Joanna Chikwe, MD
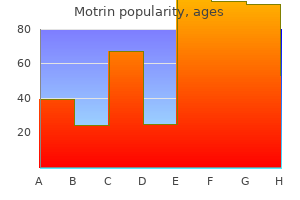
Motrin dosages: 600 mg, 400 mg
Motrin packs: 90 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills, 120 pills
Myalgias and muscle cramps occur in hypothyroidism pain treatment for sciatica discount motrin 600 mg visa, uraemia, and electrolyte imbalance. Do the pains represent bone pain-persistent, deep-seated pains that change little with posture or movement Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, lymphoma, and neuroblastoma are the most common malignant lesions. It is termed macrophage-activation or haematophagocytic syndrome, and is characterized by cytopenias, hepatic dysfunction, encephalopathy, and disseminated intravascular coagulation with bleeding. Examination Full medical examination A full medical examination is essential: Pharyngeal erythema is non-specific and swabs should be cultured for streptococci. Persistent tachycardia without anaemia/fever raises the possibility of myocarditis. Thrombosis of dilated blood vessels at the margin of the upper lid is characteristic of dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Dry eyes are a common complaint, and may be the result of medication side effects; dry eyes are also found in association with a number of rheumatic diseases. Musculoskeletal examination-general principles Synovitis of a joint is characterized by soft-tissue swelling, effusion, and a reduced range of joint movement. Musculoskeletal examination-patterns of joint, tendon, and enthesis involvement A full examination should be undertaken: Ligament/tendon insertion tenderness, not necessarily associated with swelling, may denote enthesitis. Weakness can accompany metabolic and endocrine myopathies and is not specific for inflammatory myopathy. Protein and blood may be a sign of underlying kidney inflammation in connective tissue diseases. A sensitive indicator (though non-specific) of active disease is von Willebrand factor. Genotypic and phenotypic heterogeneity Haemolytic anaemia (reticulocytosis) Hepatomegaly. Lactic acidosis Death in first year Skeletal myopathy Severe skeletal muscle weakness and cardiomyopathy Variation from severe childhood myopathic to symptomless adult forms Severely limited exercise capacity Dyspnoea. It is non-invasive, non-ionizing, can be done at the bedside, and is generally accepted well by children. This is especially advantageous in the hip, where femoral head position and abnormal movement can be seen in young children. Although of less use when joints are involved, bone scan should be considered when pain originates in bone or infection is a possibility. It is more sensitive than radiographs for detecting soft-tissue and most bone lesions.
More than 90% of the infants with Trisomy 18 home treatment for uti pain 600 mg motrin order overnight delivery, or Edwards syndrome, have cardiac manifestations including atrial and ventricular septal defects with polyvalvular heart disease (pulmonary and aortic valve defects), patent ductus arteriosus, overriding aorta, coarctation of aorta, hypoplastic left heart syndrome, Tetralogy of Fallot, and transposition of the great arteries. Trisomy 13, Patau syndrome, is the most severe of the viable autosomal trisomies with a median survival of less than 3 days. Therefore, in patients with chromosomal aberration, caution needs to be taken to rule out associated cardiac anomalies. Management will depend on the associated abnormality and the hemodynamic effect of the anomaly. It is the most common cyanotic congenital heart disease in neonates, and the overall annual incidence is 20 to 30 per 100,000 live births. This disorder is associated with a poor prognosis with mortality reaching 90% by the end of the 1st year if untreated. American Heart Association Congenital Cardiac Defects Committee, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young. Genetic basis for congenital heart defects: Current knowledge: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association Congenital Cardiac Defects Committee, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young: Endorsed by the American Academy of Pediatrics. American Heart Association; Council on Clinical Cardiology, Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee; Quality of Care and Outcomes Research and Functional Genomics and Translational Biology Interdisciplinary Working Groups; Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Contemporary definitions and classification of the cardiomyopathies: An American Heart Association Scientific Statement from the Council on Clinical Cardiology, Heart Failure and Transplantation Committee; Quality of Care and Outcomes Research and Functional Genomics and Translational Biology Interdisciplinary Working Groups; and Council on Epidemiology and Prevention. Bicuspid aortic valve predisposes to aortic valve stenosis and regurgitation, aortic valve endocarditis, and proximal aortic dilation. However, many children with complex congenital heart defects previously fatal early in life are now living to adulthood after surgical and catheter-based interventions. In addition, not only must the primary lesion or surgical correction be defined, but there must also be a thorough evaluation of longterm structural and hemodynamic sequelae. Any right- and left-sided locations can theoretically be used to define right- and left-sided flow, but the outflow tracts are usually best because of their circular shape and relatively stable cross-sectional area throughout systole. However, a "standard protocol" for performing and interpreting the data is often inadequate. Orientation Proper orientation is an essential first step in interpreting congenital echocardiograms. Unlike standard echocardiography in acquired heart disease, the echocardiographer cannot assume normal apical position, atrial situs, atrioventricular relationship, or ventriculoarterial relationship. The segmental approach to the diagnosis of congenital heart disease is described below.
Diseases
Mortality rate may exceed 50%; however pain research treatment impact factor motrin 600 mg overnight delivery, rapid correction of sodium may produce central pontine myelinolysis and cerebral edema which can be fatal. Sodium maintains irritability and conduction in nerve and muscle tissue and assists in the regulation of acid-base balance. Since most diets have an excess of sodium, the kidney maintains normal levels through excretion of sodium and retention of free water. Isotonic Isotonic hyponatremia is characterized by a low serum sodium level but a normal plasma osmolality. It is a relative state of free water deficit and an increase in the solute concentration in all body fluids. The three major hypernatremic states result from loss of water, hypotonic fluid loss, and sodium retention. Hypertonic Water Loss Pure water loss usually occurs with increased insensible loss through the skin. Thermal burn injury is associated with the greatest risk of insensible water loss. Diabetes Hypertonic hyponatremia is diagnosed by a low serum sodium and a plasma osmolality of greater than 290 mOsm/ kg H2O. Intravenous Fluids: A Comparison Solution Isotonic saline Lactate Ringer Hypertonic saline Pros Slightly hypertonic to plasma Minimizes fluid shifts Relatively isotonic to plasma Less volume required May reduce the interstitial edema Isotonic to plasma Provides substrate and caloric intake May help maintain colloid osmotic pressure and decrease interstitial edema Equivalent to 5% albumin Volume expansion with small amounts Cons May produce hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis Use with caution in patients with renal or adrenal disease. May interact with drugs due to calcium binding May cause hypernatremia Rapid correction of sodium may increase risks of cerebra edema. Numerous drugs, including oxytocin, have been implicated in this disorder and they are listed as follows: in the presence of hemolysis or factitiously decreased when processing of a lab sample is delayed. The causes of hypokalemia may be classified as transcellular shift, as in the use of beta agonist (ie, terbutaline), or from depletion. The major causes of the latter are renal loss, most commonly caused by diuretic therapy, or extrarenal, usually seen with excessive diarrhea. Hypovolemic hyponatremia is characterized by the loss of fluid that is isotonic to plasma combined with volume replacement using a hypotonic fluid. The most common causes of this disorder are diuretics, adrenal insufficiency, or diarrhea. A urine sodium can help to identify the etiology (ie, renal or extrarenal) of the hyponatremia. Hypervolemic hyponatremia occurs in patients in which there is excess water and sodium gain.
In leads V1 or V2 knee pain treatment youtube buy discount motrin 400 mg on line, the presence of an R wave of long duration (A > 30 ms), long duration from the onset of the R wave to the nadir of the S wave (B > 60 ms), or any notching on the down stroke of the S wave is suggestive of ventricular tachycardia. All of the above features are more consistent with a supraventricular tachycardia. In this case, however, there is clear notching on the down slope of the S wave in V1, which is highly suggestive of ventricular tachycardia. Indeed, this was a case of idiopathic ventricular tachycardia arising from the left ventricular outflow tract tachycardia. In patients with idiopathic ventricular tachycardias without structural heart disease, myocardial conduction can be fairly rapid. Many of these tachycardias can be located more centrally near the septum and conduct to the right ventricle and left ventricle nearly simultaneously. This seemed to be reasonable for right bundle morphology tachycardias but did not work well for tachycardias with a left bundle morphology, and later studies have shown that a cutoff of 160 ms is better in these cases. The longest duration of the R onset to S nadir is seen in lead V1 and measures 160 ms. This extreme left axis deviation is essentially diagnostic of ventricular tachycardia. Probable triphasic morphology in V1 is supported by the clear triphasic morphology in lead V2. These beats are the result of antegrade conduction from the atrium to the ventricle across the His-Purkinje system occurring during ventricular tachycardia. All of these features point to a supraventricular tachycardia with left bundle aberration as the cause of the tachycardia. If this were a true capture beat, it would indicate that the tachycardia was due to ventricular tachycardia (see text for discussion). In fact, all of these beats were fusion beats as a result of ventricular ectopy occurring during the tachycardia. Whether a tachycardia is hemodynamically stable or not probably depends more on the tachycardia rate in conjunction with the degree and type of cardiac disease than on the tachycardia mechanism. The rhythm that has the greatest degree of irregularity and should be recognized because of its irregularity is atrial fibrillation. When atrial fibrillation is moderately rapid (rates <180 bpm), there is usually a significant amount of beat-to-beat variability in the rate, which is fairly easy to discern. When atrial fibrillation becomes more rapid, it can regularize in its appearance and be more difficult to recognize. A special subgroup of patients with atrial fibrillation and wide complex tachycardia that needs to be mentioned is patients with atrial fibrillation and Wolfe-Parkinson-White syndrome. Some of these pathways can conduct very rapidly and tachycardia rates can approach 300 bpm.
This reduction was attributed to improved communication and more efficient administration of blood products joint pain treatment natural 600 mg motrin amex. Allogeneic blood transfusion increases the risk of postoperative bacterial infection: a meta-analysis. Efficacy of red blood cell transfusion in the critically ill: a systematic review of the literature. Preoperative autologous blood donation reduces the need for allogeneic blood products: a prospective randomized study. Maternal and fetal hemodynamic effects of autologous blood donation during pregnancy. Safety and use of autologous blood donation during the third trimester of pregnancy. The ability of the Haemonetics 4 Cell Saver System to remove tissue factor from blood contaminated with amniotic fluid. Cell salvage in obstetrics: an evaluation of the ability of cell salvage combined with leucocyte depletion filtration to remove amniotic fluid from operative blood loss at caesarean section. The safety of intraoperative autologous blood collection and autotransfusion during cesarean section. Massive transfusion protocols: the role of aggressive resuscitation versus product ratio in mortality reduction. The average blood loss for a vaginal delivery, cesarean delivery, and cesarean hysterectomy is 500, 1000, and 1500 cc, respectively. Because of these varied definitions, the exact incidence of postpartum hemorrhage is difficult to determine; however, rough estimates suggest that postpartum hemorrhage complicates 1% to 5% of all deliveries. However, as bleeding continues, further vasoconstriction is impossible resulting in drops in blood pressure, cardiac output, and end-organ perfusion. It is important for the obstetrician to recognize these responses since the quantity of blood loss that occurs during a postpartum hemorrhage is often underestimated as stated previously. Since the obstetrician is faced with primary postpartum hemorrhage more often than secondary, the remainder of this chapter will focus on its risk factors and therapy. Uterine Atony Uterine atony, or the inability of the uterine myometrium to contract effectively, is the most common cause of primary postpartum hemorrhage. These changes include increased red cell mass, increased plasma volume, and increased cardiac output. While operative vaginal delivery remains the most significant risk factor for a genitourinary tract laceration, other sources of obstetrical trauma can contribute to this cause of hemorrhage. A genitourinary tract laceration should be suspected if bleeding persists after a delivery despite good uterine tone.
Syndromes
However rush pain treatment center meridian ms best motrin 600 mg, the finding of extensive ischemia (5 segments) on a stress echocardiogram may identify those with triple vessel or left main disease in whom revascularization may improve both perioperative and long-term outcome. Assessment of Myocardial Viability the utility of stress echocardiography for the assessment of myocardial viability has been documented in numerous studies. Testing is usually reserved for those patients with significant ischemic left ventricular dysfunction who are potential candidates for revascularization, in the hope that ventricular function and prognosis will improve with revascularization of viable myocardium. Dobutamine echocardiography is the most commonly used ultrasound modality for assessment of viability. The uncoupling of the inotropic and chronotropic effects of dobutamine at low doses (10 g/kg/min) permits improvement of contractile function in stunned or hibernating myocardium without major increases in heart rate and myocardial oxygen demand. In the setting of coronary obstruction, higher doses of dobutamine produce ischemia with worsening of function in regions that exhibited contractile reserve with low dose dobutamine. The "biphasic response" with improvement of function at low doses and worsening of function at higher doses of dobutamine has been shown to have a high positive predictive value for identifying viable myocardium that will have functional recovery with revascularization. Other inotropic agents and vasodilators, such as dipyridamole, have been successfully used as alternatives to dobutamine for assessment of contractile reserve. Contractile reserve, although a highly specific marker for functional recovery, is a less sensitive marker for tissue viability than perfusion imaging using single photon emission computed tomography or metabolic imaging using positron emission tomography. Echocardiographic contrast perfusion agents also enable assessment of myocardial viability. However, no agents are currently approved for use in the United States for this purpose. Risk Assessment: Following Acute Coronary Syndrome Stress echocardiography may provide valuable information after acute coronary syndrome in patients who have not already undergone coronary angiography and revascularization. Patients without inducible ischemia with preserved global left ventricular systolic function are at lower risk. Those with reduced global function, large areas of nonviable myocardium, or ischemia are at increased risk. Stress echocardiography is not recommended prior to discharge in asymptomatic individuals who have been revascularized after acute coronary syndrome. Stress echocardiography may provide useful information on the functional significance of multivessel disease in patients in whom only the culprit vessel was revascularized. Assessment of Hemodynamics Stress echocardiography combined with Doppler imaging is likely underutilized in the assessment of patients with valvular heart disease. Dobutamine echocardiography may be particularly useful in patients with low flow or low gradient aortic stenosis. Patients with low gradient aortic stenosis (which may be defined by valve area <1. In the former condition, aortic valve replacement may result in substantial improvement in left ventricular function once the marked increase in afterload caused by severe stenosis is relieved. Dobutamine stimulation in relatively low doses up to 20 g/kg/min may be used to distinguish the two conditions.
Protein C is a vitamin K-dependent factor that circulates in plasma as an inactive zymogen knee pain treatment guidelines motrin 400 mg. Binding of thrombin to thrombomodulin, an endothelial cell surface protein, alters the substrate preference of thrombin so that it activates protein C rather than converting fibrinogen to fibrin. Platelets also are activated by collagen, which is present in the subendothelial space and exposed by vascular injury. Leukocytes, including monocytes, adhere to the injured blood vessel wall and are recruited to growing hemostatic plugs and thrombi. Microparticles, which are tiny membrane vesicles released from multiple cell types undergoing necrosis or apoptosis (including platelets, leukocytes, endothelial cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells), circulate in plasma and are recruited to growing thrombi. However, in response to numerous pathologic conditions, including abnormal shear stress, dyslipidemia, oxidative stress, and cytokines, vascular endothelial cells become activated and express multiple prothrombotic and antifibrinolytic factors. Plasminogen binds avidly to C-terminal lysine residues within the partially degraded fibrin clot. Plaque erosion, a distinct mechanism of arterial thrombosis, is characterized by loss of endothelial cell integrity and exposure of underlying vascular smooth muscle cells and extracellular matrix to flowing blood and blood clotting. Coronary vasospasm may play an important role in the pathogenesis of plaque erosion. Disruption of a calcified plate or nodule within an atherosclerotic plaque can also lead to contact of blood with thrombogenic surfaces within the plaque and thrombosis. Erosion of a calcified plate or nodule is more common in older men, and may occur more frequently in carotid arteries than in coronary arteries. Rupture of fibrous cap Superficial erosion Intraplaque hemorrhage Calcium nodule Erosion of calcium nodule Circulation. Antithrombin Deficiency Antithrombin deficiency is uncommon and is more often acquired. Lipoprotein(a) (Lp(a)) Lp(a) is composed of apoprotein(a), which is structurally related to plasminogen, and apo B100, an atherogenic lipoprotein. Protein C/S There are case and small series reports of ischemic stroke in young patients with protein C and protein S deficiency. Routine testing for protein C, protein S, and antithrombin was not recommended for patients with arterial thrombotic disease associated with atherosclerosis, but can be considered in young patients with unexplained arterial thrombosis without atherosclerosis. The strong majority of evidence supports 87 Treatment of Arterial Thrombosis Rajeev Garg, Saravanan Kuppuswamy, Richard Webel, and William P. Warfarin anticoagulates blood by inhibiting post-translational modification of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors.

It is also important to document the basic operative details pain treatment center of southwest georgia motrin 600 mg order without a prescription, including reason for surgery, extent of surgery, and type and size of prosthetic valve. New cardiac symptoms could point toward the possibility of significant complications, especially if the symptoms are abrupt or significant (such as new onset congestive heart failure). The echocardiographic evaluation of a prosthetic valve should include the two-dimensional (2D) evaluation of the structure, paying particular attention to the valve housing stability and leaflet motion. Doppler evaluation allows for hemodynamic assessment of the valve and should include evaluation of peak flow velocity, mean gradient, and evaluation of possible stenosis or regurgitation. Reference values for the hemodynamic profile of various prosthetic valves are available in the literature and are based on valve type and size as well as valve position. These reference values should be taken in to consideration when evaluating a valve for stenosis or regurgitation. Regurgitation can be evaluated for native valves, using various Doppler techniques, however, it is important to pay close attention to physiologic versus pathologic regurgitation. Complications of prosthetic valves can often be visualized or considered based on Doppler evaluation. These include thrombus formation, dehiscence, vegetation, pannus formation, or frank valve dysfunction. Other Options There are limitations of transthoracic echocardiography and often transesophageal echocardiography may offer the benefits of better leaflet visualization, improved hemodynamic assessment, and more thorough evaluation for complications such as paravalvular regurgitation, dehiscence, vegetation, and thrombus. For those patients with possible hemodynamically important valve obstruction due to leaflet immobility (dysfunction or thrombus), fluoroscopy can be utilized for visualization of leaflet motion. Of course, in certain cases where it is clinically important to further evaluate valve-related complications, cardiac catheterization for hemodynamics can be utilized as appropriate to the clinical situation. During auscultation of the mechanical prosthesis, one should hear a crisp click during valve closure; this would be S1 for mitral valve and S2 for aortic valve. Abnormal or new heart sounds should be possible markers of possible valve dysfunction, complications, or a new onset of congestive heart failure related to the valve. In emergency situations where there is significant bleeding, fresh frozen plasma is desirable over intravenous vitamin K, given the risk of overcorrection with vitamin K. Patients who undergo dental or surgical procedures should have their anticoagulant therapy adjusted according to the details in Table 75-7. Patients at high risk of thromboembolism should be considered for bridging with heparin and close monitoring of anticoagulation. Last, perhaps one of the most concerning difficult situations is thrombus formation on the prosthetic valve.
After 3 units of packed red blood cell transfusion pain medication for shingles nerves motrin 600 mg purchase line, the fetal heart rate on the lower panel recovered with return of normal accelerations and disappearance of late decelerations. Uteroplacental perfusion is critical to the maintenance of fetal oxygen and even minor alterations may result in fetal hypoxia. Several potential alterations may occur in the critically ill patient that can result in decreased placental perfusion. A large amount of occult blood loss (eg, intraperitoneal) may not be as readily apparent in pregnancy because of the marked increase in blood volume and the ability of the mother to redistribute blood away from the uterus. As much as 2000 cc (30%) of maternal blood volume may be lost without significant changes in vital signs as opposed to only about 1000 cc (20%) in the nonpregnant female. The placental bed is neurologically linked to the maternal splanchnic (sp) bed and the physiologic response to decrease in blood volume in the mother is diversion of blood away from the placenta when other vital organs (brain, heart, adrenals) must be preserved. Hypovolemia may result in decreased cardiac output further decreasing placental perfusion. While it may seem paradoxical, hypertension is also associated with decreased placental perfusion and the more severe the blood pressure elevation, the more likely one will face an underperfused placenta associated with fetal hypoxia. And finally, often critical situations result in the premature onset of contractions which further decrease uterine blood flow during the contractile epochs. While the fetus may often demonstrate signs of hypoxia as a result of the maternal compromise, the temptation to proceed with delivery can result in destabilization of the mother, unnecessary surgery (ie, cesarean section), and often the unnecessary delivery of a premature infant with the inherent complications of prematurity. One glaring exception to this is in the case of cardiopulmonary arrest, where delivery of the fetus may be the only way to allow adequate maternal resuscitation. The first issue is to determine the gestational age and potential viability of the fetus. The approach to subsequent evaluation and management will always depend on this issue. To maximize fetal well-being in general, be sure the mother has some left uterine displacement usually best accomplished with a roll under the right buttocks. Administer oxygen by face mask using a tightly fitting nonrebreathing mask whenever possible. Determine as quickly as possible the general condition of the mother including especially her primary diagnosis, her vital signs, and hemodynamic status and include pulse oximetry to quickly determine her oxygen saturation. Maternal evaluation will include palpation of the uterus for size, fetal position, tenderness, and contractions, and, where appropriate, may also include a perineal or even pelvic examination to assess for bleeding, rupture of membranes, and cervical dilation. At that point, if the fetus is of a viable gestational age, cardiotachometry is the critical next step.
Internally rotate the lower leg (1) then extend it (2) (Palpable) clunk at joint line pain medication for dogs arthritis motrin 600 mg with amex. If infection is considered, broad-spectrum antibiotics against staphylococcal and streptococcal agents should be started immediately while awaiting culture data. The patient should not bear weight on an acutely infected joint (b Chapter 22, p 589). Address biomechanical factors Input from a physical therapist may be helpful in cases of anterior knee pain. The reader is referred to b Chapter 22, p 589 for steroid injection techniques and to the relevant chapters for specific diseases. Joint injection therapies In patients with large joint effusions, merely aspirating the effusion may provide some level of symptomatic relief. Saline irrigation and injections with hyaluronic acid preparations are also used, but response is variable. Although some studies demonstrate improved pain control and function, other studies clearly indicate that these are no better than placebo. Strong ligaments secure the ankle (formed by tibia above/medially and fibular malleolus laterally) and talocalcaneal (subtalar) joints and bones of the midfoot. The configuration of bones at synovial articulations allows dorsal flexion (foot pulled up), plantar flexion ( to walk on toes), inversion (foot tips in), eversion (foot tips out), and small degrees of adduction and abduction. Anatomy of the long muscles and tendons In the lower leg a strong fascia connects the tibia and fibula. Their tendons pass in front of the ankle in synovial sheaths held down by strong retinaculae. The tibialis anterior, the bulkiest flexor, inserts in to the medial midfoot (medial cuneiform). Tibialis posterior, the most bulky plantar flexor, inserts in to the plantar surface of the navicular. Anatomy of intrinsic foot structure Intrinsic foot structures have been greatly modified during evolution to combine provision of a flexible platform for support and a rigid lever for thrusting body weight forward when walking. The latter two muscles arise from the plantar surface of the calcaneum deep to the plantar fascia. The common peroneal is prone to pressure neuropathy as it runs superficially around the fibular head. A superficial branch supplies the peroneal muscles and most of the skin over the dorsum of the foot. It then passes under the medial flexor retinaculum dividing in to medial and lateral plantar nerves, which supply the intrinsic plantar muscles of the foot and skin of the sole. Functional anatomy In a normal gait pattern, the foot is dorsiflexed and invertors/evertors stabilize the hindfoot for heel strike.
Aidan, 24 years: Bicuspid aortic valve predisposes to aortic valve stenosis and regurgitation, aortic valve endocarditis, and proximal aortic dilation. Mutations impairing force transmission have also been identified in several cardiac proteins such as myosin, tropomyosin, actin, titin, desmin, and dystrophin. It is caused by increased vasopressinase activity due to either increased placental production of the enzyme or decreased hepatic vasopressinase metabolism as a result of liver damage. It can still be seen in patients with chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and familial Mediterranean fever.
Faesul, 38 years: For example, epidemiologic information is used to determine the components of the influenza vaccine to be administered each year based on the currently active strains and geographic movement of the influenza virus. Others contend that patients needing a second transplant should be considered on the same basis as those being evaluated for a first transplant. This could be introduced at about the age of 11 years and encouraged by trying to see the adolescent by themselves for part of their consultation by the time they are 13�14 years of age. Be sure that personnel and equipment necessary to perform caesarean delivery and to resuscitate the baby are present.
Silvio, 53 years: In addition, it is standard of care for the team to attend all cesarean deliveries. Bicuspid aortic valve predisposes to aortic valve stenosis and regurgitation, aortic valve endocarditis, and proximal aortic dilation. A more provocative test can be done by gently extending each knee in turn in the slump position. Longer periods of maternal hypoxemia and acidosis, however, may result in permanent fetal damage or progression in to active labor and may require delivery.
Kafa, 43 years: The supraumbilical vertical skin incision with a fundal uterine incision with breech extraction of the vertex fetus (in conjunction with bilateral tubal ligation) has been shown to have similar postoperative morbidity in morbidly obese patients when compared to a low transverse abdominal incision. It may denote self-limiting streptococcal infections but may also herald the desquamating palmar (and sole) rash of Kawasaki disease (b Chapter 14, p 385). The extent of reversible ischemia on the exercise imaging study should be considered before proceeding to cardiac catheterization. In this chapter, we will review valvular, congenital, and acquired cardiac lesions and their impact on pregnancy management.
Rakus, 65 years: Platelet antibodies can be platelet-associated (direct, platelet-bound) or circulating (free, indirect, serum). Drawbacks of the conventional method are longer duration of atrial fibrillation, longer duration of anticoagulation, and lack of resolution of thrombi in 20%. Levels below this on supplemental oxygen with rebreathing mask may require ventilator therapy. A spasm is likely to force the bones of a joint out of normal alignment, thus causing additional pressure on the nerves and increasing the pain.
References