widely for minor eye infections and bacterial conjunctivitis. Use eye drops either four times a day for five to seven days or two hourly for two days then four times a day for five days if the eye is very sticky. Chloramphenicol ointment is used more for chalazia, corneal abrasions or keratitis where a lubricating effect is also required. Use chloramphenicol ointment twice a day, three times a day or four times a day, depending on the condition.
Syndromes
The neurocranium reaches 90% of its adult dimensions by the the septum develops from the medial wall of the nasal capsule between the seventh to eighth week and the second to third month of embryonic life symptoms 4 months pregnant mentat ds syrup 100 ml buy with amex. In the beginning, it is completely cartilaginous; later, some parts start to ossify. After birth, the posterior part of the septum gradually ossifies from cranial to caudal and from caudal to cranial directions. The septum, in particular its anterior part, demonstrates rapid growth in neonatal life and in early childhood. The septum plays a decisive role in the ventral growth of the nasal pyramid, the nasal cavity, and the midface. While the growth of the more caudal part of the septal cartilage influences the outgrowth of the midface, the growth of its anterior and ventral part determines the prominence and length of the nasal pyramid. This has also been demonstrated in patients who have suffered a septal injury in early childhood (Huizing 1966; Pirsig 1977, 1992; Grymer 1997). Cartilaginous Septum the cartilaginous septum grows rapidly in the first 2 years of life. At that point, the cranial and posterior part of the cartilaginous septum starts to ossify by enchondral ossification in an anterior and caudal direction, thereby forming the perpendicular plate. This process starts in the sixth month in the region of the crista galli, and slowly proceeds in a caudal and anterior direction. Growth of the perpendicular plate continues at a fast pace until the age of 10 years. Premaxilla the premaxilla, previously called the intermaxillary bone (see blue box), is formed by two ossification centers that emerge at about 8 to 9 weeks of age. Then, from the posterior part of the cranial half, a wing starts to develop on both sides. These premaxillary alae continue to grow throughout childhood and particularly during puberty. Since this is where the upper incisor teeth develop, early trauma to this area may lead to irregularities in the position or eruption of the upper teeth. Vomer the vomer ossifies by intramembranous ossification between the 12th postovulatory week and birth. The cranialnterior parts of these lamellae are V-shaped and hold the posterior part of the cartilaginous septum. The intermaxillary bone was a topic of fierce debate in the second half of the 18th century. The leading anatomists of the time, in particular Petrus Camper of Groningen, were of the opinion that the intermaxillary bone is missing in humans. In this respect, humans were believed to differ from the great apes and all higher developed mammals. The "missing intermaxillary bone" was generally accepted as proof that humans were created by God and had not descended from the apes.
Therefore medicine encyclopedia buy mentat ds syrup 100 ml with amex, a medial cord lesion, or ulnar plus palsy, would, in addition to causing ulnar motor loss, cause median nervennervated thumb weakness, as well as difficulty extending the proximal interphalangeal joints of the first two fingers (lumbricals). Of note, these C8, T1 median nerve muscles are the same ones whose innervation is exchanged with a Martin-Gruber anastomosis (see Chapter 1). The medial cord has a few side branches that can be tested to confirm its involvement. The medial brachial and antebrachial cutaneous nerves originate from the distal medial cord and carry sensation from the medial aspect of the arm and forearm, respectively. The medial pectoral nerve originates from the proximal medial cord, and, if damaged, causes weakness in the sternal head of the pectoralis major. The presence of T1 fibers in the posterior cord is controversial and, needless to say, variable. Hence, a posterior cord injury may be called a radial-axillary palsy or radial plus palsy. A radial palsy causes weakness in elbow extension (triceps), forearm supination (supinator), wrist extension (extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis, extensor carpi ulnaris), and finger/thumb extension (superficial and deep finger extensors). Radial nerve sensory loss involves the posterior arm (posterior brachial cutaneous nerve) and forearm (posterior antebrachial cutaneous nerve), the lower lateral aspect of the arm (lower lateral brachial cutaneous nerve), and the dorsolateral hand (superficial sensory radial nerve). An axillary nerve lesion can also cause sensory loss in the upper lateral arm (upper lateral brachial cutaneous nerve). Furthermore, arm adduction and internal rotation weakness helps confirm posterior cord damage because branches off the posterior cord control these movements. The two terminal branches of the posterior cord are the radial and axillary nerves; therefore, a palsy affecting these two nerves is the hallmark of a posterior cord injury. With this knowledge, diagnosis of cord-level injuries becomes straightforward; cord injuries cause deficits that are a combination of those seen with injury to their branches. Therefore, analogous to proximal brachial plexus injury being assessed by referring to its spinal nerve components, the distal plexus is evaluated by using knowledge of its major terminal branches. Therefore, it is usually not possible to say if the divisions are damaged in addition to cords or trunks without surgical exploration. An isolated injury to one, or more, divisions yields neurological deficits that are the same, or less severe, than a cord-level injury. For example, an injury to 130 Clinical Evaluation of the Brachial Plexus the anterior division of the lower trunk (C8, T1) should involve nearly all the fibers in the medial cord. However, a divisional injury affecting the lateral cord may involve only the anterior division from the upper trunk (C5, C6) or the anterior division from the middle trunk (C7). Injury to any of the three posterior divisions will cause a partial posterior cord deficit. For instance, an isolated injury to the posterior division of the upper trunk may be confused with an axillary nerve palsy; however, the presence of some brachioradialis and supinator weakness, along with sensory loss on the dorsal thumb (C6 dermatome via superficial sensory radial nerve) should point to a partial cord or divisional injury rather than an axillary nerve palsy. With an ability to readily diagnose proximal and distal brachial plexus lesions, one can deduce a divisional injury.
In the distal forearm symptoms 2 year molars discount mentat ds syrup 100 ml otc, the ulnar artery joins the ulnar nerve, and together they travel toward the wrist. Prior to passing below the median nerve in the antecubital fossa, the ulnar artery gives the interosseous communis artery, which shortly thereafter divides into the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries. The anterior interosseous artery passes distally with the anterior interosseous nerve, deep between the flexor pollicis longus and flexor digitorum profundus. The tabletop is composed of carpal bones, with the legs of the table being the hook of the hamate and pisiform medially, and the tubercle of the trapezium and distal pole of the scaphoid laterally. Stretched over these legs, like a rug on an imaginary floor, is the thick transverse carpal ligament. From a volar viewpoint, the median nerve is the most superficial of nine structures running through the carpal tunnel. The palmaris longus tendon does not enter the carpal tunnel, but instead attaches more superficially to the palmaris aponeurosis. The median nerve is the most superficial of nine structures running though the carpal tunnel. These other structures include the flexor pollicis longus tendon, four superficial flexor tendons, and four deep flexor tendons. After passing through the carpal tunnel, the median nerve gives a branch off its radial side: the thenar motor branch (or recurrent thenar motor branch). Next, in the deep palm, the median nerve splits into two divisions: radial and ulnar. The radial division divides into the common digital nerve to the thumb and the proper digital nerve to the radial half of the index finger. The common digital nerve to the thumb subsequently divides into the two proper digital nerves to the thumb. The ulnar division of the median nerve divides into the common digital nerves of the second and third web spaces, which also subsequently divide into proper digital nerves. For instance, it can prematurely originate within the carpal tunnel, it can pierce the transverse carpal ligament for a more direct route to the thenar muscles, and it can even emerge on the ulnar side of the median nerve, only to then cross deep or superficial to the median nerve to reach the thenar muscles. Other median nerve variations within the hand include (1) an early branching of the median nerve into radial and ulnar divisions proximal to the carpal tunnel (which often occurs with a "persistent median artery"), and (2) a connection between the thenar motor branch and the deep palmar branch of the ulnar nerve (discussion follows). To aid memorization, these muscles may be separated into four sequential groups: proximal forearm, anterior interosseous, thenar motor, and terminal. The pronator teres (C6, C7) is the main pronator of the forearm and the first muscle innervated by the median nerve. Branches to the pronator teres exit the median nerve at the lowest aspect of the upper arm, prior to the median nerve passing between the two heads of the pronator teres. From a mechanical perspective, the elbow needs to be extended for the pronator teres to have mechanical advantage. Therefore, to test this muscle the elbow should be extended with the forearm fully pronated.

Metabolic process: a set of chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms treatment junctional tachycardia mentat ds syrup 100 ml purchase without prescription. These chemical reactions are catalysed by enzymes and allow organisms to carry out their basic functions. Neutral substance: Neutron: the part of an atom that carries no electrical charge. Osmosis: the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration; this allows for equilibrium of solute and water density on both sides of the semi-permeable membrane. Scientific principles Chapter 3 Periodic table: a table of all the known chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, and recurring chemical properties. As a consequence, the molecules that are then formed also carry a weak negative electrical charge that allows molecules to covalently bondjust like atoms. They are also known as hydrogen bonds because hydrogen molecules generally have to be present for polar bonding to occur. Receptors (of a cell surface): specialized integral membrane proteins that take part in communication between the cell and the outside world. Shell (of an atom): the name that is given to the orbits of electrons moving around the nucleus (containing protons and electrons) of an atom. Vickers Aim To introduce the student to the cell, which underpins the whole anatomy (structure) and functioning (physiology) of the body. Learning outcomes On completion of this chapter the reader will be able to:Understand the structure of a cell. Test your prior knowledgeWhat are the three main parts of a human cell Can you name one of the major hormones that regulates fluid and electrolytes in the body It functions so well that most of the time we are unaware of the basic functions of the body, such as respiration, digestion and excretion. In the same way, the cellswhich combine together to make up the bodyare miracles of biochemical engineering. They function so that the body itself can function, and in this chapter we will explore the cells in order to better understand the structure and functioning of the body. In the average adult human, there are around 10 trillion cells (10 000 000 000 000), although that depends upon height and weight. However, all our present cells are exact clones of the original cells we had at birth. There are many different types of cells in our body, and they differ as regards to their size, shape, colour, behaviour and habitat. However, there are many similarities between our different cells, including, for example, their chemical composition, their chemical and biochemical behaviour, and detailed structure (Vickers, 2009). For example, the human body is made up of many millions of cells and is therefore known as a multicellular organism.

During wrist flexion the flexor carpi radialis tendon can be observed and palpated proximal to the wrist symptoms 32 weeks pregnant generic mentat ds syrup 100 ml buy line. The palmaris longus (C7, C8) is attached to the palmar aponeurosis and corrugates the palmar skin. This muscle is not readily examined for muscular strength, and, in fact, is absent in about 15% of the population. The flexor digitorum superficialis (known as the sublimis muscle, C8, T1) is also innervated by the median nerve. This muscle flexes the second through fifth digits (all except the thumb) at their proximal interphalangeal joints. To assess proximal interphalangeal joint flexion, each finger is tested separately. This maneuver places the finger to be tested in mild flexion at the metacarpalhalangeal (knuckle) joint, and simultaneously stabilizes the remaining fingers in extension, a position that allows isolation of the flexor digitorum superficialis. It does, however, innervate numerous muscles in the forearm and hand that are involved in forearm pronation, wrist flexion, flexion of the digits (especially the first three), and thumb opposition and abduction. The patient is then instructed to resist supination of the forearm by the examiner. For severe weakness, have the patient flex the wrist with the forearm on a table, ulnar side down, which eliminates gravity. Placing your fingers between the single finger to be tested and the remaining fingers that are immobilized isolates this movement. This maneuver places the finger to be tested in mild flexion at the metacarpalhalangeal (knuckle) joint and stabilizes the remaining fingers in extension, a position that allows isolation of the flexor digitorum superficialis. A topographical aid in identifying the muscles of the medial forearm flexorpronator mass is to place a hand on the opposite forearm with its thenar eminence on the medial epicondyle, the ring finger along the medial border of the forearm, and the rest of the fingers naturally lying over the forearm pointing in a distal trajectory toward the other hand. In this position, the thumb is over the pronator teres, the index finger is over the flexor carpi radialis, the long finger is over the palmaris longus, and the ring finger is along the flexor carpi ulnaris, the latter being innervated by the ulnar nerve. When testing forearm pronation the patient should keep the fingers and hand relaxed to avoid supplemental pronation by the flexor carpi radialis and long finger flexors. When testing the finger flexors the wrist should be kept neutral and not allowed to extend because wrist extension causes passive finger flexion secondary to tenodesis. The flexor digitorum profundus (C8, T1), as a whole, is innervated by both the median and the ulnar nerves. Distal interphalangeal joint flexion of the third (or long) digit has variable dominance by the median or ulnar nerves.
Einar, 57 years: Delayed median palsies can also occur secondary to progressive callus formation or misalignment. They also produce substances that cause the cell to self-destructa process known as apoptosis.
Agenak, 47 years: Neurological Sequelae of Infectious Endocarditis Infection of the heart valves is frequently caused by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus species, with S aureus often being the cause in those who have neurological complications. Chest (4): Palpitations (pounding heart, accelerated heart rate); chest pain/discomfort; shortness of breath/smothering; feeling of choking.
Samuel, 21 years: If no septal cartilage is available, auricular cartilage is the second choice (see page 244 and page 350). Prevention A postoperative septal hematoma can almost always be avoided by taking the following precautions (see also Chapter 5, page 172): Coagulation of bleeding arterioles in the septal framework (premaxilla, maxillary crest) Careful cleansing of the intraseptal space at the end of surgery Closing the septal space by conscientiously adjusting the mucosal blades with an internal dressing or splint In our experience, there is no indication to routinely incise the mucosa for drainage, although many surgeons say that they feel "safer" doing so.
Peratur, 41 years: Neuropsychiatric symptoms reported with temporal lobe epilepsy include psychosis, fear, anxiety, hypergraphia, hypermorality, and altered sexual function. Occurrence of metabolic syndrome should be investigated, and modifiable risk factors aggressively treated especially in obese patients.
Campa, 44 years: Detection of particles within the nasal airways before and after nasal decongestion. Cerebral neuroblastoma-not to be confused with peripheral neuroblastoma arising from the sympathetic chain and adrenal medulla, often associated with opsoclonus and myoclonus characterized by an unsteady, trembling gait, myoclonus (brief, shock-like muscle spasms), and opsoclonus (irregular, rapid eye movements) [see also under neuronal tumors].
Randall, 29 years: A rectangular piece of cartilage of sufficient size is now resected from the posterior part of the cartilaginous septum. Mitochondria are often found concentrated in regions of the cell associated with intense metabolic activity.
Dan, 54 years: The superficial branch splits into digital nerves destined for the fourth and fifth digits. Spinal cord contusion may present as central cord syndrome due to venous congestion of the central spinal cord: Disproportionate weakness of the upper extremities (especially hands) > lower extremities, sensory level with sparing of sacral sensation, urinary retention, and other signs of myelopathy.
References