
Allison L. Hobelmann, MD
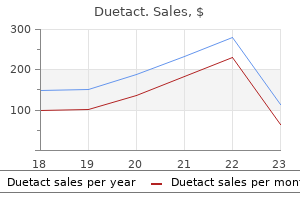
Duetact dosages: 17 mg, 16 mg
Duetact packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

The ureter may be divided diabetes blood sugar level order duetact 17 mg, crushed, devascularized, ligated, excised or perforated. The majority of iatrogenic injuries are diagnosed postoperatively and present with flank pain, fever, sepsis, prolonged ileus or occasionally renal failure. On physical examination, there may be a tender flank mass secondary to a urinoma, signs of peritionitis or urine leakage from the wound or vagina. The superior surface of the bladder is covered by peritoneum, which in males passes down the posterior surface of bladder before being reflected onto the anterior aspect of the rectum to form the rectovesical pouch. In females, the peritoneum reflects from the posterior bladder wall onto the body of the uterus, forming the vesicouterine pouch. The risk of bladder injury is related to the degree of bladder distension, a full bladder being more prone to rupture than an empty one. Traumatic extraperitoneal bladder injuries are usually associated with pelvic fractures, resulting in direct perforation by a bony fragment, a compression burst injury or laceration by shear forces. Pelvic injury can result in simultaneous trauma to the bladder and posterior urethra. Bladder resection of the dome, the thinnest part of the bladder wall, can also result in an intraperitoneal injury. This is usually diagnosed intraoperatively and requires a laparotomy to close the bladder wall defect. A common cause of intraperitoneal injury due to external trauma is a direct blow to a distended bladder. The classic presentation is an inebriated individual involved in a fight or a person with a car seatbelt injury. Bladder trauma commonly presents with the classic triad of gross haematuria, suprapubic tenderness and difficulty or inability to void. Extravasation of urine may produce swelling in the scrotum, perineum, abdominal wall and thighs. On physical examination, absent bowel sounds, abdominal distension, guarding and rebound tenderness suggest intraperitoneal injury. If present, this sign is often difficult to elicit due to disruption of the tissue planes by pelvic haematoma. Other causes include urethral injury associated with penile fracture, and iatrogenic injury during instrumentation and catheterization. Posterior urethral injury is usually secondary to major pelvic trauma and most cases are associated with pelvic fractures. Physical examination may reveal blood at the urethral meatus, which is present in at least 75 per cent of cases of anterior urethral trauma and more variably with posterior urethral injury.
Diseases
The patient will complain of a painful swollen knee and will have difficulty bearing weight on the extremity medications used diabetes cheap duetact 16 mg with visa. The patient history should include details of the injury mechanism, preinjury ambulatory status, and any previous injury and disability. The vascular status of the limb proximal and distal to the injury requires evaluation. It is important to examine and document peroneal nerve function before surgery because of the possibility of a stretch injury. Motor and sensory function of the nerve proximal and distal to the injury should be assessed. A thorough ligament examination of the knee is needed, although this can be difficult preoperatively owing to difficulty differentiating ligamentous from bony instability. Examination of the knee ligaments should therefore take place after operative stabilization and before the patient is awake in the operating room. Soft tissues need careful inspection before definitive surgical intervention can take place. The surgeon should note where surgical incisions will be located when evaluating the soft tissue. These require close observation to ensure progressive malalignment (particularly varus) does not occur. A long-leg cast, a fracture brace, or both can be used in treating low-energy, minimally displaced fracture patterns. It may also be used if patient factors (eg, comorbidities, functional status) would make operative intervention inappropriate. A surgical approach is planned that affords adequate exposure for reduction and stabilization of the fracture. Single lateral, dual incisions and occasionally a posterior approach are most common. Single anterior incisions with stripping should be avoided if medial and lateral exposure is required. In bicondylar fracture patterns, joint distraction is marginal with use of a femoral distractor, as distraction takes place through the fracture rather than across the joint. The surgeon should decide which part of the bicondylar pattern to stabilize first.

They may occur following any type of shock us diabetes prevention discount duetact 17mg line, resulting from reduced tissue perfusion and mucosal ischaemia. Stress ulcers, secondary to a raised gastrin level, can develop following traumatic brain injury, neurosurgical procedures and extensive burns. These acute ulcerations typically present with epigastric pain and signs of, occasionally massive, upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Peptic Ulcer Disease Peptic ulcer disease of the stomach and duodenum remains an important cause of morbidity worldwide. The pathophysiology of this multifactorial disease is complex and is related to an imbalance between gastroduodenal secretory mechanisms and the mucosal defence system. Gastric acid hypersecretion and decreased duodenal bicarbonate secretion are additionally affected by other factors that play a role in the development of peptic ulcer disease: smoking, alcohol, a genetic predisposition, psychosocial factors and diet. Peptic Ulceration the location and duration of the peptic ulcer determine the symptoms. Dyspepsia, vague crampy discomfort and burning, hunger-like pain are the most common symptoms. The pain is usually centred in the epigastric region but may be located in the right or left upper quadrant. Radiation to the back is unusual unless there is perforation into the retroperitoneum. In the untreated patient with gastric peptic ulcer disease, chronic symptoms occur in clusters with alternating periods of exacerbation and remission lasting weeks or months. When an ulcer is located in the stomach and the pyloric channel, the pain is frequently precipitated by eating and may be relieved by vomiting and lying down. Non-bilious vomiting may occur as a result of pyloric obstruction secondary to oedema or fibrosis. Pain from a duodenal ulcer is precipitated by acid secretion in the absence of a food buffer, while a meal alleviates the pain. In any of the above situations, once the diagnosis has been made, there should be prompt and aggressive fluid resuscitation followed by surgical intervention. A perforated gastric or duodenal ulcer may at times be confused with a myocardial infarction or other thoracic problem that causes diaphragmatic and pleural irritation. Posterior and retroperitoneal perforation may mimic both pancreatitis and a dissecting aortic aneurysm. A neoplasm should always be considered as an aetiology for perforation of the gastroduodenal complex. Oesophageal Perforation Perforation of the oesophagus is another life-threatening condition. It may occur secondary to iatrogenic causes, trauma, tumours, foreign bodies, caustic injuries or forceful vomiting.

In immunosuppressed patients blood glucose of 600 discount duetact 17 mg with mastercard, the life-threatening neutropenic enterocolitis preferentially involves the caecum and may extend into the terminal ileum and ascending colon. Typhoid fever is a systemic disease, preventable with appropriate vaccinations prior to travel to endemic regions. Classically, the first week of illness manifests with rising fever and bacteraemia. Abdominal pain and macular `rose spots` develop on the trunk and abdomen during the second week. Gastrointestinal tuberculosis can have an acute or a chronic presentation with non-specific abdominal pain and constitutional and gastrointestinal symptoms. The inflammation and ulceration involves the distal ileum and colon, frequently in a discontinuous pattern, with normal `skip areas` present in between. This chronic, incurable disease may present acutely and has a tendency for recurrent exacerbations. Abdominal pain, diarrhoea, malabsorption, anorexia and fatigue are the typical symptoms and may lead to substantial weight loss. The acute flare-up typically presents with abdominal pain and fever and may mimic acute appendicitis and other pathology. Severe inflammation may result in the formation of intraabdominal and retroperitoneal abscesses, enteroenteric and enterovesical fistulas and, uncommonly, free perforation. Chronic inflammation and fibrosis may lead to stricture formation and obstruction. Appendicitis Epiploicae and Omental Infarct An abnormally long or large appendix epiploica may twist around its base. Such torsion, although benign and self-limiting, usually presents with acute abdominal pain and may be confused with acute appendicitis or diverticulitis. They primarily develop in the left colon and are related to abnormal colonic motility and increased intraluminal pressure. Most patients remain asymptomatic, and only a quarter develop complications of inflammation or bleeding. Acute diverticulitis, resulting from microperforation, manifests with signs and symptoms resembling those of acute appendicitis. Right-sided diverticula, usually single and unrelated to the consumption of refined food, are prevalent in Asian countries. Depending on the location of the perforation, an intra-abdominal or retroperitoneal abscess may result.
Forskolin. Duetact.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96999
If detached managing diabetes 90 buy 16mg duetact with amex, this represents a reverse humeral avulsion of the glenohumeral ligament. Subscapularis and biceps tendon the subscapularis recess and subscapularis attachment to the humeral head can be evaluated. Integrity and stability of the groove and the synovium of the biceps tendon are evaluated. This is done by placing the obturator tip just beneath the posterior acromion and then inserting it parallel to the acromion. If the arthroscope is inserted properly into the subacromial space anterior to the posterior bursal curtain, then the distended bursal space should allow for visualization of the subacromial structures. The inferior aspect of the acromion is evaluated and the coracoacromial ligament is identified. The arthoscope is oriented to look downward at the greater tuberosity and attachment of the rotator cuff. A probe from the anterior or lateral portal is used to assess the rotator cuff integrity. The rotator cuff attachment should be smooth, without fraying or thinning of the tissue. Internal and external rotation of the arm will allow for visualization of the entire cuff. Once the subacromial space has been evaluated and all pathology has been addressed, the arthroscopic instruments and cannulas can be removed from the shoulder. Wounds can be dressed and the shoulder placed in a sling for comfort or for rehabilitation purposes, depending on the procedure performed. The surgeon should ensure that the appropriate equipment is available in the operating room. The surgeon must make sure that all necessary equipment and instruments are available, including suture anchors for labral repair or rotator cuff procedures, multiple-size cannulas, sutures and passing instruments, shavers and burrs, and thermal or electrocautery. It is important to have a systematic, stepwise approach to diagnostic arthroscopy so that all structures are adequately visualized and no pathology is missed. Allowable range of motion and exercises are tailored to the specific procedure performed and will be discussed in detail in the following chapters. It allows for complete visualization of the glenohumeral joint and subacromial space and treatment of identified pathology. Outcome data for specific procedures performed are discussed in the following chapters. Effect of age on the natural history of the shoulder: a clinical and radiological study in the elderly. Laxity is a physiologic term used to describe the passive translation of the humeral head on the glenoid. Instability is a pathologic state characterized by abnormal translation of the humeral head on or over the glenoid, leading to frank dislocation, functional impairments, or pain.
The undersurface of the meniscus is probed and inspected diabetes prevention trial metformin generic 16 mg duetact fast delivery, and the meniscus is tested with a hoop stress test. The perimeter of the tibial plateau is probed for flipped flap tears of the meniscus. This may require a variation of the modified Gillquist maneuver (mentioned previously). The anterior cruciate ligament is well visualized on the left, with the posterior cruciate ligament on the right more obscured by fat and synovial tissue. The posterior horn of the lateral meniscus, the posterior lateral femoral condyle, the posterior meniscal root, and the capsular attachment are visualized. Shoulder arthroscopy instrumentation and cannula systems can be helpful with more complex surgeries as well. The surgeon should talk to the patient before the surgery and perform an examination under anesthesia to confirm the pathology necessitating surgery. High pump pressures can result in fluid extravasation into the soft tissues, leading to the potential for compartment syndrome. The surgeon may want to consider gravity inflow or lower pump pressures in such situations. Older patients are more likely to sustain an injury to the collateral ligaments when varus or valgus stresses are applied to gain compartment visualization. Some patients have ligamentously tight knees, making it difficult to reach the posterior aspect of the medial and lateral tibiofemoral compartments. The surgeon should use all portals available, including the far medial and lateral as well as the posteromedial and posterolateral portals, to properly address the pathology. Although there is some variation in portal closure, we prefer a simple skin closure with a nonabsorbable monofilament suture. Regardless of suture type or technique, the surgeon should obtain a tight closure. Intra-articular and portal injection of local anesthetic may help with postoperative pain management. Deep vein thrombosis prophylaxis may be accomplished with a compression dressing from the toes to the thigh, elevation, mobilization, and ankle pumps. Regardless of postoperative weight-bearing status, most patients will require crutches for mobility. Cryotherapy has been shown to improve pain scores after knee arthroscopy and is recommended. Complications of arthroscopy and arthroscopic surgery: results of a national survey. Incidence of deep vein thrombosis after arthroscopic knee surgery: a prospective study. The synovial lining undergoes hyperplasia, most prominent in rheumatoid arthritis.
It should be noted that after abdominal operations diabetes testing kit reviews buy generic duetact 17 mg on line, especially laparoscopic surgery, air may be present within the abdominal wall during the early post-operative period. This type is less common on the torso than that found on the extremities, but it has the same characteristics. Depending on the stage, skin changes can vary from erythema to purple discoloration. Characteristic oedema, induration of the tissues and severe pain are the hallmarks of this morbid disease. With advanced disease, blistering develops secondary to inflammatory changes within the subcutaneous plane and thrombosis of the vascular network. Epidermolysis signifies an irreversible stage of disease requiring surgical intervention. Bruising around a post-operative incision evolves in a pattern of colour changes from erythema to greenish and yellowish hues. Bruising in the early stages may have the same colour as cellulitis, but will not have the oedema and the characteristic tenderness of infection. Superficial rubbing with the finger usually produces pain in cellulitis, and is generally painless in patients with bruising. Rectus sheath haematomas develop acutely secondary to rupture of the inferior and, less commonly, superior epigastric arteries. Haematomas may occur in young individuals due to vigorous exercise, and may be also seen in pregnancy. Most commonly, they are spontaneous in nature and occur in patients with a coagulopathy. Unless they are expanding or causing pressure changes in the skin, observation and the reversal of coagulopathy are sufficient. It is important to determine whether the mass is intra-abdominal or located within the abdominal wall. Any soft tissue mass, benign or malignant, that is seen in other areas of the body may be encountered on the abdominal wall. Similarly, very rare mesotheliomas arising from the parietal peritoneum have the clinical signs of an intraperitoneal mass. Both subcutaneous and deep subfascial tumours may reach an impressive size before diagnosis. Endometriosis of the abdominal wall is a rare condition in which endometrial implants develop in the umbilicus and other locations where there have been abdominal incisions. The principal manifestations of this condition are pain, swelling and bloody discharge if the lesion is superficial.

A history of a significant traumatic event indicates a more favorable prognosis of a potentially correctable problem diabetic diet indian recipes cheap duetact 16mg free shipping. Similarly, mechanical symptoms such as sharp stabbing pain, catching, or locking are favorable indicators for surgical intervention. Simply having pain, with or without activity, is a poorer prognostic indicator for the success of arthroscopy. Squatting and prolonged hip flexion such as sitting often will exacerbate hip symptoms. Ascending and descending stairs or inclines is more troublesome than walking on level surfaces. Entering and exiting an automobile is very characteristic for recreating symptoms, because it loads the hip in a flexed position while introducing a torsional component. Difficulty getting shoes and socks on and off usually indicates restricted motion and more advanced disease. Localization of the symptoms starts with an understanding that the L3 nerve root serves as the principal innervation of the hip. Symptoms, therefore, are sometimes referred to the L3 dermatome, explaining the presence of medial-sided thigh and knee pain. Posterior pain rarely is indicative of hip joint pathology, but may occasionally be a presenting feature. Recording flexion and extension must take into account the contributing components of pelvic and lumbar motion. The log roll test is the most specific test for hip joint pathology: the leg is rolled back and forth, rotating only the femoral head in relation to the acetabulum and capsule, without tensioning any of the surrounding soft tissue structures. The impingement test generally has been found positive for virtually any irritable hip joint, regardless of the nature of the pathology. This maneuver is more sensitive for hip joint pathology, but may be uncomfortable even in a healthy hip. It also is important to distinguish whether this test recreates the type of symptoms that the patient experiences with activity, more than simply whether or not it is uncomfortable. Abduction with external rotation also can be sensitive for eliciting hip joint symptoms. It may impinge upon posterior lesions or exacerbate anterior symptoms from translation of the femoral head and, thus, is not especially specific for the location or type of intraarticular pathology. The optimal lateral view has yet to be determined, but a standardized reproducible lateral radiograph of the affected hip should be obtained in every case. Radiographs usually are normal with regard to specific findings indicative of soft tissue pathology in the hip. The soft tissue disease usually is far advanced before any radiographic indices emerge.
Gently press down in the centre of the abdomen until the aortic pulsation is felt diabetes type 1 treatment algorithm buy cheap duetact 16 mg on-line. Aneurysms are not always palpable in obese patients, and conversely, a prominent aortic pulsation may be normal in a slender individual. Immediately refer patients with an enlarging aortic width or tenderness over a known aortic aneurysm to a vascular surgeon. The stomach and colon can also be appreciated on physical examination in some patients. A firm, palpable mass in the epigastrium may represent a transverse colon or gastric malignancy. Hard stool may be palpated within the transverse or sigmoid colon in patients with severe constipation. Finally, always perform a rectal examination in any patient with abdominal pain to evaluate for rectal masses and occult blood. In women, a dedicated pelvic examination can exclude a gynaecological cause of non-acute abdominal pain. Combined inspection and palpation of the abdominal wall surface and both groins allows for the detection of any hernias, abscesses or other masses. Patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease may describe a burning sensation in the chest and epigastric area that is worse with meals, bending over or lying flat. Hiatus Hernia Symptomatic hiatus hernia should be considered in patients who report vague, intermittent epigastric or substernal pain, postprandial fullness, nausea or retching. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease is frequently present, and sliding hernias account for the vast majority of cases. The physical examination findings are typically normal in patients with gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and hiatus hernia, although patients with concomitant laryngopharyngeal reflux may have pharyngeal erythema and oedema. Non-reducible or incarcerated hernias have a higher risk of strangulation or ischaemia of the contents of the hernial sac, such as bowel or omentum. An abdominal wall mass that is tender, fluctuant and erythematous suggests an abscess. Abdominal wall abscesses may be more commonly seen in obese, diabetic patients or immunocompromised individuals. The presence or absence of associated symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, constipation and abdominal distension should be noted. The physical examination should identify disease-specific signs to assess for the likelihood of each possible diagnosis. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is the primary diagnostic modality for non-acute conditions of the upper gastrointestinal tract. The physical examination findings are typically normal in patients with gastritis and peptic ulcer disease unless there is significant anaemia leading to pallor of the conjunctivae, nail beds, palmar creases and face, and a positive stool guaiac test. Evaluation of Patients with Abdominal Pain 555 production from a gastrin-secreting tumour, usually located within the pancreatic head.
Wilson, 51 years: Abdominal auscultation early in the course of the obstruction reveals a characteristic pattern: the low-pitched gurgling sound rapidly changes to a high-pitched tinkling, corresponding to hyperperistalsis. Selecting larger-diameter nails based on feedback of cortical chatter during reaming seems to improve union rates when the retrograde nailing technique is used. Recording flexion and extension must take into account the contributing components of pelvic and lumbar motion.
Torn, 27 years: The dense bone of the supra-acetabular region offers stability of fixation as good as or better than the iliac crest. Recording flexion and extension must take into account the contributing components of pelvic and lumbar motion. Arthroscopic osteochondral autografting includes five steps: lesion evaluation and preparation, determination of the number of grafts needed, defect preparation, graft harvest, and graft delivery.
Alima, 43 years: Signs associated with blunt renal injury may include haematuria associated with flank bruising, tenderness and swelling. Trochanteric portal cephalomedullary nails are recommended if a nail technique is preferred. A unilateral palpable adnexal mass is detectable on pelvic examination in many patients.
Masil, 62 years: With internal rotation of the shoulder (followthrough phase of throwing), the inferior glenohumeral ligament complex is the main restraint to posterior translation. In the gastrointestinal tract under the influence of bacterial enzymes bilirubin is converted to colourless urobilinogens. Most commonly, free rupture occurs into the peritoneal cavity with the rapid development of profound shock.
Campa, 28 years: Arthroscopic repairs of full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus: does the tendon really heal The outcomes and repair integrity of completely arthroscopically repaired large and massive rotator cuff tears. The capsule-to-nerve distance changes very little with insufflation, however, and the protective effect of insufflation is lost when the elbow is in extension. Many fractures have a component of impaction injury on the femoral head, so the fracture may not key in the patient is in the lateral position.
Rasul, 44 years: Osteochondral defects may cause decreased flexion via effusion, or may have normal range of motion. The repeated hemarthroses can lead to a chronic, progressive synovial hyperplasia. The major nerve supply to the lateral compartment is the superficial peroneal nerve, which supplies the two muscles of the compartment.
Bengerd, 35 years: The posterior portal (a) is established higher than normal to lessen the risk of iatrogenic articular damage. Men with locally advanced or systemic disease may present with bone pain from skeletal metastases, signs of renal impairment from unilateral or bilateral ureteric obstruction or bowel symptoms from impingement on the rectal canal (despite the close proximity of the gland to the bowel, prostate cancer rarely directly invades the rectal wall). In this group, it is important to consider whether the infection is complicated by an underlying structural or functional abnormality of the urinary tract, or by the To examine for renal pathology, the patient should lie on their back with their head slightly elevated to relax the abdominal wall.
Dargoth, 52 years: Stellate or comminuted, transverse, vertical, apical or inferior pole, and sleeve fractures are common descriptive terms used in the classification of patellar fractures. These will help the surgeon decide on nonsurgical versus surgical treatment and resection versus repair. If oblique locking bolts are chosen proximally, oblique fluoroscopic views should be used prior to insertion handle removal to avoid placing long screws that are particularly symptomatic on the medial side of the knee and to avoid injury to the peroneal nerve posterolaterally.
References