
J. Matt Pearson, MD
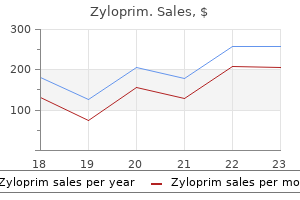
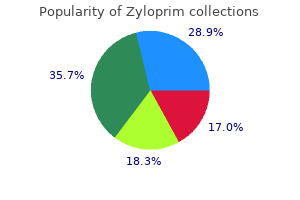
Zyloprim dosages: 300 mg, 100 mg
Zyloprim packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

The results identified not only previously documented interactions treatment 9mm kidney stones order 100 mg zyloprim with visa, but also new connections with cellular proteins and pathways that are potential targets for future pharmacological intervention. In Silico Drug Discovery via Virtual Screening With all the advances in the "-omics" (genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics), an enormous number of potential targets for drug discovery have been identified. Furthermore, as a result of advances in chemistry, the number of chemical structures that can be tested as antiviral compounds has increased dramatically. In fact, one estimate suggests that as many as 1064 chemicals can be made to test for activity against human protein targets. Despite the paucity of lead antiviral compounds that engage such targets, no one would seriously think of urging medicinal chemists and biologists to do random screening with all possible compounds. Structural biologists have provided atomic-resolution models for numerous viral and cellular proteins, and homologs of the vast majority of possible enzymatic active sites are present in current protein structure databases. When a virtual small molecule "fits" into a pocket, the molecule is obtained or synthesized and then tested in a mechanism- or cell-based assay. Modifications to improve activity are made, and the computational analysis and testing are reiterated (Box 9. Further technological advances, such as improved systems for homology modeling from known structures, and development of algorithms for predicting protein structures de novo from coding sequences are expected to increase the future effectiveness of in silico approaches. The paradigm of virtual screening has been called "genome-to-drug-to-lead," and it has the potential to reduce the formidable human resource requirements for chemistry and biology. Research and lead identification, the "R" of "R&D," represent only the beginning of the process of producing a drug for clinical use. The "D" of "R&D" is development, comprising all the steps necessary to take an antiviral lead compound through safety testing, scale-up of synthesis, formulation, pharmacokinetic studies, and clinical trials. Black lines correspond to interactions between host proteins (289) that were obtained from publicly available databases; dashed lines correspond to links found in a virus interaction database. Virtual, in silico screening of some 200,000 commercially available compounds that satisfied these features yielded several likely candidates. Analyses of structure-activity relationships led to the synthesis, by various groups of investigators, of structurally related inhibitors with ever-increasing potency when tested for antiviral activity in cell cultures. Related compounds are now being tested for use in the clinic (see panels B and C). Most surprising, however, was the discovery that their antiviral potency was determined primarily by their ability to block proper virus particle maturation, not by their effects on enzymatic activity. The compounds promote integrase multimerization, a reaction that, for as yet unknown reasons, hinders formation of the normal electron-dense progeny viral cores. Most importantly, this research demonstrated that allosteric sites on retroviral integrase are valid targets for antiviral drug discovery, and that in silico screening is a practical approach to identifying relevant lead compounds.
The entire cardiac output passes over the very large surface area of the pulmonary capillary bed symptoms genital warts discount zyloprim 300 mg with mastercard, allowing the lungs to act as a site of blood filtration and storage as well as for the metabolism of vasoactive constituents of the blood. Reservoir for the Left Ventricle the pulmonary circulation, because of its high compliance and the negative intrapleural pressure, contains 250 to 300 mL of blood per square meter of body surface area. If left ventricular output is transiendy greater than systemic venous return, left ventricular output can be maintained for a few strokes by drawing on blood stored in the pulmonary circulation. The Pulmonary Circulation as a Filter Because virtually all mixed venous blood must pass through the pulmonary capillaries, the pulmonary circulation acts as a fllter, protecting the systemic circulation from materials that enter the blood. The particles illtered, which may enter the circulation as a result of natural processes, trauma, or therapeutic measures, may include small fibrin or blood clots, fat cells, bone marrow, detached cancer cells, gas bubbles, agglutinated erythrocytes (especially in sickle cell disease), masses of platdets or leukocytes, and debris from stored blood or intravenous solutions. If these particles were to enter the arterial side of the systemic circulation, they might occlude vascular beds with no other source of blood flow. This occlusion would be particularly disastrous if it occurred in the blood supply to the central nervous system or the heart, causing a stroke or a myocardial infarction. Obviously, no gas exchange can occur distal to a particle embedded in and obstructing a capillary, and so this mechanism is limited by the ability of the lung to remove such flltered materiaL If particles are experimentally suspended in venous blood and are then trapped in the pulmonary circulation, the diffusing capacity usually decreases for 4 to 5 days and then returns to normal. The mechanisms for removal of material trapped in the pulmonary capillary bed include lytic enzymes in the vascular endothdium, ingestion by macrophages, and penetration to the lymphatic system. Patients on cardiopulmonary bypass do not have the benefit of this pulmonary capillary fil~ tion, and blood administered to these patients must be filtered for them. Fluid Exchange and Drug Absorption the colloid osmotic pressure of the plasma proteins normally exceeds the pulmo~ nary capillary hydrostatic pressure. This tends to pull fluid from the alveoli into the pulmonary capillaries and keep the alveolar surface free of liquids other than pul~ monary surfactant. This protects the gas exchange function of the lungs and opposes transudation of fluid from the capillaries to the alveoli. As noted in Chapter 1, type I alveolar epithdial cdls may also activdy pump sodium and water from the alveolar surface into the interstitium. Drugs or chemical substances that readily pass through the alveolar~capillary barrier by diffusion or by other means rapidly enter the systemic circulation. The lungs are frequently used as a route of administration ofdrugs and of inhalant anes~ thetic gases. Aerosol drugs intended for the airways only, such as the bronchodila~ tor isoproterenol, may rapidly pass into the systemic circulation, where they may have large effects. The effects of isoproterenol, for example, could include cardiac stimulation and vasodilation.
The decrease in intrapleural pressure is equal to the sum of the elastic recoil pressure treatment effect definition generic 100 mg zyloprim fast delivery, which increases as the lung inflates and the pressure drops along the airways as gas flows into the lung from higher (atmospheric or 0 pressure) to lower pressure (alveolar, subatmospheric pressure). On exhalation, the diaphragm moves back into the chest, intrapleural pressure increases. In the alveoli, the driving pressure for expiratory gas flow is the sum of the elastic recoil of the lung and the intrapleural pressure. However, when an individual is supine, the position of the diaphragm is changed due to gravitational effects, and the result is that the recoil pressures for the chest wall, and as a consequence for the respiratory system, are shifted to the right. Upright, the diaphragm is pulled down by gravity; supine, the abdominal contents push inward against the relaxed diaphragm. The displacement of the diaphragm into the chest decreases the overall outward recoil of the chest wall and displaces the chest wall elastic recoil pressure to the right. These curves are obtained by asking participants to breathe into a spirometer (see Chapter 4) to measure lung volumes. An esophageal balloon is placed in the distal onethird of the esophagus to measure intrapleural pressure. Participants then inspire to a specific lung volume; a stopcock in the spirometer tubing near the mouth is closed, and the participant is instructed to relax the respiratory muscles. The pressure at the mouth is equal to alveolar pressure because there is no airflow, and this is equal to the recoil pressure of the lungs (Pl) and the chest wall (Pw). Because the intrapleural pressure is known, the individual recoil pressure of the lungs and the chest wall can be calculated. If the esophageal pressure is -5 cm H2O and the pressure at the mouth in the absence of airflow is -5 cm H2O what is the transpulmonary pressure Surface tension is a measure of the attractive force of the surface molecules per unit length of the material to which they are attached. The units of surface tension are those of a force applied per unit length (dynes/cm). Similar to That is, this transpulmonary pressure would result in no airflow into the lung and would represent either end inspiration or end exhalation.
Host Range Can Be Expanded by Mutation medications similar buspar zyloprim 100 mg order without prescription, Recombination, or Reassortment Canine Parvoviruses: Cat-to-Dog Host Range Change by Two Mutations Canine parvovirus was identified in several countries in 1978 as the cause of a new enteric and myocardial disease in dogs. Canine parvovirus apparently evolved from the feline panleukopenia virus that infects cats, mink, and raccoons, but not dogs. Because canine parvovirus appeared less than 40 years ago, it has been possible to analyze dog and cat tissue collected in Europe in the early 1970s to search for the progenitor canine parvovirus. The ancestor of canine parvovirus began infecting dogs in Europe during the early 1970s, and within 8 years, it had spread to several other continents. The stability of the new virus and its efficient fecal-oral transmission were important factors in its emergence. These critical amino acids are located on a raised region of the capsid that binds the host transferrin receptor, the protein used to establish infection. The emergence of the canine parvovirus group provided an extraordinary opportunity to study virus-host adaptation and host-range shifts in the field. Influenza Epidemics and Pandemics: Escaping the Immune Response by Reassortment Influenza serves as the paradigm for the situation in which continued evolution of the virus in several host species is essential for its maintenance. The life cycle of influenza virus, while comparatively well understood at the molecular level, is remarkable for its complexity in nature (Box 10. Sequencing data indicate that the H1N1 virus, which claimed 25 million human lives in the pandemic of 1918 (Table 11. The transferrin receptors for feline and canine parvoviruses have a large extracellular domain (ectodomain) that is a homodimer of a single protein (see Box 10. The binding of the canine parvovirus virion to the ectodomain is determined by combinations of amino acid residues on the surface of the capsid. Only a small number of transferrin receptors bind to each capsid, and in the model, only one is shown. Residues that are known to affect binding of the canine transferrin receptor or the host range are indicated in yellow. H5N1 influenza virus has its origins in wild waterfowl, where it is relatively nonpathogenic. Infection is thought to have spread to domestic ducks and chickens, and the virus evolved to be highly pathogenic in chickens. Transmitted back to ducks and geese, the viral genome underwent reassortment with the genomes of other influenza viruses of aquatic birds, resulting in a virus that could be transmitted directly to domestic chickens, humans, and pigs. Spread to humans without need for an intervening "mixing host" is a particularly worrisome feature of this virus. In birds, influenza virus reproduces in the gastrointestinal tract and particles are excreted in large quantities, a most efficient virus distribution system. The widespread dispersal of virus particles in water, the facile changing of hosts, and the ease of genetic reassortment form a powerful engine for creation of new pathogenic strains. Outbreaks of swine and avian influenza periodically devastate agricultural operations that produce these animals for food. Despite large-scale immunization programs, virulent strains of swine influenza virus continue to emerge in these animal hosts.

Diseases

One formidable problem for delivery of antiviral drug therapy medicine qvar inhaler quality 100 mg zyloprim, even if available, is that many acute viral infections cannot be diagnosed accurately within sufficient time for effective intervention. Another arises from the fact that many debilitating viral infections affect people in the developing world, a population that lacks the means and possesses limited infrastructure for the delivery of antiviral drugs. Persistent infections such as those caused by the human immunodeficiency virus, herpes simplex virus, and the hepatitis B virus present a special set of challenges. Often patients must take the drug, or more likely a combination of drugs, for the rest of their lives, a prospect that is both difficult and expensive. New approaches have been undertaken, and many promising lead compounds and therapies for treatment, and even cure, of persistent infections are being investigated. For example, in the future it may be possible to reduce viral load by antiviral drugs and then promote clearance of the remaining infection by treating with drugs that bolster immune responses. In most cases, however, selection of resistant mutants remains a problem for antiviral research and public health. Despite the problems that remain, the successes in clinical development and distribution of increasingly effective antiviral drugs and drug combinations that target the human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus can be considered nothing less than a triumph, considering the millions of people whose lives have been saved not only in the United States and other high-income countries but also worldwide. In their cases, access to the new and expected antiviral therapies can promise a cure and elimination of the threat of fatal liver disease. Based on experience gained from the successes with human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus, significant advances in technology, and increased understanding of virus biology and virus-host cell interactions, progress in developing drugs that block or even cure other viral infections should be more rapid in the future. Structure-Based Drug Design: Diseases, Targets, Techniques and Developments, vol 1. In silico drug discovery: solving the "target-rich and leadpoor" imbalance using the genome-to-drug-lead paradigm. In Mills J, Corey L (ed), Antiviral Chemotherapy: New Directions for Clinical Application and Research. Two distinct loci confer resistance to acycloguanosine in herpes simplex virus type 1. Herpes simplex virus helicase-primase inhibitors are active in animal models of human disease. Poly(sodium 4-styrene sulfonate): an effective candidate topical antimicrobial for the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. For currently circulating viruses, evolution is not only contemporary (and rapid), but also has profound effects on both viruses and their hosts: as host populations change or become resistant to infection, viruses that can overcome such changes are selected.
The average volume of gas in the conducting airways is approximately 100 to 200 mL kapous treatment buy 100 mg zyloprim visa, whereas the average volume of gas in the terminal bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli is approximately 3000 to 4000 mL at functional residual capacity. Although the derivation of the alveolar gas equation is beyond the scope of this book, in its simplest terms, it represents the oxygen that is delivered to the alveolus minus the oxygen that has been consumed. The alveolar air equation is one of the most important equations in respiratory medicine. The partial pressures of oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and water from ambient air to the alveolus to the blood are shown in Table 5. The fraction of carbon dioxide in the alveolus is a function of the production of carbon dioxide by the cells during metabolism and the rate at which the carbon dioxide is removed or eliminated from the alveolus. Ptot is less in venous than in arterial blood because Po2 has decreased more than Pco2 has increased. Even though ventilation is not continuous, it is useful to view it as if it received continuous minute ventilation (V e). Alveolar ven tilation (V a) is that part of the minute ventilation that reaches the alveoli and participates in gas exchange. Anatomic dead space (V ds) is that part of the ventilation that fills the conducting airways effectively bypassing the alveoli and thus not par ticipating in gas exchange. This relationship is specific to alveolar ventilation and not to tidal volume, of which alveolar ventilation is a part (see the discussion of dead space later in this chapter). Clinically, this principle is used in individuals who are being mechanically ventilated and cannot self-regulate their breathing. If the partial pressure of carbon dioxide increases in their blood, it is an indication that the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the alveolus has increased. Specialized chemoreceptors monitor the Pco2 in arterial blood and in the brainstem with changes in minute ventilation in accordance with the level of Pco2. Increases or decreases in arterial Pco2, particularly when associated with changes in pH, have profound effects on cell functions including enzyme and transport functions. Because of its high diffusibility (see Chapter 8), the difference between alveolar Pco2 (Paco2) and arterial Pco2 (Paco2) is small. Alveolar Pco2 is difficult to measure and arterial Pco2 is easy to measure, thus Paco2 = Paco2, and the two terms are used interchangeably. Each line corresponds to a given metabolic rate associated with a constant production of carbon dioxide (V co2; isometabolic line). Normally, alveolar ventilation is controlled to maintain an alveolar Pco2 of about 40 torr. During hypoventilation, the alveolar ventilation is low relative to Vco2, and alveolar Pco2 rises. During hyperventilation, the alveolar ventilation is excessive relative to Vco2, and thus the alveolar Pco2 falls. There are regional differences in ventilation due in large part to the effects of gravity.
In contrast to arteries medications qt prolongation zyloprim 100 mg free shipping, arterioles, and capillaries, which closely follow the branching patterns of the airways, venules and veins run quite distant from the airways. Unlike systemic arteries, the arteries of the pulmonary circulation are thin-walled with minimal smooth muscle. This has important physiologic consequences, including less resistance to blood flow. Pulmonary arteries are also more distensible and compressible than systemic arterial vessels, and they are seven times more compliant. This highly compliant state requires much less work (lower pressures throughout the pulmonary circulation) for blood flow through the pulmonary circulation compared with the more muscular, noncompliant arterial walls of the systemic circulation. Furthermore, the vessels in the pulmonary circulation, under normal circumstances, are in a dilated state and have larger diameters compared with similar arteries in the systemic circulation. All of these factors contribute to a very compliant, low-resistance circulatory system, which aids in the flow of blood through the pulmonary circulation via the relatively "weak" pumping action of the right ventricle, which is less muscular than the left ventricle. It is almost 15 times less than the pressure gradient differential of 87 mm Hg present in the systemic circulation (90 mm Hg in the aorta minus 3 mm Hg in the right atrium). With exercise, pulmonary blood flow increases and pulmonary vascular resistance decreases due to distention and recruitment of pulmonary vessels. Influence of pulmonary arterial and left atrial pressure on pulmonary vascular resistance. Blood flows through the pulmonary circulation in a pulsatile manner following the pressure gradient in this low resistance system. All of the available vessels are not utilized under normal resting conditions; this allows for compensation and recruitment of new vessels upon increased demand, such as during exercise, with little or no increase in pulmonary artery pressure. In general, blood flow to alveoli at the bottom of the lung is greater than blood flow at the top at total lung capacity when an individual is in the upright position, even though at the very bottom of the lung, there is a small decrease in blood flow per alveolus. At rest, about one-third of the resistance to blood flow is located in the pulmonary arteries, one-third is located in the pulmonary capillaries, and one-third is located in the pulmonary veins. In contrast, in the systemic circulation, most (70%) of the resistance to blood flow is located in the highly muscular systemic arterioles. This gravitational effect contributes to an uneven distribution of blood flow in the lung. Similarly, when a person is supine, blood flow is less in the uppermost (anterior) regions and greater in the lower (posterior) regions but equal in the apical and basal regions of the lung. Under conditions of stress, such as exercise, the difference in blood flow in the upright position in the apical and basal regions becomes less, due mainly to the increase in flow and the increase in arterial pressure. Upon leaving the pulmonary artery, blood must travel up to the apex of the lung, against gravity, in the upright position. It is estimated that for every 1 cm increase in height above the heart, there is a corresponding decrease in hydrostatic pressure relative to the change in height.

Occasionally symptoms 3 days after conception 300 mg zyloprim purchase free shipping, the cyst may be multiloculated without communication between the locules of fluid. In these cases, it is usually preferable to create communication using endoscopic techniques, allowing drainage through a single catheter and reservoir. Aspiration of large craniopharyngioma cysts often changes the anatomic relationships of the tumor with surrounding structures. Appropriate placement of a catheter within a cyst also allows aspiration during radiotherapy, when cysts often expand. Optimal perioperative management involves recognizing these risks and minimizing them with judicious use of appropriate strategies. Intraventricular Craniopharyngiomas As described previously, pure intraventricular craniopharyngioma is rare. As it sits entirely above the thinned hypothalamus, approaches from below are contraindicated. Access is afforded via either the lamina terminalis or the foramen of Munro based on the individual topography of the tumor. Infection Like all invasive procedures, surgery for craniopharyngioma introduces the risk of bacterial contamination with resulting surgical site infection or meningitis. If a patient is carrying an organism resistant to standard prophylaxis, a different antibiotic must be employed. Most units carrying out transsphenoidal, especially extended endoscopic resection, institute a prolonged prophylaxis of up to 5 to 7 days of antibiotic administration. In fact, with use of appropriate pre-, intra-, and postoperative precautions, infection rates with extended endoscopic transsphenoidal techniques are no higher than that for transcranial surgery. Reducing the risk of this devastating complication starts in the preoperative planning stage, with recognition of possible vessd involvement, and, if indicated, vascular imaging to ddineate vessel position to predict areas of dissection that are at particularly high risk. It is usually prudent to leave portions of tumor highly adherent to vessel walls in situ to be dealt with by adjuvant treatment rather than to attempt complete removal with injury to the adventitia. Postoperatively, a neurologic examination should be carried out as soon as possible after recovery from general anesthesia to assess any potential neurologic deficit. The black arrow points to the decompressed hypothalamus and floor of the third ventricle. Although the former appears to be primarily a radiologic phenomenon without clinical sequelae, vasospasm can potentially be a source of delayed. As oudined earlier, all patients should have a detailed ophthalmic examination, including formal perimetry, documented prior to surgery.
Roy, 60 years: However, Steinbok and associates have suggested that the neurosurgical morbidity is high in radical resections and, due to the low-grade nature of these tumors, that subtotal resection is acceptable in order to preserve quality of life. The cilia of the epithelial cell reside in the periciliary fluid layer with the mucus on top.
Rasul, 34 years: Conversely, a segment of lung 5 cm below the heart will experience an increase in arterial pressure of 3. The epidemic spread of bovine spongiform encephalopathy (mad cow disease, see below) among cattle in Britain can be ascribed to the practice of feeding processed animal by-products to cattle as a protein supplement.
Karmok, 31 years: Synthesized locally, IgG neutralizes viruses, is an opsonin (a macromolecular coat around bacteria) for macrophage handling of bacteria, agglutinates particles, activates complement, and in the presence of complement causes lysis of Gram-negative bacteria. Commonly seen features are mitotic figures, necrotic foci, hemorrhage, and ill-defined margins with adjacent brain tissue or dura mater.
References