
C. Ineke Neutel, PhD, FACE, FISPE
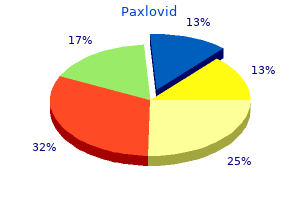
Paxlovid dosages: 200 mg
Paxlovid packs: 40 caps, 80 caps, 120 caps, 160 caps, 200 caps

In addition antiviral vitamins for herpes buy 200 mg paxlovid overnight delivery, the symptoms of motor aura do not have obvious positive and negative phases that spread with time, and no twitching or migratory spasm is noted prior to weakness by patients with hemiplegic migraine. However, there does seem to be sequential weakness of body areas during attacks of hemiplegic migraine [10]. Migraine with motor aura (hemiplegic migraine) A) At least two attacks fulfilling criteria B and C B) Aura consisting of both of the following: 1) Fully reversible motor weakness 2) Fully reversible visual, sensory and/or speech/ language symptoms C) At least two of the following four characteristics: 1) At least one aura symptom spreads gradually over five minutes, and/or two or more symptoms occur in succession. Most patients with this type of aura present in early adolescence, and their aura reverts to a more typical aura in their 40s and 50s [16]. This subtype of aura was previously termed basilar migraine, as it was thought to be related to spasm and/or compromised blood flow in the basilar artery territory [17]. As a result, patients with hemiplegic and basilar-type migraine were excluded from clinical trials involving triptans and, as such, triptans are contraindicated in these patients. Patients may have difficulty distinguishing a hemianopia from vision loss from one eye. This type of aura is extremely rare, and other causes of monocular vision loss should be investigated before making this diagnosis. Proposed pathophysiology for this aura type is thought to be a spreading depression 198 Neurobiological Basis of Migraine Retinal aura A) At least two attacks fulfilling criteria B and C B) Aura consisting of fully reversible monocular positive and/or negative visual phenomena. This spreading quality is not characteristic of an ischemic event [7], in which neurological deficits tend to appear suddenly and are simultaneously experienced in several body parts. The recognition of these characteristics was a seminal observation that led to the formulation of the neurogenic theory of migraine aura [22]. In addition, although a migratory pattern may also be seen in partial seizure disorders, the progression of symptoms in a partial seizure is much more rapid. It is also notable that neither ischemia nor seizure-based symptoms are associated with the return of function in the areas of the cortex which were first affected, even as symptoms are simultaneously appearing in newly affected areas. Lastly, in contrast to transient ischemic attacks, migrainosus aura is stereotypic and repetitive. In migraine aura where more than one aura symptom occurs, different neurological symptoms occur one after the other, and not simultaneously. Some patients experience all three typical auras in sequence during a single attack [7]. In over 20 years of asking patients to describe their aura, none have reported the appearance of all aura types at the same time [7]. In contrast to migraine aura, the simultaneous appearance of multiple types of neurological symptoms is, however, fairly common in cerebral ischemia.
It is a rare condition that presents initially with severe shoulder pain that resolves antiviral resistant herpes buy paxlovid 200 mg low price, followed by weakness of muscles associated with one or more nerve distributions. It is thought to be benign and self-limited, with 90% of patients having full recovery by 3 years. E Notochord develops Of the following listed events, notochord development occurs first, during the gastrulation stage. The notochord allows the embryo to organize in a rostral-caudal orientation and helps induce formation of the neural tube. The other answers listed here all deal with neural tube development and differentiation. C Parotid gland In this figure, the structure labeled "1" is the otic ganglion, and it supplies innervation to the parotid gland. Innervation of the parotid gland is via the glossopharyngeal nerve through the otic ganglion. B Type Ia sensory nerve the myotatic reflex (stretch reflex) is the only monosynaptic reflex in the body, and afferent impulses are sent via type Ia sensory nerves from muscle spindles. C p53 mutation p53 mutations can be seen in glioblastoma, but they are often present in patients who initially had a low-grade glioma that transformed into a higher grade neoplasm over time. You can appreciate that the subcortical U fibers are spared in this case, and of the answer choices, only metachromatic leukodystrophy spares the subcortical U fibers, making it the correct answer. They occur after ischemia, and in this patient, artery to artery embolism resulting in cerebral infarction was the cause of death. The vast majority of cephalohematomas resolve, but occasionally they will persist and calcify. Surgical decompression/resection is indicated in patients where there is documented calcification of a hematoma such as demonstrated here. C Alpha synuclein the structure demonstrated is a Lewy body, and it is composed primarily of alpha synuclein. It is often quoted that 50% of patients will experience a 50% or greater reduction in seizure frequency. Up to 30% of patients may require mechanical ventilation, but there is a less than 5% mortality.
Disability Several reliable and valid self-assessment questionnaires are available to determine the level of disability in neck pain patients hiv infection blood splash discount paxlovid 200 mg visa, including the Neck Disability Index63 and the Neck Bournemouth Questionnaire. According to the Task Force on Neck Pain, patients experiencing such pain-related disability require further assessment and treatment to prevent long-term disability (see Box 9-1). Screening of the Cervical Spine As described in Box 9-1, the Task Force on Neck Pain introduced a four-grade classi- 212 Screening of the Cervical Spine Table 9-1Testing procedures of manual provocation tests for cervical radiculopathy67 Name Spurling test Description the patient is seated. A sequence of movements is passively performed to elongate the median nerve: depression of the scapula, abduction and external rotation of the shoulder, extension of the elbow, supination of the forearm, and dorsiflexion/extension of the wrist. Positive test outcome Symptom reproduction Symptom reduction or elimination Symptom reproduction Symptom reproduction Neck distraction test Valsalva maneuver Upper limb tension test* *Note: Passive evaluation of the neck should not be attempted unless the clinician has had specific training in this technique. Signs of nerve compression Nerve compression should be suspected in patients with neck pain that radiates to the arm (for a detailed description of this condition, see Radiculopathy below). Neck pain from this origin is caused by an irritation of the cervical nerve root, mostly due to prolonged compression. In typical cases, the irradiating pain closely follows the area innervated by the affected nerve root. When nerve compression is suspected, a cluster of clinical provocation tests is recommended, such as the Spurling test, traction/neck distraction, Valsalva maneuver, and upper limb tension test. These diagnostic procedures have high predictive value when compared with gold standards of nerve conduction/magnetic resonance imaging and myelography. The upper limb tension test, on the other hand, has high sensitivity, so a negative result is highly suggestive of the absence of nerve compression. In the absence of acute trauma and symptoms of serious pathology, the use of diagnostic procedures such as routine imaging, anesthetic facet or medial branch blocks, or surface electromyography for the diagnosis of nerve compression is not supported by the literature. Important cervical muscles or muscle groups to evaluate are the sternocleidomastoid, suboccipital, paravertebral (scalenes), posterior deep cervical, and upper trapezius muscles. Dynamic (head movements against a slight manual resistance) and static (strong manual resistance while no movement occurs) resistance tests are performed in the same directions as described by range of motion. Positive test outcome Limited or irregular movements and/ or reproduction of neck pain Symptom reproduction Resistance tests Symptom reproduction (more dynamic than static pain is indicative of arthrogenous pain; more static than dynamic pain is indicative of myogenous pain) *Note: Passive evaluation of the neck should not be attempted unless the clinician has had specific training in this technique. If further evaluation of the cervical region is indicated, patients should be referred to an appropriately trained clinician (eg, a physical therapist with special training in the craniocervical region). This overview should be considered a description of possible causes of neck pain, allowing pattern recognition but not claiming criteria for objective diagnoses. The Task Force on Neck Pain defined neck pain as symptoms "located in the anatomical region of the neck with or without radiation to the head, trunk, and upper limbs. The evidence for the effectiveness of this multimodal approach in the short, intermediate, and long term is growing and has been translated into clinical practice guidelines. Pain referral to sites distant from the original injury is common, as is the presence of headache, dizziness, tinnitus, dysphagia, and visual disturbances. When recovery is delayed (ie, complaints are still present after 3 to 6 weeks), referral for further therapy should be considered. Conservative treatments including active exercise, manual techniques, and physical therapy can be useful to reduce pain and increase cervical range of motion.
Ecological momentary assessment versus standard assessment instruments for measuring mindfulness hiv infection woman to man purchase paxlovid 200mg overnight delivery, depressed mood, and anxiety among older adults. Using new technologies to improve the prevention and management of chronic conditions in populations. Weight bias among professionals treating eating disorders: Attitudes about treatment and perceived patient outcomes. Health behavior models in the age of mobile interventions: Are our theories up to the task Reducing eating disorder onset in a very high risk sample with significant comorbid depression: A randomized controlled trial. Attitudinal and perceptual factors in body image distortion: an exploratory study in patients with anorexia nervosa. Mixing online and Darcy, Sadeh-Sharvit 503 face-to-face therapy: How to benefit from blended care in mental health care. However, the common face-to-face delivery of these interventions has a number of limitations, including high cost and limited accessibility. E-mental health, referring to the use of information and communication technology-particularly the Internet-in interventions for mental health disorders, has the potential to overcome these barriers and enhance the treatment and prevention of eating disorders. To date, the limited number of evaluations have documented small to moderate effect sizes in the improvement of eating disorder symptomatology through Internet-based treatment and prevention. Beyond efficacy, major questions remain regarding content, structure, and modes of delivery of Internetbased interventions; suitable diagnostic tools and safety measures; and cost-effectiveness, dissemination, and implications for public health programming. These aspects deserve attention in future research before widely recommending Internet-based interventions for eating disorders. Key Words: eating disorder, E-mental health, Internet, intervention, prevention, treatment Introduction the number of worldwide Internet users increased by 900% between 2000 and 2016 (Internet World Stats, 2016). This huge global expansion of the availability and use of the Internet not only caused remarkable changes in daily life, but also influenced healthcare, including mental healthcare, by opening up numerous new ways of delivery. E-mental health refers to the use of information and communication technology, particularly the Internet, to support and improve mental health conditions and mental healthcare (Riper et al. Internet-based delivery of psychological treatments has the potential to result in substantial improvements of mental healthcare, but at the same time bears several risks that must be considered as well. On the part of the affected individuals, exploratory studies documented reasons for low healthcare-seeking such as social barriers. One major benefit of Internet-based interventions is their lack of geographic boundaries, making widespread dissemination easily possible. Their remarkable local and temporal flexibility in comparison to face-to-face therapies is especially relevant for individuals who would otherwise be hard to reach, for example, people living in remote or psychotherapeutically undersupplied areas, individuals with reduced mobility. Moreover, Internet-based interventions have the advantage of allowing patients to retain a greater sense of anonymity, which makes them attractive for individuals who are reserved in emotional disclosure or who wish to have independence from a therapist (Kersting et al. The anonymous aspect is crucial especially for patients who would otherwise not seek help out of shame or fear of stigmatization (Burns et al.
Atheroma covered by severe calcification has less tendency to rupture or erode antiviral movie discount paxlovid 200 mg online, thus some cardioprotection emerges. Location of Pain In most patients, pain of a heart attack is in the center of the chest under the breastbone (retrosternal). The next most common area for pain is the upper half of the breastbone and the pit of the stomach. Heart pain occurs mainly in the center of the chest, and doctors often use the term "central retrosternal chest pain" as being typical of a heart attack. Pain from all three areas can move (radiate) up or down to involve the entire chest, neck, throat and lower jaw (not higher than the upper jaw) and may extends to the arms, forearms and hands. Most of the arm or a small part such as the wrist may be the site of pain or discomfort without involvement of the chest. Arm, jaw, or throat pain, however, is usually accompanied by pain in the chest, but rarely can be at these locations without chest pain. If there is associated shortness of breath, nausea and/or sudden generalized, yet mild weakness, the arm pain can be a manifestation of a heart attack. Some of these patients have an unstable form of angina pectoris, chest wall pain, with some panic, stomach problems (in particular, reflux esophagitis with esophageal spasm), gallstones and very rarely pericarditis. Negative troponin levels have Physical Signs the patient appears apprehensive, anxious, cold and clammy. Patients with other cause of chest pain (other than aortic dissection, pulmonary embolism or both rare) do not usually experience these features. An increase in blood pressure caused by increased sympathetic tone is observed in approximately 50% of patients with anterior infarction. Bradycardia less than 55 beats/min and a decrease in blood pressure in about twothirds of inferior infarcts; many of these patients become hypotensive, sometimes profoundly, and may get transient dizziness. S4 gallop is common, S3 and S4 in some with an elevated jugular venous pressure caused by heart failure. Reciprocal depression is not diagnostic of infarction but is an important confirmatory sign that strongly supports the diagnosis. The absence of reciprocal depression helps to exclude myocardial injury in individuals of this type presenting at age older than 40. The terms "transmural" and "nontransmural" have been abandoned and the Q wave or the non-Q wave infarction cannot be categorized in the early phase. Torsades de pointes and transient left ventricular dysfunction have been associated with both entities.
Which of the following antibiotics has the highest risk of significantly increasing the creatinine You are evaluating a 78-year-old patient with long-standing atrial fibrillation who suddenly presented with aphasia and right-sided weakness hiv transmission statistics canada purchase paxlovid 200 mg online. It has been determined that this patient could benefit from mechanical thrombectomy. How long from onset of symptoms does mechanical thrombectomy remain a viable treatment option Cribriform plate Subiculum Basal nucleus of Meynert Septal area Pyriform cortex 85. What is the rate of Engel I seizure control after surgical resection of structural temporal lobe epilepsy in children The final pathology report states "nests of cells that are diffusely positive for chromogranin A. You are caring for a 28-year-old woman who was thrown from a horse and suffered a depressed skull fracture, severe brain trauma, and elevated intracranial pressure now status post hemicraniectomy. Her caloric intake should be what compared to her predicted basal energy expenditure Paraganglioma Myxopapillary ependymoma Metastatic tumor Schwannoma Neurofibroma 323 I Questions 87. If this tumor is due to an inherited condition, what other tumor might you see in this patient What segment of the vertebral artery is at risk during exposure of the superior aspect of the C1 posterior arch Optic glioma Meningioma Parathyroid carcinoma Renal cell carcinoma Subungual fibromas A. Petrous bone to clivus C1 lateral mass to occiput C1 lateral masses Dens to basion C1 lamina to C2 spinous process 88. Ventrolateral preoptic nucleus Paraventricular nucleus Supraoptic nucleus Posterior region Ventromedial region 93. Alobar holoprosencephaly Hydranencephaly Anencephaly Lobar holoprosencephaly Semilobar holoprosencephaly Facial and cochlear Superior vestibular and inferior vestibular Inferior vestibular and cochlear Superior vestibular and facial Inferior vestibular and facial 324 18 Stand-Alone 375-Question Examination 94. Ipsilateral olfactory groove meningioma Retinoblastoma Carotid cavernous fistula Optic glioma Thyrotoxicosis 98. You are called to evaluate a newborn with the findings demonstrated in the images.
We suggest that adaptations within central descending pain modulatory circuits amplify signals from the periphery promoting chronification of migraine antiviral brandon cronenberg trailer 200mg paxlovid for sale. Approximately 25 years after the triptan drugs revolutionized the treatment of migraine (Goadsby et al. Nonetheless, the continued examination of safety concerns should be of highest priority. Although acute therapy may be effective, the frequency of migraine headache can increase over time, until episodic migraine transforms into chronic migraine ("chronification"). Chronic migraine is characterized by the occurrence of headache on 15 or more days per month (Olesen et al. Approximately 14% of episodic migraine sufferers can be expected to develop chronic migraine, representing 1. Non-modifiable risk factors that are associated with chronic headache (>15 days per month) in those with migraine include female sex, age, low education, low socioeconomic status, and head injury (Diamond et al. In addition, risk factors that can be modified, such as stressful life events, sleep disturbances, obesity, depression, and increased caffeine consumption have been identified (Bigal et al. There continues to be considerable debate as to whether patients should be initially managed with early discontinuation, early discontinuation plus preventive therapy, or preventive therapy without early discontinuation of the overused medication (Chiang et al. There is a growing awareness that the drugs used to treat migraine can, themselves, promote neural adaptations that affect susceptibility to initiating factors for migraine and subsequent pain processing. Consequently, there exists a need for multiple research strategies, including brain imaging (Lai et al. However, the use of functional imaging still faces technological challenges, due to the temporal limitations of the imaging techniques (seconds to minutes), and the duration of a single migraine, which ranges from hours to days (May, 2009). The use of neuroimaging technology has facilitated the testing of hypotheses, and has increased our understanding. This increased blood flow was reduced in most areas, except the brainstem, by treatments with sumatriptan (Weiller et al. Later studies, however, have established that primary headache syndromes are likely not related to vasodilation (Goadsby, 2009a, 2009b; Sprenger and Goadsby, 2010). No changes in cerebral artery diameters or cerebral blood flow were observed during induced (Schoonman et al. These, and other observations, have resulted in growing consensus that migraine is a disorder of the brain, with secondary changes in blood flow related to underlying brain activity (metabolic-flow coupling). Consistent with the idea that migraine is a disorder of the central nervous system, cutaneous allodynia develops in about 80% of migraineurs during individual headaches (Burstein et al. Similarly, preclinical observations have demonstrated hyperexcitability of sensory neurons in the posterior thalamus of rats, in response to innocuous and noxious stimulation of the paw following chemical stimulation of the dura mater (Burstein et al. These findings suggest that sensitization of thalamic neurons mediates the spreading of cutaneous allodynia in 8 Central circuits promoting chronification of migraine 143 migraineurs by processing nociceptive information from the cranial meninges with sensory information for the skin (Burstein et al. Collectively, both clinical and preclinical findings demonstrate the contribution of central sensitization to migraine (see chapter 7).
Adenosine receptors exist throughout the body (brain hiv infection symptoms in pregnancy discount 200 mg paxlovid, lungs, heart, kidney, blood vessels, etc. Atropine-(1 to 3 mg) muscarinic blocker-results in 25% to 50% increase in sinus rate. Autonomic blockade: blockade of sympathetic and parasympathetic systems is achieved by 0. Supraventricular tachycardia mimicking ventricular tachycardia during flecainide treatment. A new approach to the classification of antiarrhythmic drugs based on their actions on arrhythmogenic mechanisms. These two vital organs are in the chest "married to each other" Thus, the text also gives salient symptoms of. The resolution of this symptom is sometimes easy, but often it presents considerable difficulty for the physician. A systematic approach is necessary; taking an accurate and relevant history is crucial to the diagnosis. The great vessels: Aortic dissection, pulmonary embolism and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulmonary Causes Pleurisy: the pain becomes worse on deep breathing and coughing and is unrelated to change in posture. Pulmonary embolism: the pain may be severe, central, or pleuritic and is often associated with acute shortness of breath; the patient is often apprehensive and may be sweaty. Pulmonary embolism should be suspected when chest pain occurs in a setting that predisposes to thromboembolism. Underlying causes include asthma, pneumocystis pneumonia, emphysema, tuberculosis, cystic fibrosis, interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, sarcoidosis, eosinophilic granuloma, blunt or penetrating trauma, and positive-pressure ventilation. Pneumonia: Shortness of breath, fever and chills are associated with pleuritic or nonpleuritic pain and cough, with or without sputum production. Pulmonary embolism Tension pneumothorax A patient in cardiogenic shock is usually sweaty, pale and apprehensive; there may be associated clouding of consciousness. Bradycardia may be caused by treatment with betablockers, diltiazem, or a combination of these two agents. Bradycardia usually requires no treatment, unless it is symptomatic Chest Wall Pain A common cause of chest wall pain is costochondritis. Pain is usually mild to moderate; it is usually localized to a fingertip area and is often present over the second or third costochondral junction. Pain is unrelated to exertion or activities and may seem to respond to nitroglycerin in some patients. Chest wall pain accompanies most types of heart disease, particularly ischemic heart disease and mitral valve prolapse syndrome.
Tamkosch, 53 years: Higher risk of infection Worsened hydrocephalus Higher risk of spinal cord tethering More difficult watertight closure Inclusion dermoid 366 18 Stand-Alone 375-Question Examination 340.
Delazar, 48 years: C Subgranular layer There are two known sites of neurogenesis in the adult brain, the subependymal zone in the lateral ventricle (neurons and glia are generated and migrate to the olfactory bulb), as well as the subgranular layer of the dentate gyrus within the hippocampus.
Mason, 36 years: Quantifying the test-retest reliability of cerebral blood flow measurements in a clinical model of on-going post-surgical pain: A study using pseudo-continuous arterial spin labelling.
Vigo, 21 years: Brain derived neurotrophic factor, but not nerve growth factor, regulates capsaicin sensitivity of rat vagal ganglion neurones.
Pyran, 43 years: When uncal herniation is suspected, making sure the craniectomy reaches the floor of the middle fossa is important to fully decompress the temporal lobe.
Finley, 62 years: In the head and neck, the most common node to be enlarged is the jugulodigastric node, secondary to a viral upper respiratory tract infection.
Lisk, 55 years: Worldwide this fact is still unknown and the drug is avidly prescribed by experts and family physicians.
References