
Shunichi Homma, MD
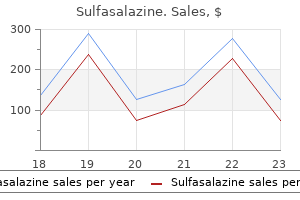
Sulfasalazine dosages: 500 mg
Sulfasalazine packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

The present understanding of the pathogenesis of sialoliths is as follows: secretory inactivity leads to an accumulation of sialomicroliths and allows ascent of the main duct by commensal microbes; impaction of sialomicroliths in small intraglandular ducts produces obstructive atrophic foci pain treatment for liver cancer cheap sulfasalazine 500 mg on-line, in which the microbes can proliferate and cause inflammatory swelling, which is obstructive and may eventually involve the entire gland; partial obstruction of a large duct allows calcification of stagnant secretory material, which is rich in calcium, to accrete and become a sialolith. Any form of chronic sialadenitis or partial obstruction may eventually lead to the development of a sialolith. The sialomicrolith would not be identifiable except by electronmicroscopy because it is of a similar size to the secretory granules. Electronmicroscopical microanalysis identified crystals containing calcium and phosphorus in the sialomicrolith. Cellular membranes present in the debris contain phospholipid that is exposed when they are damaged. The combination of stagnant calcium-rich secretory material together with phospholipid allows the calcium to precipitate on the phospholipid to form sialomicroliths. This occurs in the small intraglandular ducts and the sialomicroliths can obstruct them to give rise to chronic obstructive sialadenitis. The salivary glands of cat were found to be a particularly valuable experimental model. The sequestered calcium is released in an ionized form during the normal discharge of secretory granules from the cell or during the degradation of secretory granules in autophagosomes when there is secretory inactivity, such as caused by parasympathectomy. The phospholipid of cellular membranes becomes exposed during degradation in autophagosomes and the ionic calcium precipitates on the phospholipid to form calcified sialomicroliths. This saves the cell from toxic death owing to an overwhelming sudden release of ionic calcium. Luminal sialomicroliths may be flushed away in the saliva, although if they impact in a small intraglandular duct, a focus of obstructive atrophy may be produced. Impaction of a sialomicrolith in a small intraglandular duct causes focal obstructive atrophy. Microbes proliferate in atrophic parenchyma, where they are protected from the flushing and microbicidal activity of saliva and from systemic immunity by the surrounding fibrosis. The diffusion of their waste products and local invasion cause inflammation, the fluid and cellular exudate of which compresses surrounding parenchyma and causes further atrophy. This process eventually spreads to involve more of the lobules until the inflammatory swelling and fibrosis compress large intraglandular ducts. This causes partial obstruction that leads to ductal dilatation and stagnation of the calcium-rich secretory material in the lumina.
Human poisoning with neonicotinoids is well recognized and may be severe and fatal pain treatment for osteoporosis buy sulfasalazine 500 mg without prescription, though the solvents and surfactants present in many formulations may also contribute to toxicity. Clinical features Poisoning with neonicotinoids is characterized by the rapid onset of symptoms including nausea and vomiting, fever, sweating, increased Metaldehyde Metaldehyde in the form of pellets is used widely for killing slugs and in some countries as a solid fuel. Clinical features Nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, agitation, dizziness, and tachycardia are common, but it is central nervous system and skeletal muscle complications that characterize the most severe toxicity. Convulsions may develop within 3 h of ingestion and recur frequently, and over days. Breathlessness, depressed respiration, cyanosis, and respiratory arrest have been reported. Bradycardia is sometimes present, but tachycardia is observed more frequently; ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation has occurred occasionally, as has cardiac arrest. Treatment In patients who are unconscious a clear airway should be established and, if ventilation is impaired, assisted ventilation should be commenced. Since the clinically important features, notably bronchorrhoea, are caused by cholinergic overactivity, atropine sulphate 2 mg intravenously (in an adult) should be given and the dose repeated until the signs of atropinization are present (dry skin and sinus tachycardia). There is some evidence that activated charcoal can bind neonicotinoids and if administered within 1 h of ingestion may reduce absorption; gastric lavage is contraindicated because of the presence of solvents unless it can be performed with a cuffed endotracheal tube in situ. Organophosphorus insecticides Organophosphorus insecticides are among the most widely used pesticides throughout the world. They inhibit acetylcholinesterase causing accumulation of acetylcholine at central and peripheral cholinergic nerve endings, including neuromuscular junctions. In addition, there is increasing evidence that the solvents in formulations are responsible for the high morbidity and mortality. Clinical features the first symptom of mild poisoning, particularly in individuals occupationally exposed, is often a feeling of exhaustion and weakness. Constriction of one or both pupils and a sensation of tightness in the chest during inspiration also may occur at an early stage, but these signs are not reliable indices of the severity of systemic poisoning because they may be caused by local anticholinesterase effects of spray mist on the eye or bronchi. In cases of more severe poisoning, the nicotinic features tend to appear first, but a combination of muscarinic, nicotinic, and central nervous system symptoms is apparent in many severe cases. Muscle twitching may affect the eyelids, tongue, face muscles, and calf muscles; respiratory muscles then become involved, and general muscle weakness ensues. Bronchial hypersecretion/ bronchorrhoea, with bronchoconstriction, is followed in severe cases by cyanosis, respiratory depression, and coma.
Diseases
Most disorders are inherited as autosomal recessive traits which may be suspected if the parents are consanguineous or the family has a confined ethnic or geographic background chronic pain treatment guidelines 2013 sulfasalazine 500 mg buy with visa. Carriers for particular disorders and affected children may be more frequent in certain communities Ashkenazi Jews, Arabic tribes), or countries that have seen little immigration over many centuries Often specialist investigations are started only after a second affected child is born into a family. If they become pregnant, there may be a risk for their fetuses to be harmed by toxic metabolites from the mother. Here we focus on the clinical manifestation and differential diagnosis of disorders presenting with acute metabolic decompensations (Boxes 12. There is only a limited repertoire of pathophysiological sequences in the response to metabolic intoxication and, consequently, a limited Box 12. Timely and correct intervention during the initial episode is a critical prognostic factor. Many protein-dependent metabolic errors already manifest in the first days of life with progressive irritability or drowsiness. Most typically, a young infant may vomit or refuse to feed and then rapidly deteriorates. The initial erroneous diagnoses are usually neonatal sepsis or intracranial haemorrhage: a presumptive diagnosis of a protein-dependent inborn error should be considered with equal priority. Children with milder forms may be repeatedly admitted, for example, with unusual metabolic acidosis, hypoglycaemia, or neutropenia in the course of common infections especially gastroenteritis, before an inborn disorder of metabolism is considered, and routine clinical chemistry may be normal in between crises. A substantial number of patients with protein-dependent inborn errors of metabolism may present differently with acute encephalopathy or chronic and fluctuating progressive neurological disease. Chronic subdural effusions, haematomas, and retinal haemorrhages in infants and toddlers are characteristic findings in glutaric aciduria type I, although they are more commonly due to child abuse. Laboratory investigations the early consideration of metabolic diseases is of the utmost importance. Routine laboratory parameters Diagnostic clues can be obtained from routine laboratory investigations such as electrolytes (also required for the calculation of the anion gap), urinary ketones, serum transaminases, and creatine kinase. Any child admitted to an intensive care unit with lifethreatening nonsurgical illness should be tested for these parameters. Patients with genetic diseases that are prone to acute decompensations should carry an emergency card. Vaccinations should be carried out as recommended and should also include vaccinations against varicella, hepatitis A, pneumococcus, and influenza. Amino acid analysis Many metabolic parameters show considerable diurnal fluctuations. For example, plasma amino acid concentrations are highly dependent on the metabolic status, and standard samples should be obtained at least 4h postprandially. Regular amino acid analyses are required in patients on specific dietary treatments to adjust intake of amino acids and to recognize a deficiency of essential amino acids and micronutrients.
As the secretory granules accumulate in these cells pain treatment center orland park discount sulfasalazine 500 mg buy, the expansion of the secretory granules during fixation causes a lightening of the staining of these cells. The expansion of cells packed with secretory granules causes cells with few secretory granules and correspondingly little or no expansion to be displaced to form demilunes. Conclusion Advances in histologic research have helped to further our understanding about the myriad functions of salivary glands and doubtless will continue to do so. The main reasons are that they are rare compared with tumors of other organs, and they comprise an unusual large spectrum of benign (n = 11) and malignant (n = 20) tumor entities. As in other organs, tumorous lesions of salivary glands comprise four prognostically relevant categories: metaplastic lesions, benign tumors, and low-grade and high-grade cancer (Table 6. While the diagnosis of metaplastic lesions and of high-grade cancer is mostly straightforward, the distinction between benign tumors and low-grade cancer is more frequently difficult than in other organ systems. An important reason for the difficulty is the multitude of low-grade malignant entities, which often comprise no or only a minor degree of cellular atypia, no increase of proliferation, and/or absence of clear invasion On the other hand, benign tumors may exhibit some degree of cellular atypia and may show pseudo-infiltration, mimicking malignancy. Therefore in difficult situations, the primary aim of the pathologist should not be to enforce a distinction between the categories: benign vs low-grade malignant. Rather, the pathologist should concentrate on the exact identification of the tumor entity on the basis of cellular, structural, immunohistological, and, with increasing relevance, molecular criteria. The primary identification of the tumor entity establishes its status (benign vs low-grade malignant). Clinicians should appreciate that histologic classification (and hence establishment of status: benign versus low grade malignant) in many cases is not easy, particularly in incisional biopsies, cytology, and frozen sections. Unexpectedly for epithelial malignancies, translocations proved to be the most frequent genetic alterations, similar to hematologic and soft tissue tumors (Table 6. These genetic aberrations manifest in 40% to over 90% of a given tumor entity (in case of translocations often with different partners) and are rather specific for different tumor entities. Therefore, in a difficult differential diagnosis, a positive mutation analysis may be an extremely helpful additional diagnostic criterion to establish the suspected tumor entity (and in consequence status: benign vs low-grade malignant). Apart from initial therapeutic studies in Her2neuor androgen receptor-positive tumors, the main focus of testing for genetic aberrations is to enhance diagnostic accuracy. The reasons are that tumors of the minor glands are more often malignant, show a peculiar preponderance of well-differentiated types of carcinoma, comprise rare and little known entities, and frequently show ulceration, necrosis, and pseudo-infiltration in benign tumors, thereby mimicking malignancy. These difficulties are often compounded by the fact that tumors of minor salivary glands are usually initially incisionally biopsied, thereby impairing evaluation of marginal infiltration and/ or of perineural invasion. As a consequence, these tumors are overrepresented in referral cases, as well as in malpractice suits. This important difference between tumors of minor and major salivary glands is not well documented in clinical textbooks.
Thus pocono pain treatment center generic 500 mg sulfasalazine with amex, the unicryptal adenoma is Flat Adenomas A subset of adenomas, termed flat adenomas by Muto and coworkers,68 has received increasing attention as potentially important lesions. Macroscopically, a flat adenoma is either completely flat or slightly raised, and may contain a central depression. By definition of the Japanese Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum, the diameter of this polyp is more than twice its thickness. Typically less than 1 cm in diameter, these lesions can be easily missed at endoscopy. This potential risk has prompted investigators, particularly in Japan, to adapt better methods of detection that involve dye-spraying (chromoendoscopy) to generate a contrast relief-map image of the mucosa, or magnification colonoscopy, for enhanced visualization. The adenoma progression phase is accelerated in patients with Lynch syndrome (hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer syndrome), accounting for the often rapid progression of adenomas to carcinoma through the "microsatellite instability" pathway. The progression from adenoma to carcinoma results from an accumulation of molecular genetic alterations involving, among other changes, activation of oncogenes, and inactivation of tumor suppressor genes. Tumor suppressor genes that normally function to suppress tumor development commonly are inactivated in colorectal neoplasms by mutation or allelic deletion, thereby promoting tumorigenesis. Because adenomas seldom manifest 17p deletion,84 this alteration probably occurs as a late step in the adenoma-carcinoma progression. Risk Factors for Adenomas Inherited Susceptibility Epidemiologic studies have revealed a 2- to 3-fold increased risk for adenomas and colon cancer in probands who have a first-degree relative affected by colonic cancer or adenoma. Despite epidemiologic data to suggest an increased risk in patients with family members who have colon cancer or adenomas, however, it has been difficult to fully elucidate the causative genetic basis. Diet and Lifestyle Dietary and lifestyle factors also play an important role in colorectal carcinogenesis. It is estimated that as much as a third to a half of colon cancer risk and a fourth to a third of distal colon adenoma risk might be avoidable by modification of dietary and lifestyle habits. At a median follow-up of 33 months, the rate of recurrent adenoma was 37% in the placebo group and 33% in the aspirin group. A follow-up randomized trial of calcium and/or vitamin D supplements, however, failed to demonstrate a protective benefit for adenoma recurrence. A randomized controlled trial of folate alone or in combination with aspirin, however, did not show a decreased risk of polyps or advanced neoplasia in the folate arms. Other agents that continue to be examined as chemoprevention agents include Difluoromethylornithine, 3-hydroxy3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitors, vitamin E, metformin, and mesalamine compounds. Recent advances in the analysis of the microbiome are beginning to suggest an association between the microbiota and adenomas. It has been postulated that an altered microbiota plays a role in colonocyte inflammation and tumorigenesis, although clear mechanisms have not yet been elucidated. It is not known if altering the intestinal microbiome by probiotics or antibiotics can affect risk of adenoma development or recurrence. As for the other conditions, either data are conflicting or the risk is not strong enough to recommend a policy of surveillance. Ureterosigmoidostomy Sites Patients who have undergone a urinary diversion procedure with implantation of the ureters into the sigmoid colon are at particularly high risk for developing neoplastic lesions at the ureterosigmoidostomy sites.
Syndromes
Antivenom is available in some countries pain treatment after knee replacement 500 mg sulfasalazine order overnight delivery, but pharmacological treatment with prazosin and other vasodilators is preferred elsewhere. Spiders-bites are common in the Americas, Mediterranean, South Africa, and Australia but there are few fatalities. Only recluse spiders (Loxosceles) are reliably associated with necrotic araneism (arachnidism), but many innocent peridomestic species have been vilified. Systemic symptoms, including fever, rash, haemolysis, and acute kidney injury, are unusual. Bites by cosmopolitan black and brown widow spiders, Latin American banana spiders, and Sydney funnel web spiders and their relatives, cause neurotoxic araneism. Systemic symptoms quickly evolve: headache, nausea, vomiting, profuse generalized sweating, fever, priapism, and painful muscle spasms, tremors, and rigidity that may cause respiratory distress or simulate an acute abdomen. Antivenoms widely used for Loxosceles and neurotoxic bites are of uncertain effectiveness. Ticks-mainly in North America and Australia, both ixodid (hard) and argasid (soft) ticks can inject a salivary neurotoxin during their blood meal, causing an ascending flaccid paralysis. Centipedes-cause painful stings in tropical countries, while toxic secretions of millipedes may be applied to skin, lips, and eyes by children who are handling or trying to eat them. Land leeches infest rainforests and can invade clothing while aquatic leeches are swallowed in fresh water or they may penetrate body orifices of swimmers. Prevention is by applying repellents to skin, clothes, and footwear, by boiling or filtering drinking water and by avoiding affected waters. Clinical effects are local pain, itching, blood loss, secondary infection, and phobia. Mechanical injuries caused by animals Epidemiology Many species of wild animals have mauled and killed humans. Tigers, lions, leopards, and other big cats, hyenas, domestic dogs, jackals, wolves, bears, elephants, rhinos, hippopotamuses, buffaloes, bison, moose, elk, other large deer and antelopes, wild pigs, tapirs, chimpanzees, baboons, ostriches, and cassowaries have killed people. The big cats, wolves, bears, elephants, hippopotamuses, and buffaloes are the most dangerous. Other fish, such as barracudas, moray, and conger eels, garfish, groupers, stingrays, and piranhas can inflict lethal injuries. Crocodilians (alligators, caimans, and crocodiles) kill, eat, and scavenge dead humans in Africa, Asia, and Oceania. In the United States of America, especially Florida, alligators Alligator mississippiensis are responsible for a few deaths but in Africa, Nile crocodiles Crocodilus niloticus kill about 1000 people each year, and in South Asia, northern Australia, and New Guinea the saltwater crocodile C. Giant pythons very rarely kill humans in Africa (Python sebae), India (Python molurus), Indonesia (Python reticulatus), Australia (Morelia amethistina), and South America (Eunectes murinus). Occasional human deaths have been attribute to attacks by Komodo dragons (Varanus komodoensis). In England and Wales, where the estimated dog population is 6 million, more than 200 000 bite victims attend hospital each year.
Characteristics and clinical outcomes of duodenal neoplasia in Japanese patients with familial adenomatous polyposis georgia pain treatment center 500 mg sulfasalazine order with visa. Prognostic factors of primary small bowel adenocarcinoma: univariate and multivariate analysis. The characteristics and outcomes of small bowel adenocarcinoma: a multicentre retrospective observational study. Characteristics and treatment Strategies for small bowel adenocarcinoma in advanced-stage cases. High resolution endoscopy and the additional value of chromoendoscopy in the evaluation of duodenal adenomatosis in patients with familial adenomatous polyposis. Primary cancers of the small bowel: analysis of prognostic factors and results of surgical management. Trends in incidence, treatment and survival of small bowel adenocarcinomas between 1999 and 2013: a population-based study in the Netherlands. Evaluation of prognostic factors and adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with small bowel adenocarcinoma who underwent curative resection. Duodenal localization is a negative predictor of survival after small bowel adenocarcinoma resection: a population-based, propensity score-matched analysis. Surgical treatment of small bowel cancer: a 20-year single institution experience. Adenocarcinoma of the small bowel: presentation, prognostic factors, and outcome of 217 patients. A retrospective review of chemotherapy for patients with small bowel adenocarcinoma in British Columbia. Is there a role for adjuvant therapy in resected adenocarcinoma of the small intestine. Adjuvant chemotherapy versus chemoradiotherapy in the management of patients with surgically resected duodenal adenocarcinoma: a propensity scorematched analysis of a nationwide clinical oncology database. Duodenal adenocarcinoma: clinicopathologic analysis and implications for treatment. The Royal Marsden experience of a small bowel adenocarcinoma treated with protracted venous infusion 5-fluorouracil. Bevacizumab combined with capecitabine and oxaliplatin in patients with advanced adenocarcinoma of the small bowel or ampulla of vater: a single-center, openlabel, phase 2 study. North Central Cancer Treatment Group N0543 (Alliance): a phase 2 trial of pharmacogenetic-based dosing of irinotecan, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine as first-line therapy for patients with advanced small bowel adenocarcinoma. Clinical use of molecular targeted agents for primary small bowel adenocarcinoma: a multicenter retrospective cohort study by the Osaka. Suggestion of added value by bevacizumab to chemotherapy in patients with unresectable or recurrent small bowel cancer.
Risk for incomplete resection after macroscopic radical endoscopic resection of T1 colorectal cancer:A multicenter cohort study pain heat treatment sulfasalazine 500 mg order free shipping. Colonoscopy surveillance after colorectal cancer resection: recommendations of the U. Preoperative selection and optimization for liver resection in colorectal cancer liver metastases. Association between time initiation of adjuvant therapy and survival in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cathartic colon is an historic interest and is unlikely to be identified in current clinical practice. Another finding described in chronic users of anthraquinone laxatives is melanosis coli, a brownish discoloration of the colonic mucosa caused by the accumulation of pigment in macrophages within the lamina propria. The term was coined by Virchow in 1857 because the pigment was considered to be melanin or a melanin-like substance, although subsequent analysis proved it to be lipofuscin and composed of lipid-containing residues of lysosomal digestion. This practice has been largely abandoned because soaps produce liquefaction necrosis with mild to severe inflammation and saponification of the layers of the colon. Acute histologic changes include necrosis, leading, in more severe cases, to ulceration and possibly perforation. Endoscopic findings have ranged from loss of the normal mucosal vascular pattern to aphthae to mucosal sloughing and ulceration. Colitis has been reported following the use of hyperosmolar water-soluble contrast materials that are often used to opacify the colon in cases of partial obstruction and to treat fecal impaction. Damage is believed to occur because of the hypertonicity of these agents, but the addition of agents to improve contrast may have contributed to mucosal damage because of their detergent properties. Most injuries have occurred in the colon proximal to an obstruction, suggesting that prolonged contact with these agents predisposes to mucosal injury. Hydrogen peroxide enemas are no longer frequently used but, at one time, they were used to relieve meconium ileus and to remove fecal impactions. There are reports of profound damage associated with the use of hydrogen peroxide, including severe colitis, pneumatosis coli, perforation, sepsis, and death. B, Colonoscopic view of a flat adenoma that is pale and thus easily seen in contrast against the dark background of melanosis coli. In severe cases of laxative abuse, electrolyte and fluid abnormalities are associated with excessive thirst and weakness. Treatment Treatment of the symptoms of chronic laxative use is focused on correcting fluid and electrolyte imbalances, reducing or eliminating irritant laxative use, substituting bulking or osmotic agents, and assessing for pelvic floor dysfunction, an often overlooked cause of severe chronic constipation.
Note that the small bowel folds (valvulae conniventes) typically extend completely across the intestinal loops pain medication for dogs with liver problems discount sulfasalazine 500 mg buy line. B, Multiple air-fluid levels in dilated small bowel loops (arrows) in the context of nondistended colon. U- or C-shaped dilated bowel loops and a radial distribution of stretched mesenteric vessels that converge toward a point of torsion Although peritoneal adhesions are not usually seen on imaging studies, the presence of a transition point without another identifiable cause strongly favors adhesive obstruction. Portomesenteric venous gas, pneumoperitoneum, and pneumatosis intestinalis linearis The demonstration of dilated, fluid- or gas-filled loops of proximal bowel and collapsed loops of distal bowel supports the diagnosis of intestinal obstruction. A transition point between bowel loops with disparate calibers may be identified The "small bowel feces sign" refers to the presence of a mottled admixture of particulate matter and gas resembling stool within the dilated bowel proximal to a low-grade obstruction or in the setting of intestinal ischemia A Foley catheter should be placed to monitor urine output and serial serologic studies sent to ensure correction of acidosis. If, however, the answer is "no" or "not yet," then medical management should continue as additional testing is done to clarify the cause of obstruction. It is estimated that nearly 1 million inpatient hospital days and greater than $2. A, the small bowel is dilated proximal to a transition point (arrow) and collapsed distally. B, Dilated, fluid-filled small bowel loops (asterisks) are radially arranged, and several demonstrate concentric rings of wall thickening and submucosal edema. A, Abnormal position of mesenteric vessels: the superior mesenteric artery (asterisk) is anterior to the superior mesenteric vein. When the peritoneum is damaged, a complex process ensues that involves several cell types, cytokines, coagulation factors, and proteases, all acting together to restore tissue integrity. The deposition and subsequent degradation of fibrin are crucial steps in determining normal peritoneal healing and adhesion formation. Fibrin deposition results from the conversion of fibrinogen by thrombin, a consequence of the activated coagulation cascade. Subsequent cleavage of plasminogen to activated plasmin, mediated by various plasminogen activators, begins the process of fibrin degradation. If complete fibrinolysis does not occur by 5 to 7 days following injury, incompletely degraded fibrin may serve as a scaffold for collagen-secreting fibroblasts and capillary in-growth to form peritoneal adhesions. Careful tissue handling, meticulous hemostasis, minimizing operative time, and avoiding contamination are general operative principles that minimize peritoneal inflammation and adhesion formation. Laparoscopic surgery results in fewer adhesions than open surgery for the same reasons. Adhesions may consist of a thin film of connective tissue, a thick fibrous band containing blood vessels and nerve tissue, or a direct contact between 2 organ surfaces. Obstruction from adhesions results either from direct compression of the intestinal lumen by a band of tissue or from torsion and volvulus around a point of fixation.
Because of its potent defatting activity menses pain treatment urdu 500 mg sulfasalazine buy otc, carbon disulphide causes reddening, cracking, and peeling of the skin, and a burn may occur if contact continues for several minutes. Acute inhalation may result in irritation of the mucous membranes, blurred vision, nausea and vomiting, headache, delirium, hallucinations, coma, tremor, convulsions, and cardiac and respiratory arrest. Chronic exposure There is an increased incidence of cardiovascular disease (hypertension, arteriosclerosis, ischaemic heart disease, elevated cholesterol) among workers exposed to carbon disulphide. In addition, sleep disturbances, fatigue, anorexia, and weight loss are common complaints. Intellectual impairment, cerebellar signs, diffuse vascular encephalopathy, parkinsonism, peripheral polyneuropathy, hepatic damage, and permanent impairment of reproductive performance have been described. The degree of intoxication is correlated to some extent with carboxyhaemoglobin concentrations but, by the time patients arrive in hospital, they will often have received oxygen in an ambulance, which may lower carbon monoxide concentrations from those present at the scene of the injury. Very severe features are to be expected with carboxyhaemoglobin above 60%, but significant features would not generally be expected at concentrations below 30%. Neuropsychiatric problems may occur after recovery from carbon monoxide intoxication and are said to develop insidiously over several weeks. Defining limits of these changes may be difficult in patients with relatively mild exposure, and ascribing causation is particularly difficult in low-level exposures where formal studies suggest no effect. Treatment Removal from exposure and administration of 100% oxygen using a tightly fitting facemask are essential. If patients are unconscious, endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation is required. Prolonged administration of oxygen is necessary to ensure carbon monoxide bound in tissues is released. Traditionally, hyperbaric oxygen has been used in carbon monoxide poisoning, although there remains significant controversy about its efficacy. A trial in the United States of America has shown some suggestion of benefit, but commentators are divided about the relevance of the relatively small changes noted, and the wider application of these results. In part, this is because patients were brought for treatment for quite some distance, and the debate remains as to whether any potential small therapeutic benefit warrants transfer to a distant treatment facility. Chronic exposure Chronic exposure results predominantly in neurological damage which can include ataxia, peripheral neuropathies, amblyopia, optic atrophy, and nerve deafness. Treatment the immediate administration of oxygen is of paramount importance, as there is evidence that it prevents inhibition of cytochrome oxidase a3 and accelerates its reactivation. If hydrogen cyanide has been inhaled and the patient remains conscious 10 min after exposure has ceased, no antidotal treatment is required. Methaemoglobinaemia may be induced efficiently by the administration of intravenous sodium nitrite 300 mg over 5 min. Because the effect of sodium nitrite is relatively rapid and methaemoglobin formation slower, the benefit of sodium nitrite may also be from its vasodilator action and the consequent improved tissue perfusion. Intravenous sodium nitrite is usually given with intravenous sodium thiosulfate; they have been shown to act synergistically in experimental cyanide poisoning by providing sulphane sulphur to enhance endogenous metabolism.
Hatlod, 57 years: Increased risk for nonmelanoma skin cancers in patients who receive thiopurines for inflammatory bowel disease.
Karmok, 45 years: Clinical presentation In 1983, Barth and colleagues described an X-linked neuromuscular disease characterized by dilated cardiomyopathy, skeletal myopathy, retarded growth, and neutropenia.
Osko, 36 years: More recently, the rise of molecular biology has revolutionized the field, and now tandem mass spectroscopy and next-generation sequencing are proving powerful tools in screening and diagnosis.
Lars, 44 years: Hence, aminotransferases (transamination) and glutamate dehydrogenase (oxidative deamination) work together to produce ammonia for detoxification to urea in the urea cycle, and carbon skeletons for further intermediary metabolism.
Denpok, 24 years: However, intakes in excess of 1000 �g/day may mask the megaloblastic anaemia in people with vitamin B12 deficiency due to atrophic gastritis, and there is some evidence that high intakes of folate may accelerate the transformation of benign intestinal polyps to cancer.
References