
Peter Bartlett Bressler, MD

https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/peter-bartlett-bressler-md
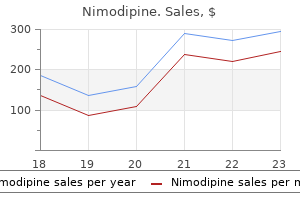
Nimodipine dosages: 30 mg
Nimodipine packs: 30 caps, 60 caps, 90 caps, 120 caps, 180 caps, 270 caps, 360 caps

As part of the ongoing molecular revolution in biology muscle relaxant safe in pregnancy nimodipine 30 mg buy mastercard, fungal taxonomy is ever more strongly influenced by our greatly increased understanding of population genetics (6). Dermatophytes show two population genetics patterns differing among species having "population hosts" (7) in different zoological families, orders, or classes (8, 9). Other species, particularly those with human, ungulate, equine, or avian population hosts, have no access to a soil-based location suitable for sexual reproduction and host reinfection; not surprisingly, these species are found on investigation to be asexual and clonal. They consist, in all known cases, of genetically highly uniform isolates (1012) sharing, where known, a single mating type factor (8, 13). Most appear to have evolved from a single strain of a sexual ancestral species that was able to make the rare, successful switch to ongoing contagious infection of a new animal host. A few epidemiological and phenotypic characters in the clonal species appear to have undergone accelerated evolution due to strong selection for increased compatibility with the new host. This process has tended to produce differences allowing relatively easy laboratory identification of these species. At the same time, the basic cellular "housekeeping" genes investigated in phylogenetic taxonomic studies have evolved at a normal rate and thus strongly tend to resemble forms seen in ancestral species complexes or in sibling species. This suggests that further genetic study will tend to support the lineages in question as recently diverged but nonetheless separate at the species level. In this respect, it is important to note that recent proteomic approaches support essentially the same phylogenies as those previously proposed based on phenotypic, clinical, and epidemiological characters (18). Thus, the present chapter retains a relatively cautious approach to the ongoing debates in this area (19), synonymizing traditionally recognized species only when there is unequivocal, multigene molecular evidence that they are not supported at the species level. Dermatophytoses and Superficial Mycoses n 2129 No pH change Neg Neg Yellow colony on LowensteinJensen medium (compare T. They are grouped into three categories based on host preference and natural habitat (Table 2) (20). Anthropophilic species almost exclusively infect humans; animals are rarely infected. Geophilic species are soil-associated organisms, and soil per se or soilborne keratinous debris. Zoophilic species are essentially pathogens of nonhuman mammals or, rarely, birds; however, animalto-human transmission is not uncommon. Understanding this ecological classification for case isolates may be helpful in determining the source of infection;. Clinical species identification of dermatophytes assists in controlling infections that may have a family pet or other domesticated animal as an ongoing source of inoculum. However, the ability of dermatophytes to spread to new geographical niches in conjunction with population movements should not be underestimated. Thus, care should be taken against complacent assumptions based on historical epidemiological patterns.
Eurytrema pancreaticum Diplostomida Diplostomoidea Schistosomatoidea Plagiorchiida Gymnophalloidea Echinostomatoidea Clinostomidae Gymnophallidae Echinostomatidae Opisthorchioidae Fasciolidae Heterophyidae Fasciola hepatica spasms of pain from stones in the kidney nimodipine 30 mg order free shipping, Fasciolopsis buski Opisthorchidae Paramphistomoidea Plagiorchioidea Zygocotylidae Lecithodendriidae Paragonimidae Plagiorchiidae Troglotrematidae Achillurbainiidae Dicrocoeliidae Clonorchis sinensis, Opisthorchis felineus, O. There are 14 orders in the class Cestoda, of which two contain species that infect humans: the Pseudophyllidea, which attach by means of grooves on the sides of the scolex, and the Cyclophyllidea, which attach by means of four cuplike suckers assisted in some cases by hooks. The classification adopted here (Table 4) is based on the one given by Khali (27) and widely used in textbooks. More information about the cestodes that affect humans can be found in chapter 145 of this volume. An interim utilitarian ("user-friendly") hierarchical classification and characterization of the protists. Principles of protein and lipid targeting in secondary symbiogenesis: eugelenoid, dinoflagellate, and sporozoan plastid origins and the eukaryote family tree. Early evolution of eukaryote feeding modes, cell structural diversity, and classification of the protozoan phyla. Two species are occasional parasites of humans, Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus and Moniliformis moniliformis. An outline classification of the acanthocephalan worms that affect humans is shown in Table 5. The aim of this chapter is to present an outline classification of the parasites that affect humans in order to provide a framework within which particular genera or species can be placed. There are several lists of parasites available in the literature, the most authoritative and comprehensive, but now somewhat dated, is Ashford and Crewe (28); there is also an excellent list of foodborne intestinal parasites by Fried and colleagues (29). There is also a lot of information on various websites, but much of this must be treated with caution. A new system for Nematoda combining morphological characters with molecular trees, and translating clades into ranks and taxa, p 633653. The new higher level classification of eukaryotes with emphasis on the taxonomy of protists. New insights on classification, identification and clinical relevance of Blastocystis spp. Parasite identification is frequently based on brightfield microscopic analysis of concentrated and/or stained preparations. Small organisms often require high magnification such as with oil immersion (Ч1,000). Furthermore, new commercial test kits designed especially for detection of fecal antigens. Diagnostic techniques are available to detect a large range of protozoan and helminth species in different clinical specimens. An important precondition for reliable diagnostic results is the proper collection, processing, and examination of clinical specimens.
Light infections are usually asymptomatic muscle relaxant usage generic nimodipine 30 mg buy on line, but heavy infections can induce disease. Symptoms most commonly are associated with an acute phase of infection and may include fever, abdominal pain, hepatitis-like symptoms, and eosinophilia. A number of asymptomatic hepatobiliary abnormalities are associated with infection (49). Severe infestations with these liver flukes, which are rare, might cause obstructive jaundice, cirrhosis, cholangitis, cholecystitis, bile peritonitis, biliary obstruction, intrahepatic stone formation, cholelithiasis, biliary and liver abscesses, pancreatitis, and hepatitis. Acute disease arises because of extensive tissue damage as parasites migrate through the hepatic parenchyma to gain access to the bile ducts. Parasite activity in the bile ducts leads to proliferation of ductal epithelium, inflammation, and fibrosis. Heavy infections can lead to cholestasis and result in hepatic atrophy and periportal cirrhosis (23). These isolates generally display reduced sensitivity to the anthelminthic triclabendazole, which remains a problem in livestock industries but not yet in human treatments (55). Liver fasciolids have a long (2-month) prepatent period, and because of this, fascioliasis is one disease where serological diagnosis is valuable. Commercial and government laboratories in many countries have serological tests for human fascioliasis, including a reference laboratory at the University of Puerto Rico. Anthelminthic Susceptibility and Treatment Treatment for clonorchiasis or opisthorchiasis relies on oral administration of praziquantel (25 mg/kg three times per day for up to two consecutive days is a dosage commonly used in hospitals, while a single oral dose of 40 mg/kg is Collection, Transport, and Storage Diagnosis is made by detection of characteristic embryonated eggs in feces. Recent proof-of-concept studies have shown that the Chinese anthelminthic tribendimidine possesses high activities against O. Fasciola species are insensitive to praziquantel, and triclabendazole is the drug of choice (Table 2). There have been reports of triclabendazole-insensitive isolates in livestock (55). Artemether and artesunate have undergone trials for use in humans, but they have demonstrated only little effect against Fasciola spp. The current drug of choice is praziquantel, but albendazole and mebendazole have also undergone trials (61, 63). Family Heterophyidae Many species of heterophyid trematodes are known to infect humans (61, 65). Commonly encountered heterophyids of humans are Heterophyes heterophyes, Metagonimus yokogawai, and Haplorchis species. The adult flukes are intestinal inhabitants of a wide range of piscivorous birds and mammals. Humans are infected by consumption of raw, freshly salted, or undercooked fish (Table 3). Disease symptoms in humans relate to infection intensity and arise because of parasite irritation of the intestinal mucosa. Diagnosis of heterophyids is facilitated by observation of eggs in feces (Table 3).
Subsequently muscle relaxant liver disease 30 mg nimodipine overnight delivery, it became apparent that a clear distinction between the two syndromes was often difficult. Even though it had been postulated for a long time that massive thrombus formation was due to the presence in the circulation of substance(s) that aggregated platelets intravascularly, the putative aggregating agent had remained elusive. It remained to be explained why ultra-large multimers, normally absent, were present in patient plasma. Tools to accurately differentiate one disease from the other are not yet readily available. Recently, greater awareness and perhaps improved diagnostic facilities give the impression that incidence is increasing. Failure of cleavage leads to the persistence in plasma and onto endothelial cells of ultra-large multimers, which aggregate platelets, especially in conditions of high shear forces. There are also forms secondary to metastatic tumors, organ transplantation (particularly allogeneic bone marrow and solid organ transplants) and the use of such drugs as ciclosporin, mitomycin and interferon. Because of the variability of presenting symptoms and associated comorbid conditions (see Table 43. Microthrombi are found in several organs (mainly brain, kidney, myocardium, adrenal gland, digestive tract and pancreas) and lead to multiorgan failure, whereas grossly detectable thrombi in large arterial and venous blood vessels are usually lacking. It usually occurs early after birth or during early childhood, although in relatively rare instances the genetic disease may become manifest in adulthood. Most of the identified mutations are missense; the remaining are nonsense, frameshift and splicing mutations generating truncated forms of the protease. However, it can also arise secondary to other conditions: immunomediated diseases, infections, drug intake, pregnancy, sepsis, tumours and bone marrow transplantation. Signs of mechanical haemolytic anaemia (haematocrit usually <20%) include the presence of schistocytes on peripheral blood smears, reticulocytosis, high indirect serum bilirubin, low or unmeasurable haptoglobin and negative direct Coombs test. Neurological symptoms (coma, stroke, seizures or focal signs such as motor deficits, diplopia and aphasia) typically fluctuate in presentation and severity as a result of the ongoing formation and dissolution of thrombi in the cerebral microcirculation. Other symptoms or signs (such as headache, blurred vision, ataxia or mental status changes) are less typical.
Neonatal stroke (see also Chapter 50) Heritable thrombophilic defects are associated with perinatal brain injury spasms under belly button nimodipine 30 mg order fast delivery. The pathogenesis is thrombosis in either cerebral arteries or cerebral veins or sinuses. Thrombophilia is not a significant risk factor for ischaemic stroke in adults, as it does not increase the risk of arterial thrombosis (but cerebral vein thrombosis can present as stroke). In the neonate the pathophysiology of stroke is quite different and thrombophilia may increase the risk of arterial thrombosis and stroke in the neonate or fetus. There are two potential explanations for this: 1 the circulation in the neonate is different. In the fetus and neonate the lungs are bypassed by the ductus arteriosus and so it is possible for clots arising in the venous system to bypass the lungs and occlude a cerebral artery. It is possible that the coagulability of blood in fetal and neonatal arteries is influenced by thrombophilic defects. Testing for defects may therefore identify a material contributory factor, but does not typically inform management decisions. For example, anticoagulant therapy is not usually considered in children found to have a suffered a stroke in the neonatal period and there may be significant time before a neurological deficit is recognized or the cause of stroke determined. In practice, testing is sometimes performed in order to explain to parents why a stroke possibly occurred. A full blood count and platelet count are useful indicators of general health and will identify myeloproliferative disorders that increase thrombotic risk. Testing is usually delayed until at least 1 month after completion of a course of anticoagulation with a vitamin K antagonist. Sometimes testing is performed during pregnancy and so interpretation of results must be made with reference to the effect of the pregnancy on results. For example, a protein C chromogenic assay will not detect a dysfunctional protein C molecule with impaired phospholipid binding due to a mutation in the Gla domain. A clot-based protein C assay would be sensitive to this defect, but imprecision of the assay would result in reduced sensitivity and specificity for other defects compared with a chromogenic assay. For example, an assay utilizing a short heparin incubation time will detect heparin binding-site defects, which may not be associated with an appreciably increased risk of venous thrombosis. Even in families with characterized defects, a phenotypic assay may fail to accurately discriminate affected and non-affected individuals. True heritable deficiencies may not be detected and false-positive diagnoses are common, 1 in 40 will have a level below the lower limit of the reference range and few of these have inherited deficiency.
Phaeohyphomycosis Superficial Calosphaeriales Botryosphaeriales Neoscytalidium dimidiatum is a common plant pathogen in the tropics and is regularly involved in syndromes very similar to dermatophytosis on skin and nails spasms muscle twitching nimodipine 30 mg purchase line, usually leading to extensive hyperkeratosis (60). Members of the order Calosphaeriales are typical agents of subcutaneous infections. Most of the six pathogenic species of Phaeoacremonium cause this type of infection, P. Human infections by Pleurostomophora richardsiae mostly involve subcutaneous cysts (80), occasionally with bone involvement (81). Most patients have some underlying condition such as diabetes or transplantation (82). Capnodiales the halophilic species Hortaea werneckii can adhere to exceptionally salty human hands (46), causing a syndrome in the dead keratin layers known as tinea nigra. Chaetothyriales Chaetothyriales Some species of the order Chaetothyriales cause occasional superficial infections in humans. Recently described was Knufia epidermidis, which so far has almost exclusively been found on human skin (16). The species may cause asymptomatic infections, may be found in association with dermatophyte infections, or may cause mild cutaneous infections. Phialophora europaea is fairly commonly involved in mild skin and nail infections (58), but due to its slow growth, it is frequently overlooked. Exophiala dermatitidis is the most commonly encountered species in clinical settings, causing infections of cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues (83) in mostly immunocompromised patients. Exophiala jeansemei is considered an agent of mycetoma (86), often in otherwise healthy individuals. Microascales Several species of Scedosporium are common causes of subcutaneous infections and mycetoma in temperate regions, especially in North America (87, 88), having a predilection for the joints. Cutaneous and Corneal Pleosporales Botryosphaeriales Lasiodiplodia theobromae is occasionally found to cause ocular infections following injury to the cornea (61, 62). Members of the order Pleosporales (most commonly Curvularia, Exserohilum, and Alternaria) are able to cause subcutaneous infections, although more commonly they produce 124. Curvularia, Exophiala, Scedosporium, Sporothrix, and Other Melanized Fungi n 2163 allergic sinusitis with occasional cerebral involvement in otherwise healthy individuals (36, 41, 68, 89). Microascales Relatively common deep and disseminated infections caused by Scedosporium are noted for immunosuppressed or otherwise debilitated patients. In severely compromised patients, cerebral dissemination may take place from local foci.
One fungus muscle relaxant gel nimodipine 30 mg buy fast delivery, one name: defining the genus Fusarium in a scientifically robust way that preserves longstanding use. Miscellaneous opportunistic fungi: Microascaceae and other ascomycetes, hyphomycetes, coelomycetes and basidiomycetes. New Fusarium species and combinations within the Gibberella fujikuroi species complex. Molecular systematics and phylogeography of the Gibberella fujikuroi species complex. A multigene phylogeny of the Gibberella fujikuroi species complex: detection of additional phylogenetically distinct species. Phylogenetic diversity and microsphere array-based genotyping of human pathogenic Fusaria, including isolates from the multistate contact lens-associated U. Molecular phylogenetic diversity, multilocus haplotype nomenclature, and in vitro antifungal resistance within the Fusarium solani species complex. Novel multilocus sequence typing scheme reveals high genetic diversity of human pathogenic members of the Fusarium incarnatum-F. Members of the Fusarium solani species complex that cause infections in both humans and plants are common in the environment. A new dawn for the naming of fungi: impacts of decisions made in Melbourne in July 2011 on the future publication and regulation of fungal names. Fusarium infections in immunocompromised patients: case reports and literature review. Comparative assessment of genotyping methods for study genetic diversity of Fusarium oxysporum isolates. Genotyping of 44 isolates of Fusarium solani, the main agent of fungal keratitis in Brazil. Widespread occurrence of diverse human pathogenic types of the fungus Fusarium detected in plumbing drains. Phylogenetic relationships among members of the Fusarium solani species complex in human infections and the descriptions of F. Recovery of filamentous fungi from water in a paediatric bone marrow transplantation unit. Indoor mold, toxigenic fungi, and Stachybotrys chartarum: infectious disease perspective. Onychomycosis as a possible origin of disseminated Fusarium solani infection in a patient with severe aplastic anemia. Raad I, Tarrand J, Hanna H, Albitar M, Janssen E, Boktour M, Bodey G, Mardani M, Hachem R, Kontoyiannis D, Whimbey E, Rolston K. Epidemiology, molecular mycology, and environmental sources of Fusarium infection in patients with cancer.
Makas, 40 years: Detection of trophozoites and cysts does not, however, allow differentiation of the pathogenic species, E. However, in these cases, newly emerging mutations associated with resistance may not be detected by the genotypic assay and phenotypic assay may be more predictive of viral resistance. Observing the organism in permanent-stained preparations makes identification more definitive. The recent surge in development of new antifungal agents has greatly increased the number of drugs available to combat the growing number of serious fungal infections.
Spike, 45 years: These are useful for visualizing the polysaccharide capsule produced by Cryptococcus species in histological sections of tissue. The laboratory should confirm such mutations with those identified by "recombinant phenotyping" (52) if the literature is not supportive or clinical drug efficacy has not been achieved. A fatal case of babesiosis in Missouri: identification of another piroplasm that infects humans. Among the three known genera of dermatophytes-Epidermophyton, Microsporum, and Trichophyton-Trichophyton species, especially T.
Temmy, 34 years: In unusual situations, molecular direct detection methods may be invaluable: for example, in a deep dermatophytosis case in which all conventional tests had given negative results, T. Direct Examination by Microscopy Microscopic examination of the stool may demonstrate a mixture of eggs and larvae. At present, the Fungitell assay is indicated for presumptive diagnosis of fungal infection and should be used in conjunction with other diagnostic procedures. Obligate myiasis reflects the need for larvae to feed well during development because adult flies do not feed or feed poorly.
Givess, 57 years: Nymphs develop from fed larvae, and they in turn develop into the adult male and female. CaMdr1 confers intermediate-level resistance to fluconazole, in contrast to CaCdr1, which is associated with efflux of a wider range of substrates at higher capacity. There is a definite need for more standardization of both phenotypic and genotypic assays. Microsporidial species causing disseminated infection have been found in almost every organ system (1).
Dolok, 37 years: Scabies infestations can be easily diagnosed by scraping a newly developed papule (not one that has been scratched) with a scalpel coated with mineral oil. For each of the lymphatic-dwelling parasites, primers and probes have been identified that are 100% specific and provide sensitivities that are up to 10-fold greater than parasite detection by direct examination. Miscellaneous opportunistic fungi: Microascaceae and other ascomycetes, hyphomycetes, coelomycetes and basidiomycetes. Contraindications to thrombolysis include active internal bleeding, a stroke within 2 months, and an intracranial process such as neoplasm or abscess.
References