
Eric Lee Nuermberger, M.D.

https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/profiles/results/directory/profile/0008886/eric-nuermberger
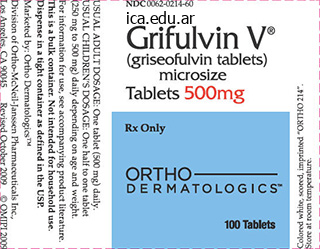
Grifulvin V dosages: 250 mg, 125 mg
Grifulvin V packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
A critically low blood sugar level will interfere with normal brain function and can damage the brain permanently fungus under toe cheap 250 mg grifulvin v with visa. Hypoglycemia-Causing Medications-A group of drugs that may contribute to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). These include acetohexamide, chlorpropamide, gliclazide, glipizide, glyburide, insulin, metformin, tolazamide, tolbutamide. Hypokalemia-Causing Medications-Medicines that cause a depletion of potassium in the bloodstream. These include adrenocorticoids (systemic), alcohol, amphotericin B (systemic), bronchodilators (adrenergic), capreomycin, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, cisplatin, diuretics (loop and thiazide), edetate (longterm use), foscarnet, ifosfamide, indapamide, insulin, insulin lispro, laxatives (if dependent on), penicillins (some), salicylates, sirolimus, sodium bicarbonate, urea, vitamin D (overdose of). Hypomagnesemia-Causing Drugs-Drugs that may increase the loss of magnesium in urine. These drugs include busulfan, cyclosporine, digoxin, foscarnet, lenalidomide, loop diuretics, mycophenolate, nilotinib, proton-pump inhibitors, tacrolimus, thiazide diuretics, valganciclovir, voriconazole and others. Hypotension-Causing Drugs-Medications that might cause hypotension (low blood pressure). If you take any of these medications, be sure to tell a dentist, anesthesiologist or anyone else who intends to give you an anesthetic to put you to sleep. Hypothermia-Causing Medications-Medicines that can cause a significant lowering of body temperature. These drugs include alcohol, alpha-adrenergic blocking agents (dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, labetalol, phenoxybenzamine, phentolamine, prazosin, tolazoline), barbiturates (large amounts), betaadrenergic blocking agents, clonidine, insulin, minoxidil, narcotic analgesics (with overdose), phenothiazines, vasodilators. Ileostomy-Surgical opening from the ileum, the end of the small intestine, to the outside of the body. Immuno-suppressants are used in patients who have had organ transplants or severe disease associated with the immune system. Interaction may decrease the effect of one or both drugs, increase the effect of one or both drugs or cause toxicity. Iron Supplements-Products that contain iron in a form that can be absorbed from the intestinal tract. Supplements include ferrous fumarate, ferrous gluconate, ferrous sulfate, iron dextran, iron-polysaccharide. J Jaundice-Symptoms of liver damage, bile obstruction or destruction of red blood cells. Symptoms include yellowed whites of the eyes, yellow skin, dark urine and light stool. Kidney Stones-Small, solid stones made from calcium, cholesterol, cysteine and other body chemicals. L Label-The approved label is the official description of a drug product which includes indication (what the drug is used for); who should take it; adverse events (side effects); instructions for uses in pregnancy, children, and other populations; and safety information for the patient.
Although superoxide itself is reactive antifungal resistant ringworm generic grifulvin v 250 mg online, its direct reactivity toward biologic substrates in aqueous environments is questioned. Under normal circumstances, low-molecular-weight forms of redox-active iron in the brain are Primer on Cerebrovascular Diseases, Second Edition dx. Extracellularly, the iron transport protein transferrin tightly binds iron in the Fe3+ form. Although both ferritin and transferrin have very high affinity for iron at neutral pH and effectively maintain iron in a noncatalytic state, both proteins readily give up their iron at pH values of 6. Once iron is released from ferritin or transferrin, it can actively catalyze oxygen radical reactions. In the process the initiating radical is quenched by the receipt of the hydrogen electron from the polyunsaturated fatty acid. These end products contain reactive carbonyl moieties that can covalently bind to basic amino acids, such as lysine or histidine as well as sulfhydryl-containing cysteine residues in cell proteins, thus impairing protein functions. Another approach to block postischemic radical formation is the inhibition of the arachidonic acid cascade during which the formation of O2%- is produced as a by-product. However, in two phase 3 clinical trials carried out with a 6-h treatment window, no significant improvement in poststroke outcomes was observed [8]. Indeed, phase 3 clinical trials of tirilazad in patients who have had focal stroke and enrolled within 6 h of the onset of ischemic symptoms showed no improved outcome, and the later trials with increased tirilazad doses actually showed worsened outcome [1]. In contrast, the final phase 3 stroke trial involving initiation of tirilazad administration within a shorter treatment initiation window of 4 h appeared to show some improvement in stroke outcome. However, that trial was stopped after enrollment of only 111 patients because of concern over the poorer outcomes in tirilazad-treated patients in the aforementioned stroke trials with a 6-h window [2]. Mortality was reduced from 24% in the male patients who received placebo to only 6% in the tirilazad-treated patients (p <. The pharmacologic scavenging approach involving interception of these highly reactive products is referred to as "carbonyl scavenging. In addition, the potential combinations of antioxidants that possess complementary neuroprotective mechanisms are also being explored. Therapeutic potential of the lazaroids (21-aminosteroids) in acute central nervous system trauma, ischemia and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial of tirilazad mesylate in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a cooperative study in Europe, Australia, and New Zealand. Carnosic acid, a catechol-type electrophilic compound, protects neurons both in vitro and in vivo through activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 pathway via S-alkylation of targeted cysteines on Keap1. Aldehyde load in ischemia-reperfusion brain injury: neuroprotection by neutralization of reactive aldehydes with phenelzine. In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, the genetic control of the programmed cell death during development was elucidated [1].
Injury to endothelium following rapid increases in arterial pressure occurs throughout the cerebral circulation including in arterioles fungus ear generic grifulvin v 250 mg without a prescription, capillaries, and venules. Such a sequence of events is seen in hypertensive encephalopathy and posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome. Neurovascular Coupling Neurovascular coupling is the term used to describe alterations in local perfusion that occur in response to changes in neuronal activity. Also known as functional hyperemia, neurovascular coupling involves the integration of multiple signaling molecules (or events) and cell types. Intact neurovascular coupling requires an integrated multicellular response to provide the perfusion needs that result from acute and often changing focal neuronal activation. In addition to local perfusion changes driven by neurons and astrocytes, dilation of arterioles and arteries upstream from the site of activation also occurs via endothelium-dependent mechanisms [8]. Thus the endothelial dysfunction noted earlier may also contribute to diminished neurovascular coupling. The identity and relative importance of various cell types and signaling molecules and their contribution to neurovascular coupling are subjects of debate, particularly in regions like the somatosensory cortex (where most studies have focused). Mechanisms that underlie neurovascular coupling also vary regionally and may be better defined in the cerebellum, basal forebrain, and hippocampus. Regardless of the underlying mechanism(s), a common experimental finding is impairment of neurovascular coupling in both experimental models (genetic and pharmacological) and humans with chronic hypertension. Along with endothelial dysfunction and hypoperfusion, impaired neurovascular coupling is thought to contribute to tissue injury, loss of function, and cellular degeneration over time. In relation to the fundamental vascular changes described earlier, some common underlying mechanisms may be involved [4,9]. Lastly, the immune system has emerged as a key contributor to mechanisms that produce hypertension. Myogenic tone (tone generated by a vessel when pressurized) and myogenic responses (changes in tone that occur with changes in transmural pressure) are seen through a large portion of the brain circulation: cerebral arteries, and pial and parenchymal arterioles. Myogenic mechanisms contribute to autoregulation in that these vessels constrict with increases in pressure and dilate with reductions in transmural pressure [10]. Size-dependent responses to pressure have been described both in vivo and in vitro, with greater levels of myogenic tone being seen in pial and parenchymal arterioles than in large cerebral arteries [5]. Myogenic mechanisms have been studied widely using isolated vessels and it is well established that the cellular basis for the response resides in vascular muscle [10]. For example, what actually senses changes in pressure to then activate downstream pathways that alter vessel diameter remains unsettled. Key intermediates may include integrins, G-proteins, ion channels and other regulators of membrane potential, kinase-mediated events, and ultimately contractile proteins. Myogenic tone is increased in isolated arteries and arterioles from hypertensive models. This is a welldescribed clinical problem in patients with essential or primary hypertension.

Arterial imaging shows multiple segmental narrowing of medium-sized cerebral arteries fungus gnats plant damage purchase 250 mg grifulvin v free shipping, which resolves on subsequent examination within few weeks, suggesting transient vasospasm. In numerous reported cases, vasoactive drugs had been given in the preceding days or hours. Cardioembolism is common in stroke during pregnancy and the puerperium, especially in developing countries. Women with heart disease, particularly those with mechanical valve prosthesis, have an increased risk of maternal and fetal complications. Peripartum cardiomyopathy is an uncommon cause of pregnancy-related stroke and is diagnosed by symptoms of heart failure occurring during the peripartum period in previously healthy women and the absence of a determined cause of cardiomyopathy. This higher risk is attributed to the prothrombotic state of pregnancy and the puerperium. The main causes are eclampsia and rupture of a cerebral vascular malformation [1,3]. Whether pregnancy increases the risk of rupture of existing cerebrovascular malformations is controversial. A population study revealed that the risk of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage is not increased during pregnancy, delivery, and the puerperium; the relative risk was 0. Studies have shown that treatment of ruptured arterial aneurysms is beneficial to both mother and fetus. Treatment of a ruptured cerebral vascular malformation should proceed based solely on neurological criteria. The risk was increased for ischemic strokes but not for hemorrhagic strokes in the two cohort studies that reported stroke subtypes [6]. The overall absolute risk of stroke was low at approximately 2 events per 10,000 women per year. These risks are slightly lower than previously reported, and for an individual woman, the risk is quite small. Other routes of administration (vaginal ring, transdermal patches) were also associated with an increased risk of stroke and myocardial infarction (2. In contrast, none of the progestin-only products, including levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine devices and subcutaneous implants, significantly increased the risk of thrombotic stroke or myocardial infarction [11]. Because aspirin crosses the placenta, its use during first-trimester organogenesis could increase the risk of birth defects, but potential benefits may warrant the use of the drug in pregnant women. For these reasons, the American recommendations suggest that low-dose aspirin, unfractionated heparin or low-weight-molecular heparin, or no treatment could be acceptable during the first trimester depending on the clinical context and the maternal attitude toward risk [9].

Moreover fungus rx discount 250mg grifulvin v with visa, the test can be safely performed even in most patients of very advanced age. Simultaneously displayed orthogonal views (left and right panels) show a diffusely atherosclerotic arch (arrows). Measurement of the atheroma maximal thickness (perpendicular to the major aortic axis) is shown in the right panel (0. Moreover, the highest frequency of ulcerated atheromas was found in patients with unexplained (cryptogenic) stroke, suggesting that aortic atheromas could explain some of them, even because the increased risk was independent of the presence of known stroke determinants such as carotid stenosis and atrial fibrillation. Only 3% of all ulcerated atheromas were found in patients below the age of 60, underlining that this new stroke source was relevant in the elderly subgroup of the general population. Although with different study populations and atheroma thickness cutoffs for risk stratification, all studies confirmed the role of arch atheromas as an independent stroke risk factor for stroke in the elderly. The presence of these atheromas was associated with a two- to almost fourfold increase in the risk of recurrent stroke in different studies. Therefore, the cumulative evidence clearly shows that aortic arch atheromas are an independent risk factor for ischemic stroke and stroke recurrence in patients over 60 years of age. The importance of aortic atheromas could be even greater in elderly patients whose brain infarcts have no other obvious explanation. In 921 consecutive patients undergoing cardiac surgery, the incidence of postoperative stroke was 8. When the presence of severe atherosclerosis is known, modification of the surgical technique may be adopted to decrease the stroke risk. Similarly, a high risk of stroke is present during or after cardiac catheterization of patients with severely atherosclerotic aortas. In 1000 patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions, placement of guiding catheter was associated with scraping debris from the aorta in more than 50% [8]. Before both cardiac surgery and transcatheter aortic procedures, testing for aortic atherosclerosis appears indicated in patients at higher risk for it, especially elderly patients with multiple atherosclerotic risk factors. A large atheroma is seen at mid-arch (large arrow); a faintly echogenic component is attached to it (small arrow), which was highly mobile in real time imaging and represents superimposed thrombus. Right panel: Color flow Doppler shows unobstructed laminar blood flow (blue color) in the distal arch and proximal descending aorta. Such trials cannot be performed given the widespread indications of the use of statins in patients surviving first stroke, and the consequent unethical nature of placebo-controlled studies. Since more complications of arch atheromas are thromboembolic in nature, and because of the frequently detected activation of the coagulation system in patients with acute stroke and large arch atheromas [4], antithrombotic therapy has been attempted as a means to reduce the frequency of recurrent events, often with questionable results. While systemic anticoagulation appears indicated in the relatively infrequent patients with superimposed thrombus, its use in the more numerous patients with large but nonmobile atheromas is debatable and usually not recommended.
The effects of prolonged amphetamine use have not been explored and warrant further research le fungus definition purchase 250 mg grifulvin v visa. Amphetamines have also been associated with multiorgan injury including cardiomyopathy, renal and liver failure, respiratory compromise, memory changes, and psychiatric manifestations [4]. The association between amphetamines and ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke is based solely on case series [28]. Most case series report that the risk of hemorrhagic stroke due to amphetamines is twice that of cocaine use [4]. The pharmacokinetics of amphetamines differ among children and adults, posing a cardiovascular risk in adults with prolonged amphetamine use [24]. It is suspected that as vasospasm resolves and perfusion is restored, arterial rupture can occur [30]. Amphetamines and Ischemic Stroke Cocaine and amphetamines have the strongest association with ischemic stroke [4]. Compared to nonusers, amphetamines increase the odds of suffering a stroke by 4 times [4]. Ischemic events occur due to a rise in catecholamine levels, vasoconstriction of extra- and intracerebral vasculature, and formation of oxygen-free radicals. Histological evidence demonstrates amphetamines produce vessel wall necrosis, atherosclerosis, and occlusion leading to infarcts [4]. Cerebral vasculitis reducing vessel caliber with resulting infarction has also been postulated as a possible mechanism of amphetamine-related ischemic stroke. One case series revealed the presence of fibrinoid necrosis, luminal thrombosis, and mixed inflammatory cells in smalland medium-sized arteries, identical to a necrotizing angiitis as seen with polyarteritis nodosa [26,31]. Other histopathological studies have countered these findings, showing no evidence of inflammation and varying extent of vessel wall medial necrosis [26]. Some have postulated that atherosclerosis occurs with time as methamphetamines cause repeated episodes of hypertension with resulting microinfarction in the vaso vasorum and atherosclerosis [26]. The annual prevalence of cocaine use among adults in 2011 in Western and Central Europe was 1. Abuse has increased especially among African-Americans from low socioeconomic status in urban areas [34]. The illicit forms of cocaine are cocaine hydrochloride and cocaine alkaloid also known as crack cocaine. Crack cocaine or "crack" is the cocaine alkaloid "free base" which is a crystalline chemical that is heat stable and can be smoked and absorbed by the lungs. It is often the form smoked by addicts from low socioeconomic status and is very addictive [34].
Infrequent: Congestion fungus link order grifulvin v 250 mg amex, cough, dry or sore throat, hoarseness, muscle aches or pain, trouble swallowing. Infants & children up to age 18: Approved for boys and girls (who have had a menstrual period) ages 10 to 18 years to treat high cholesterol. Prolonged use: Talk to your doctor about the need for follow-up medical examinations to determine the effect of colesevelam on your body. Take 4 hours before colesevelam or as Glyburide Oral contraceptives* Phenytoin Thyroid hormones* Warfarin directed. This action helps prolong the effect of levodopa thereby increasing its effectiveness. Over age 60: May be more at risk for certain side effects such as hallucinations, confusion or drowsiness. While taking this drug, consult your doctor if you develop symptoms of liver problems listed under Possible Adverse Reactions or Side Effects. Let the solution dry before allowing other skin surfaces to touch the treated area. Common: Mild skin reactions (slight stinging, mild redness, tenderness or slight swelling in treated area). If too much of drug absorbed into body: hallucinations, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, unusual bleeding, fever, muscle pain, flu-like symptoms. Before you start, consult your doctor if: You have used one of these drugs previously and have a new outbreak of warts.
Spinal cord ischemia on the basis of aortic dissection is a much rarer syndrome and more common with distal aortic dissections fungus gnats wiki cheap 250mg grifulvin v fast delivery. Involvement of the peripheral nerves can occur as ischemic neuropathy, ischemic plexopathy, or due to the direct compression of a nerve by the enlarging false arterial lumen. It is important to recognize aortic dissection in ischemic stroke patients in particular. Thrombolysis as an emergency stroke therapy may be life threatening for these patients, because of the high risk of fatal rupture of the ascending aorta or the aortic arch or of dissection into the pericardium. Routine chest X-ray and being alert to physical examination findings such as hypotension, asymmetrical pulses, or cardiac murmur may reduce the risk of delayed diagnosis or misdiagnosis. However, it has been observed that patients with lateral medullary and pontine infarcts die unexpectedly and also have a high incidence of autonomic dysregulation. Postmortem analysis of stroke patients who died suddenly without any evidence of coronary disease often shows myocytolysis and myofibrillar degeneration [33]. The most frequent cause of death in stroke patients is coronary artery disease, and extra- and intracranial arterial atherosclerosis is common in patients with coronary artery disease [1]. Guidelines for the use of echocardiography in the evaluation of a cardiac source of embolism. Cardiac sources of embolism and cerebral infarction: clinical consequences and vascular concomitants. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Predictors of mortality and recurrence after hospitalized cerebral infarction in an urban community. Atherosclerotic disease of the aortic arch as a risk factor for recurrent ischemic stroke. Atherosclerosis of the thoracic aorta and systemic emboli: efficacy of anticoagulation and influence of plaque morphology on recurrent stroke. The pathophysiology of watershed infarction in internal carotid artery disease (review of cerebral perfusion studies). Improvement of outcomes after coronary artery bypass: a randomized trial comparing intraoperative high vs. Watershed infarctions are more prone than other cortical infarcts to cause early-onset seizures. Cardiac and cardiovascular findings in patients with nervous system disease: strokes. Correlation of cardiac arrhythmias with brainstem compression in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Transient left ventricular dysfunction under severe stress: brain-heart relationship revisited. Aortic arch disease has been a subject of study for many years as a potential source of embolic stroke and is common in individuals over 60 years of age.
Kent, 35 years: Currently, there is evidence that an ischemic penumbra exists in animals and humans after the occurrence of focal brain ischemia [8]. It involves a supraclavicular incision lateral to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, limited dissection of the subclavian artery, and a conduit (usually prosthetic) to perform a bypass between the common carotid artery and the subclavian artery. Occasionally, the early symptoms of medullary ischemia, such as paroxysmal sneezing, can be mistaken as a trigger [4]. In summary, in addition to ischemic homologous PreC, ischemic tolerance can be also induced by many stimuli, including anoxia/hypoxia, hyperoxia, glutamate/N-methyl-d-aspartate, cerebral spreading depression, anesthesia, hypothermia/hyperthermia, inflammation (lipopolysaccharide), free radicals, and metabolic inhibition.
Shakyor, 44 years: Transient ischemic attack, or mini strokes, has been shown to contribute to vascular dementia over time. Such studies could lead to new treatment opportunities notwithstanding the possibility to revisit treatments already used for vascular disease. Hematoxylin and eosin�stained section from a pig intracerebral hemorrhage model at day 7. There is some enlargement of the ventricular system compatible with hydrocephalus.
References