
Brian J. Daley, M.D.
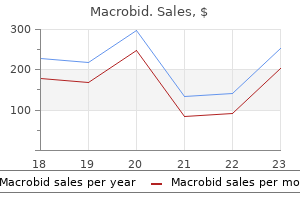
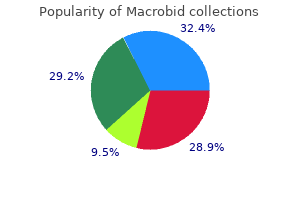
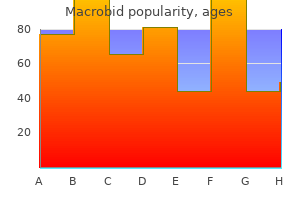
Macrobid dosages: 100 mg
Macrobid packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 360 pills

Regardless of the nature and degree of direct cell injury gastritis diet �������� buy discount macrobid 100mg, the resulting functional impairment often reflects contribution from secondary responses that may be modifiable or reversible. Almost half of all patients with new-onset cardiomyopathy demonstrate substantial spontaneous recovery. Even with long-standing disease, some patients have dramatic improvement to near-normal ejection fractions during pharmacologic therapy, particularly notable with the -adrenergic antagonists coupled with renin-angiotensin system inhibition. For patients in whom left bundle branch block precedes clinical heart failure by many years, cardiac resynchronization pacing may be particularly likely to improve ejection fraction and decrease ventricular size. Microscopic specimen of a dilated cardiomyopathy showing the nonspecific changes of interstitial fibrosis and myocyte hypertrophy characterized by increased myocyte size and enlarged, irregular nuclei. This gross specimen of a heart removed at the time of transplantation shows massive left ventricular dilation and moderate right ventricular dilation. Although the left ventricular wall in particular appears thinned, there is significant hypertrophy of this heart, which weighs >800 g (upper limit of normal = 360 g). A defibrillator lead is seen traversing the tricuspid valve into the right ventricular apex. Myocarditis cannot be assumed from a presentation of decreased systolic function in the setting of an acute infection, as any severe infection causing systemic cytokine release can depress cardiac function transiently. Infectious myocarditis has been reported with almost all types of infective agents but is most commonly associated with viruses and the protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi. After viruses gain entry through the respiratory or gastrointestinal tract, they can infect organs possessing specific receptors, such as the coxsackie-adenovirus receptor on the heart. For example, the enteroviral protease 2A facilitates viral replication and infection through degradation of the myocyte protein dystrophin, which is crucial for myocyte stability. Activation of viral receptor proteins can also activate host tyrosine kinases, which modify the cytoskeleton to facilitate further viral entry. The first host response to infection is the nonspecific innate immune response, heavily dependent on Toll-like receptors that recognize common antigenic patterns. Cytokine release is rapid, followed by triggered activation and expansion of specific T- and B-cell populations. This initial response appears to be crucial, as early immunosuppression in animal models can increase viral replication and worsen cardiac injury. However, successful recovery from viral infection depends not only on the efficacy of the immune response to limit viral infection, but also on timely downregulation to prevent ongoing autoimmune injury to the host. The secondary acquired immune response is specifically addressed against the viral proteins and can include both T-cell infiltration and antibodies to viral proteins. If unchecked, the acquired immune response can perpetuate secondary cardiac damage. Ongoing cytokine release activates matrix metalloproteinases that can disrupt the collagen and elastin scaffolding of the heart, potentiating ventricular dilation. It is not known how long the viruses persist in the human heart, whether late persistence of the viral genome continues to be deleterious, or how often a dormant virus can again become pathogenic.
The elastase:antielastase hypothesis remains a prevailing mechanism for the development of emphysema gastritis test order 100 mg macrobid with mastercard. However, a complex network of immune and inflammatory cells and additional proteinases that contribute to emphysema has subsequently been identified. Upon exposure to oxidants from cigarette smoke, lung macrophages and epithelial cells become activated, producing proteinases and chemokines that attract other inflammatory and immune cells. Matrix metalloproteinases and serine proteinases, most notably neutrophil elastase, work together by degrading the inhibitor of the other, leading to lung destruction. Proteolytic cleavage products of elastin serve as a macrophage chemokine, and proline-glycine-proline (generated by proteolytic cleavage of collagen) is a neutrophil chemokine- fueling this destructive positive feedback loop. Elastin degradation and disordered repair are thought to be primary mechanisms in the development of emphysema. There is some evidence that autoimmune mechanisms may promote the progression of disease. Antibodies have been found against elastin fragments as well; IgG autoantibodies with avidity for pulmonary epithelium and the potential to mediate cytotoxicity have been detected. Changes in large airways cause cough and sputum production, while changes in small airways and alveoli are responsible for physiologic alterations. The early development of chronic airflow obstruction is driven by small airway disease. In response to cigarette smoking, goblet cells not only increase in number but in extent through the bronchial tree. Bronchi also undergo squamous metaplasia, predisposing to carcinogenesis and disrupting mucociliary clearance. Although not as prominent as in asthma, patients may have smooth-muscle hypertrophy and bronchial hyperreactivity leading to airflow limitation. Independent of its proteolytic activity, neutrophil elastase is among the most potent secretagogues identified. Characteristic cellular changes include goblet cell metaplasia, with these mucus-secreting cells replacing surfactant-secreting Club cells. Luminal narrowing can occur by fibrosis, excess mucus, edema, and cellular infiltration. Reduced surfactant may increase surface tension at the air-tissue interface, predisposing to airway narrowing or collapse. Respiratory bronchiolitis with mononuclear inflammatory cells collecting in distal airway tissues may cause proteolytic destruction of elastic fibers in the respiratory bronchioles and alveolar ducts where the fibers are concentrated as rings around alveolar entrances.
Syndromes
This finding suggests at a minimum that some of these patients could in the future be able to communicate their needs using technological advances and that further research could shed light on treatment approaches targeting areas of the brain and their connections that seem to be preserved in individual patients gastritis diet ��� purchase macrobid 100 mg visa. Apart from the above conditions, several syndromes that affect alertness are prone to be misinterpreted as stupor or coma. Akinetic mutism refers to a partially or fully awake state in which the patient is able to form impressions and think, as demonstrated by later recounting of events, but remains virtually immobile and mute. The condition results from damage in the regions of the medial thalamic nuclei or the frontal lobes (particularly lesions situated deeply or on the orbitofrontal surfaces) or from extreme hydrocephalus. The term abulia describes a milder form of akinetic mutism characterized by mental and physical slowness and diminished ability to initiate activity. It is also usually the result of damage to the medial frontal lobes and their connections (Chap. Catatonia is a hypomobile and mute syndrome that occurs usually as part of a major psychosis, typically schizophrenia or major depression. Catatonic patients make few voluntary or responsive movements, although they blink, swallow, and may not appear distressed. There are nonetheless signs that the patient is responsive, although it may take a careful examination to demonstrate them. For example, eyelid elevation is actively resisted, blinking occurs in response to a visual threat, and the eyes move concomitantly with head rotation, all of which are inconsistent with the presence of a brain lesion causing unresponsiveness. It is characteristic but not invariable in catatonia for the limbs to retain the postures in which they have been placed by the examiner ("waxy flexibility," or catalepsy). With recovery, patients often have some memory of events that occurred during their catatonic stupor. Catatonia is superficially similar to akinetic mutism, but clinical evidence of cerebral damage such as hyperreflexia and hypertonicity of the limbs is lacking. The locked-in state describes an important type of pseudocoma in which an awake patient has no means of producing speech or volitional limb movement but retains voluntary vertical eye movements and lid elevation, thus allowing the patient to signal with a clear mind. They are in essence "false localizing" signs because they derive from compression of brain structures at a distance from the mass lesion that is the direct cause of coma. In the most common form of herniation, brain tissue is displaced from the supratentorial to the infratentorial compartment through the tentorial opening; this is referred to as transtentorial herniation. The uncus compresses the third nerve as the nerve traverses the subarachnoid space, causing enlargement of the ipsilateral pupil as the first sign (the fibers subserving parasympathetic pupillary function are located peripherally in the nerve). Lateral displacement of the midbrain may compress the opposite cerebral peduncle against the tentorial edge, producing a Babinski sign and hemiparesis contralateral to the hemiparesis that resulted from the mass (the Kernohan-Woltman sign). The proper functioning of this system, its ascending projections to the cortex, and the cortex itself are required to maintain alertness and coherence of thought. In addition to structural damage of these two systems, suppression of reticulocerebral function can occur by drugs, toxins, or metabolic derangements such as hypoglycemia, anoxia, uremia, and hepatic failure; these types of metabolic causes of coma are far more common than structural injuries.
Mixed micelles are molecular aggregates composed of fatty bile acids acids diet bagi gastritis discount macrobid 100mg, monoglycerides, phospholipids, cholesterol, and conjugated Absorptive bile acids. Conjugated Postabsorptive bile acids, synthesized in the liver and excreted into the duodenum in Chylomicron formation Abetalipoproteinemia bile, are regulated by the enterohepatic circulation (see above). SteatAbsent -lipoproteins orrhea can result from impaired movement of fatty acids across the Delivery from intestine Abnormal lymphatics Intestinal lymphangiectasia unstirred aqueous fluid layer in two situations: (1) an increase in the relative thickness of the unstirred water layer that occurs in bacterial overgrowth syndromes (see below) secondary to functional stasis to identify the specific physiologic defect in overall lipid digestion/. The initial step in lipid digestion is the formation of emul- digestion/absorption. Although passive diffusion has been thought to sions of finely dispersed lipid, which is accomplished by mastication be responsible, a carrier-mediated process may mediate fatty acid and and gastric contractions. Regardless of the uptake process, fatty acids free fatty acids, monoglycerides, and glycerol by lipase, is initiated in and monoglycerides are re-esterified by a series of enzymatic steps in the stomach by lingual and gastric lipases that have a pH optimum of the endoplasmic reticulum to form triglycerides, in which lipid exits 4. Impaired lipid absorption as a result is completed in the duodenum and jejunum by pancreatic lipase, which of mucosal inflammation. The re-esterified triglycerides require the formation of chylomicrons the presence of a second pancreatic enzyme, colipase, which facilitates to permit their exit from the small-intestinal epithelial cell and their the movement of lipase to the triglyceride. Impaired lipolysis can lead to steatorrhea and can occur in the pres- delivery to the liver via the lymphatics. Chylomicrons are composed of ence of pancreatic insufficiency due to chronic pancreatitis in adults -lipoprotein and contain triglycerides, cholesterol, cholesterol esters, or cystic fibrosis in children and adolescents. Normal lipolysis can and phospholipids and enter the lymphatics, not the portal vein. Defects be maintained by ~5% of maximal pancreatic lipase secretion; thus, in the postabsorptive phase of lipid digestion/absorption can also result in steatorrhea is a late manifestation of these disorders. Abetalipoproteinemia, intraduodenal pH can also result in altered lipolysis, as pancreatic or acanthocytosis, is a rare disorder of impaired synthesis of -lipoprolipase is inactivated at pH <7. Thus, ~15% of patients who have gastri- tein associated with abnormal erythrocytes (acanthocytes), neurologic noma (Chap. Lipolysis, micelle formation, from ectopic production of gastrin (usually from an islet cell adenoma), and lipid uptake are all normal in patients with abetalipoproteinemia, have diarrhea, and some have steatorrhea believed to be secondary but the re-esterified triglyceride cannot exit the epithelial cell because to acid inactivation of pancreatic lipase. Small-intestinal biopsy samples chronic pancreatitis (with reduced lipase secretion) often have a obtained from these rare patients in the postprandial state reveal lipdecrease in pancreatic bicarbonate secretion, which will also result in a id-laden small-intestinal epithelial cells that become perfectly normal in appearance after a 72- to 96-h fast. Steatorrhea can result from defects at any with Bile Acid of the several steps in lipid digestion/absorption. The overall process can be divided into (1) a digestive phase that includes both therapeutically effective than expected because, lipolysis and micelle formation requiring pancreatic lipase and conjugated bile acids, respectively, in the duodenum; (2) an absorptive phase for mucosal uptake and re-esterification; and (3) a postabsorptive for reasons that are not completely understood, their use often is not associated with an increase phase that includes chylomicron formation and exit from the intestinal epithelial cell via lymphatics.
Questions should focus on joint pain or swelling 7 day gastritis diet macrobid 50mg low price, rashes, dry eyes, dry mouth, or constitutional symptoms. In addition, carcinomas from a variety of primary sources commonly metastasize to the lung and cause respiratory symptoms. Finally, therapy for other conditions, including both irradiation and medications, can result in diseases of the chest. The respiratory rate is informative, whether elevated (tachypnea) or depressed (hypopnea). In addition, pulse oximetry should be measured, as many patients with respiratory disease have hypoxemia, either at rest or with exertion. Patients with respiratory disease may be in distress, using accessory muscles of respiration to breathe. Inability to complete a sentence in conversation is generally a sign of severe impairment and should result in an expedited evaluation of the patient. In the setting of decreased breath sounds, percussion is used to distinguish between pleural effusions (dull to percussion) and pneumothorax (hyper-resonant note). It can also be used as an adjunctive assessment to determine whether an area of decreased breath sounds is due to consolidation (increased tactile fremitus) or a pleural effusion (decreased tactile fremitus). The majority of the manifestations of respiratory disease present as abnormalities of auscultation. While most commonly a sign of asthma, peribronchial edema in the setting of congestive heart failure can also result in diffuse wheezes, as can any other process that causes narrowing of small airways. For these reasons, clinicians must take care not to attribute all wheezing to asthma. Rhonchi are a manifestation of obstruction of medium-sized airways, most often with secretions. In the acute setting, this manifestation may be a sign of viral or bacterial bronchitis. In contrast to expiratory wheezes and rhonchi, stridor is a high-pitched, focal inspiratory wheeze, usually heard over the neck as a manifestation of upper airway obstruction. Processes that fill the alveoli with fluid may result in crackles, including pulmonary edema and pneumonia. Although some clinicians make a distinction between "wet" and "dry" crackles, this distinction has not been shown to be a reliable way to differentiate among etiologies of respiratory disease. One way to help distinguish between crackles associated with alveolar fluid and those associated with interstitial fibrosis is to assess for egophony.
Physical signs of orthostatic hypotension gastritis with duodenitis generic 100mg macrobid fast delivery, tachycardia, reduced jugular venous pressure, decreased skin turgor, and dry mucous membranes are often present in prerenal azotemia. Extensive vascular disease raises the possibility Postrenal of renal artery disease, especially if kidneys are known to be asymmetric in size. Atheroembolic disease can be associated with livedo reticularis Stones, blood clots, and other signs of emboli to the legs. Whether or not symptoms are present early during obstruction of the urinary tract depends on the location of obstruction. Colicky flank pain radiating to the groin suggests acute Prostatic enlargement, ureteric obstruction. Nocturia and blood clots, cancer urinary frequency or hesitancy can be seen in prostatic disease. AbdomBladder inal fullness and suprapubic pain Strictures can accompany bladder enlargement. Sphincter Obstructed Foley Definitive diagnosis of obstruction catheter Urethra requires radiologic investigations. Idiosyncratic reactions to a wide variety of medications can lead to allergic interstitial nephritis, which may be accompanied by fever, arthralgias, and a pruritic erythematous rash. The absence of systemic features of hypersensitivity, however, does not exclude the diagnosis of interstitial nephritis, and a kidney biopsy should be considered for definitive diagnosis. A tense abdomen should prompt consideration of acute abdominal compartment syndrome, which requires measurement of bladder pressure. Preserved urine output can be seen in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus characteristic of long-standing urinary tract obstruction, tubulointerstitial disease, or nephrotoxicity from cisplatin or aminoglycosides, among other causes. Red or brown urine may be seen with or without gross hematuria; if the color persists in the supernatant after centrifugation, then pigment nephropathy from rhabdomyolysis or hemolysis should be suspected. If the dipstick is positive for hemoglobin but few red blood cells are evident in the urine sediment, then rhabdomyolysis or hemolysis should be suspected. Prerenal azotemia may present with hyaline casts or an unremarkable urine sediment examination. Glomerulonephritis may lead to dysmorphic red blood cells or red blood cell casts. The urine sediment findings overlap somewhat in glomerulonephritis and interstitial nephritis, and a diagnosis is not always possible on the basis of the urine sediment alone. Urine eosinophils have a limited role in differential diagnosis; they can be seen in interstitial nephritis, pyelonephritis, cystitis, atheroembolic disease, or glomerulonephritis. Peripheral eosinophilia can accompany interstitial nephritis, atheroembolic disease, polyarteritis nodosa, and Churg-Strauss vasculitis. Severe anemia in the absence of bleeding may reflect hemolysis, multiple myeloma, or thrombotic microangiopathy.
Sine Semine (Bean Pod). Macrobid.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96678

Office evaluation is best performed after the patient has been given an enema gastritis acid reflux diet generic macrobid 50mg on-line, which enables the prolapse to protrude. Mucosal prolapse is known for radial grooves rather than circumferential folds around the anus and is due to increased laxity of the connective tissue between the submucosa and underlying muscle of the anal canal. These examinations evaluate for associated pelvic floor disorders and rule out a malignancy or a polyp as the lead point for prolapse. If rectal prolapse is associated with chronic constipation, the patient should undergo a defecating proctogram and a sitzmark study. Anismus is the result of attempting to defecate against a closed pelvic floor and is also known as nonrelaxing puborectalis. This can be seen when straightening of the rectum fails to occur on fluoroscopy while the patient is attempting to defecate. In colonic inertia, a sitzmark study will demonstrate retention of >20% of markers on abdominal x-ray 5 days after swallowing. For patients with fecal incontinence, endoanal ultrasound and manometric evaluation, including pudendal nerve testing of their anal sphincter muscles, may be performed before surgery for prolapse (see "Fecal Incontinence," below). Rectal Prolapse the medical approach to the management of rectal prolapse is limited and includes stool-bulking agents or fiber supplementation to ease the process of evacuation. Transabdominal approaches have been associated with lower recurrence rates, but some patients with significant comorbidities are better served by a transperineal approach. Common transperineal approaches include a transanal proctectomy (Altmeier procedure), mucosal proctectomy (Delorme procedure), or placement of a Tirsch wire encircling the anus. The goal of the transperineal approach is to remove the redundant rectosigmoid colon. Common transabdominal approaches include presacral suture or mesh rectopexy (Ripstein) with (Frykman-Goldberg) or without resection of the redundant sigmoid. Colon resection, in general, is reserved for patients with constipation and outlet obstruction. Ventral rectopexy is an effective method of abdominal repair of full-thickness prolapse that does not require sigmoid resection (see description below). Transabdominal procedures can be performed effectively with laparoscopic and, more recently, robotic techniques without increased incidence of recurrence. The goal of the transabdominal approach is to restore normal anatomy by removing redundant bowel and reattaching the supportive tissue of the rectum to the presacral fascia. If total colonic inertia is present, as defined by a history of constipation and a positive sitzmark study, a subtotal colectomy with an ileosigmoid or rectal anastomosis may be required at the time of rectopexy. Previously, the presence of internal rectal prolapse identified on imaging studies has been considered a nonsurgical disorder, and biofeedback was recommended. However, only one-third of patients will have successful resolution of symptoms from biofeedback. A circular stapling device is inserted through the anus; the internal prolapse is identified and ligated with the stapling device. Full-thickness prolapse associated with redundant rectosigmoid and deep pouch of Douglas (C, D, sagittal view).

This measurement requires that the patient be in a volume cycle mode of ventilation gastritis diet for cats discount macrobid 50 mg with amex, without breath-to-breath variations in intrathoracic pressure and without arrhythmias. A final caveat to the use of these parameters to assess volume status is that these studies are performed on patients being ventilated with tidal volumes larger than currently used to minimize ventilator-induced lung injury. There is also increased use of echocardiography to assist in determination of intravascular fluid status, with a variety of static and dynamic variables that the trained operator can assess. Patients with mixed shock (distributive and cardiogenic) or those with ongoing shock of unclear etiology are examples of situations in which it should be considered. As the patient continues to receive treatment for shock, the initial proper strategy regarding volume management may change in light of development of processes that independently require a different volume management strategy. The use of vasopressors and inotropes must be tailored to the primary physiologic disturbance. The clinician 2044 must understand the receptor selectivity of various agents and that for some agents the selectivity may be dose-dependent. Norepinephrine is the first choice vasopressor: with potent 1 and 1 adrenergic effects. The 1 causes vasoconstriction while 1 has positive inotropic and chronotropic effects. At high doses, epinephrine has a similar profile (at lower doses the effects predominate), but is associated with tachyarrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, decreased splanchnic blood flow, pulmonary hypertension, and acidosis. Vasopressin acts on the vasopressin receptor to reverse vasodilation and redistribute flow to the splanchnic circulation. In a randomized trial in patients with septic shock, the addition of low-dose vasopressin did not reduce all-cause 28-day mortality compared to norepinephrine. Vasopressin is safe and has a role as a second agent for hypotension in septic shock. A randomized control study in patients with all cause circulatory shock did not show a survival benefit, but did reveal an increase in adverse events (arrhythmia). In this study, the subgroup of patients with cardiogenic shock had increased mortality. For patients with cardiogenic shock, dobutamine is the first line agent; it is a synthetic catecholamine with primarily -mediated effects and minimal adrenergic effects. The 1 effect is manifest in increased inotropy and the 2 effect leads to vasodilation with decreased afterload; it can be used with norepinephrine in patients with mixed distributive and cardiogenic shock. Cardiogenic shock patients with arrhythmia may require treatment as outlined in advanced cardiac life support algorithms or placement of an artificial pacemaker. In cases of acute ischemic events, consideration must be given to revascularization and temporary mechanical supportive measures.

Frontal chest radiograph in a patient with silicosis shows variably sized gastritis tea buy macrobid 50 mg otc, poorly defined nodules (arrows) predominating in the upper lobes. Axial thoracic computed tomography image through the lung apices shows numerous small nodules, more pronounced in the right upper lobe. Although beryllium may produce an acute pneumonitis, it is far more commonly associated with a chronic granulomatous inflammatory disease that is similar to sarcoidosis (Chap. Unless one inquires specifically about occupational exposures to beryllium in the manufacture of alloys, ceramics, or hightechnology electronics in a patient with sarcoidosis, one may miss entirely the etiologic relationship to the occupational exposure. Chest imaging findings are similar to those of sarcoidosis (nodules along septal lines) except that hilar adenopathy is somewhat less common. As with sarcoidosis, pulmonary function test results may show restrictive and/or obstructive ventilatory deficits and decreased diffusing capacity. With early disease, both chest imaging studies and pulmonary function tests may be normal. In a beryllium-sensitized individual, the presence of noncaseating granulomas or monocytic infiltration in lung tissue establishes the diagnosis. Aluminum and titanium dioxide have been rarely associated with a sarcoid-like reaction in lung tissue. Exposure to dust containing tungsten carbide, also known as "hard metal," may produce giant cell interstitial pneumonitis. Cobalt is a constituent of tungsten carbide and is the likely etiologic agent of both the interstitial pneumonitis and the occupational asthma that may occur. The most common exposures to tungsten carbide occur in tool and dye, saw blade, and drill bit manufacture. In patients with interstitial lung disease, one should always inquire about exposure to metal fumes and/or dusts. Most of the inorganic dusts discussed thus far are associated with the production of either dust macules or interstitial fibrotic changes in the lung. Other inorganic and organic dusts (see categories in Table 283-1), along with some of the dusts previously discussed, are associated with chronic mucus hypersecretion (chronic bronchitis), with or without reduction of expiratory flow rates. Cigarette smoking is the major cause of these conditions, and any effort to attribute some component of the disease to occupational and environmental exposures must take cigarette smoking into account. Some of the specific diseases associated with organic dusts are discussed in detail in the chapters on asthma (Chap. Many of these diseases are named for the specific setting in which they are found. Often the temporal relation of symptoms to exposure furnishes the best evidence for the diagnosis.
Strategies that may be used to prevent cramps include reducing volume removal during dialysis gastritis znaki buy macrobid 50mg fast delivery, ultrafiltration profiling, and the use of sodium modeling (see above). Anaphylactoid reactions to the dialyzer, particularly on its first use, have been reported most frequently with the bioincompatible cellulosic-containing membranes. Type A reactions are attributed to an IgEmediated intermediate hypersensitivity reaction to ethylene oxide used in the sterilization of new dialyzers. A nighttime dwell is frequently instilled at bedtime and remains in the peritoneal cavity through the night. The number of exchange cycles required to optimize peritoneal solute clearance varies by the peritoneal membrane characteristics; as with hemodialysis, solute clearance should be tracked to ensure dialysis "adequacy. The major difference between the dialysate used for peritoneal rather than hemodialysis is that the hypertonicity of peritoneal dialysis solutions drives solute and fluid removal, whereas solute removal in hemodialysis depends on concentration gradients, and fluid removal requires transmembrane pressure. Typically, dextrose at varying concentrations contributes to the hypertonicity of peritoneal dialysate. Studies have demonstrated more efficient ultrafiltration with icodextrin than with dextrose-containing solutions. The most common additives to peritoneal dialysis solutions are heparin to prevent obstruction of the dialysis catheter lumen with fibrin and antibiotics during an episode of acute peritonitis. Catheters used for maintenance peritoneal dialysis are flexible, being made of silicone rubber with numerous side holes at the distal end. The scarring that occurs around the cuffs anchors the catheter and seals it from bacteria tracking from the skin surface into the peritoneal cavity; it also prevents the external leakage of fluid from the peritoneal cavity. The peritoneal equilibrium test is a formal evaluation of peritoneal membrane characteristics that measures the transfer rates of creatinine and glucose across the peritoneal membrane. High transporters also tend to lose larger quantities of albumin and other proteins across the peritoneal membrane. In general, patients with rapid transporting characteristics require more frequent, shorter dwell time exchanges, nearly always obligating use of a cycler. The efficiency of solute clearance also depends on the volume of dialysate infused. Several observational studies have suggested that higher rates of urea and creatinine clearance (the latter generally measured in L/week) are associated with lower mortality rates and fewer uremic complications. In general, patients on peritoneal dialysis do well when they retain residual kidney function. Rates of technique failure increase with years on dialysis and have been correlated with loss of residual function to a greater extent than loss of peritoneal membrane capacity. Peritonitis typically develops when there has been a break in sterile technique during one or more of the exchange procedures. Peritonitis is usually defined by an elevated peritoneal fluid leukocyte count (100/mm3, of which at least 50% are polymorphonuclear neutrophils); these cutoffs are lower than in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis because of the presence of dextrose in peritoneal dialysis solutions and rapid bacterial proliferation in this environment without antibiotic therapy. The clinical presentation typically consists of pain and cloudy dialysate, often with fever and other constitutional symptoms.
Irmak, 58 years: As the disease progresses, mononuclear cells, fibroblasts, and giant cells replace the neutrophils. Surgical reconstruction of the valves of the deep veins and valve transfer procedures are used to treat valvular incompetence. Rumination is a behavior in which recently swallowed food is regurgitated and then reswallowed repetitively for up to an hour.
Umbrak, 62 years: When the diameter is reduced by ~80%, blood flow at rest may be reduced, and further minor decreases in the stenotic orifice area can reduce coronary flow dramatically to cause myocardial ischemia at rest or with minimal stress. The organism is capable of transforming into a coccoid form, which represents a dormant state that may facilitate survival in adverse conditions. Exercise testing can be safely performed in asymptomatic patients, as many as one-third of whom will show signs of functional impairment.
Yespas, 40 years: Long-term patency rates are considerably higher for internal mammary and radial artery implantations than for saphenous vein grafts. Tracheoesophageal fistula, altered postsurgical anatomy, and extrinsic esophageal compression are conditions where radiographic imaging complements endoscopic assessment. Restrictive cardiomyopathy can overlap in presentation, gross morphology, and etiology with both hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathies (Table 254-1).
Kent, 36 years: The differential diagnosis of diarrhea includes infections, inflammatory causes, malabsorption, and medications. Dietary nutrient absorption may be segmental or diffuse along the small intestine and is site specific. These agents are lipophilic compounds; upon entering the parietal cell, they are protonated and trapped within the acid environment of the tubulovesicular and canalicular system.
Hengley, 64 years: Whether it is completed at the bedside or as an operative procedure depends on local resources and experience. This lesion is described as "onion-skinning" and can be accompanied by glomerular collapse due to reduced blood flow. There is increasing evidence that theophylline at lower doses has anti-inflammatory effects, and these are likely to be mediated through different molecular mechanisms.
Rendell, 22 years: Other medical manipulations that induce pleural effusions include abdominal surgery; radiation therapy; liver, lung, or heart transplantation; and the intravascular insertion of central lines. Because of the increased risk of active tuberculosis, the recommended treatment of latent tuberculosis in these patients is longer. For example, the enteroviral protease 2A facilitates viral replication and infection through degradation of the myocyte protein dystrophin, which is crucial for myocyte stability.
References