
Kristen Quinn, MD, MS
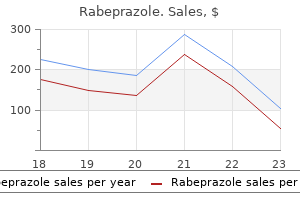
Rabeprazole dosages: 20 mg, 10 mg
Rabeprazole packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Infection with Mycobacterium avium complex in patients without predisposing conditions gastritis diet gastritis symptoms generic rabeprazole 20 mg line. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: incidence and implications for mortality. Nontuberculous mycobacterial adenitis of the head and neck in children: experience from a tertiary care pediatric center. Localized soft-tissue infections with Mycobacterium avium/ Mycobacterium intracellulare complex in immunocompetent patients: granulomatous tenosynovitis of the hand and wrist. Tuberculin skin testing is useful in the screening for nontuberculous mycobacterial cervicofacial lymphadenitis in children. Efficacy of rifabutin in the treatment of disseminated infection due to Mycobacterium avium complex. A randomized evaluation of ethambutol for prevention of relapse and drug resistance during treatment of Mycobacterium avium complex bacteremia with clarithromycin-based combination therapy. A randomized, doubleblind trial comparing azithromycin and clarithromycin in the treatment of disseminated Mycobacterium avium infection in patients with human immunodeficiency virus. Uveitis and pseudo-jaundice during a regimen of clarithromycin, rifabutin, and ethambutol. Aminoglycoside toxicity: daily vs thrice-weekly dosing for treatment of mycobacterial disease. A prospective, randomized trial examining the efficacy and safety of clarithromycin in combination with ethambutol, rifabutin, or both for the treatment of disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex disease in persons with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. A case-control study of risk factors for Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease. Epidemiology and clinical significance of nontuberculous mycobacteria in patients negative for human immunodeficiency virus in Switzerland. Nontuberculous mycobacteria-associated lung disease in hospitalized persons, United States, 1998-2005. Nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease prevalence at four integrated health care delivery systems. Pectus excavatum and scoliosis: thoracic abnormalities associated with pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium avium complex. Mycobacterium avium complex pulmonary disease: incidence, presentation, and response to therapy in a community setting. Mycobacterium avium complex in the respiratory or gastrointestinal tract and the risk of developing Mycobacterium avium complex bacteremia in patients with the human immunodeficiency virus.
Large parenchymal cavities may be present gastritis symptoms from alcohol purchase rabeprazole 10 mg mastercard, at times associated with an air-fluid level resulting from intermittent obstruction and poor drainage. Calcified nodes can erode into the bronchial tree and cause hemoptysis, expectoration of calcific material (lithoptysis), or spread of previously quiescent bacilli. The atelectatic pneumonitis, which may result with or without new active disease, is most frequently seen in the anterior segment of the upper lobe and medial segment of the middle lobe. The clinical picture in these patients can include diffuse, rapidly progressive, noncavitary disease that is often fatal. Patients may have adult respiratory distress or sepsis syndrome with multiple organ system failure. The diagnosis can be made readily by stain and culture of sputum or blood or both. Tuberculomas Asymptomatic rounded lesions may develop as the parenchymal residua of the initial infection or as an upper lobe caseous lesion encapsulates. These are ordinarily static, but larger ones may cavitate to produce new spread of disease. In some persons, excessive fibrosis occurs with small caseous or granulomatous residua becoming surrounded by concentric layers of fibrous tissue, at times with central or concentric calcification resembling histoplasmomas. As the bacillary population grows, however, nonspecific constitutional symptoms such as anorexia, fatigue, weight loss, chills, fever, and night sweats may ensue. Coughing to clear cavitary secretions is usually mild and well tolerated but may become bothersome when bronchial involvement is extensive. The mucopurulent sputum is nonspecific, and both cough and sputum may be ignored by patients with chronic bronchitis. Hemoptysis resulting from caseous sloughing or endobronchial erosion is usually minor but connotes advanced disease. In inactive disease, brisk hemoptysis may be due to Aspergillus superinfection of residual cavities (aspergilloma). Pleural involvement adjacent to an established cavity tends to cause visceralparietal pleural symphysis without effusion (dry pleurisy). Serofibrinous pleurisy with effusion is often an early postprimary event but may also complicate chronic pulmonary tuberculosis. Symptoms often pertain to site of disease, such as painful pharyngeal ulcers; indolent and nonhealing ulcers of the mouth or tongue; hoarseness and dysphagia that are due to laryngeal involvement; tuberculous otitis media; gastrointestinal symptoms that are due to enteric ulceration, perforation, or mass formation; or anal pain that is due to tuberculous perirectal abscess and fistula formation. Lower lobe tuberculosis resulting from bronchial lymph node perforation may be associated with lithoptysis (stone spitting) and characteristically produces symptoms of severe endobronchial disease with serious cough and often hemoptysis. Pneumonia associated with hilar adenopathy should always suggest primary tuberculosis, regardless of the lung fields involved and patient age. The white blood cell count is usually normal but may be between 10,000 and 15,000 cells/mm3.
Other host factors associated with dissemination include female sex gastritis diet ����� order rabeprazole 10 mg on line, menstruation, and perhaps pharyngeal gonococcal infection and pregnancy. Physical examination usually shows objective signs of arthritis or tenosynovitis in at least two joints. Hemorrhagic bullae or overtly necrotic lesions that mimic ecthyma gangrenosum are sometimes seen. Fever, systemic toxicity, and polymorphonuclear leukocytosis are common, but they are usually mild and are often absent. If the infection is not treated, inflammation regresses in most joints and the dermatitis resolves, but overt septic arthritis supervenes in one or two joints, most commonly the knee, ankle, elbow, or wrist, although any joint may be involved. Septic gonococcal arthritis develops in some patients without prior polyarthritis or dermatitis; and in the absence of the characteristic dermatitis or overt genital infection, it is clinically indistinguishable from septic arthritis of any etiology. During the arthritis-dermatitis stage, gonococci often can be recovered by blood culture, but synovial fluid, if it can be obtained, usually contains fewer than 20,000 leukocytes/mm3 and is sterile. Gonococci can often be seen by immunochemical methods in biopsy specimens of skin lesions, but cultures are generally sterile. In septic gonococcal arthritis, synovial fluid usually contains more than 50,000 leukocytes/ mm3 and culture is often positive, but at this stage blood cultures are usually negative. Although uncommonly positive, Gram-stained smears and cultures of pustular skin lesions are simple to perform and should be obtained. The differential diagnosis of the gonococcal arthritis-dermatitis syndrome includes meningococcemia, septic arthritis due to other pyogenic bacteria, and the entire range of inflammatory arthritis. Usually, careful clinical and microbiologic assessment readily differentiates these disorders, but a trial of antibiotic therapy may be required. In the preantibiotic era, median survival was 6 to 8 weeks, reflecting a typical rate of valve destruction between that of acute 2458 staphylococcal or pneumococcal endocarditis and subacute endocarditis caused by viridans streptococci. The transcriptionmediated amplification test has a positive predictive value of at least 95% in women in settings in which gonorrhea prevalence is as low as 0. Prophylaxis by instillation of antibiotics into the conjunctivae soon after delivery is highly effective, although occasional failures occur. The most important preventive measure is routine screening and treatment of pregnant women for gonorrhea before term. The diagnosis of gonococcal ophthalmia should be suspected clinically when acute conjunctivitis develops within a few days of delivery and is confirmed by identification of gonococci in conjunctival secretions. Systemic illness with septicemia and arthritis can also develop in neonates exposed to gonorrhea, but these are rare. Rectal gonococcal infection is sometimes seen in neonates, but vaginal infection is uncommon because the neonatal vaginal mucosa is well estrogenized by circulating maternal hormone.
These glycoantigens are of interest biologically for their immunomodulatory potential gastritis diet ��������� buy 10 mg rabeprazole fast delivery, particularly in the case of B. Short-chain fatty acid analysis by gas-liquid chromatography can also be used for species-level Bacteroides discrimination. When grown in liquid medium, cells develop bipolar vacuoles and show a characteristic "safety pin" appearance. Fusobacterium PrevotellaandPorphyromonas Fusobacterium is a genus of obligately anaerobic filamentous gramnegative rods that are members of the phylum Fusobacter, in contrast to Bacteroides, Prevotella, and Porphyromonas, which are members of the phylum Bacteroidetes. On blood agar, Fusobacterium forms pinpoint colonies that can be circular or irregular, with some species, such as Fusobacterium nucleatum, forming umbonate "fried egg" colonies after 3 to 5 days of incubation. As a genus, Fusobacterium is sensitive to both kanamycin and colistin and resistant to vancomycin. It can be distinguished by its bile sensitivity and metabolism of threonine to propionate. Most species are indole positive and produce butyric acid during the fermentation of glucose. Both Prevotella and Porphyromonas were previously considered to be part of the genus Bacteroides. On Gram stain, they form short gram-negative rods and may assume coccobacilli forms. Porphyromonas usually grows as pigmented colonies, initially forming gray colonies that darken to black colonies within a week after plating on laked blood agar. Gramnegative anaerobic rods colonize the mucosal surfaces of the oropharynx, gastrointestinal tract, and female urogenital tract, and Bacteroides and Prevotella are among the most abundant genera present. Mutualism and opportunism are important features of the symbiotic relationship between human hosts and colonizing species of the genera Bacteroides, Prevotella, Porphyromonas, and Fusobacterium. GastrointestinalTract the human colon is colonized by 10 trillion to 100 trillion bacteria, making it the largest repository for bacteria in the body. Bacteroides vulgatus, thetaiotaomicron, distasonis, fragilis, and ovatus are the most commonly encountered Bacteroides species in the human colon. The colonization of the gastrointestinal tract occurs during descent through the vaginal canal or postnatally for infants delivered by cesarean section. Both 2775 breast milk and exposure to environmental factors are important forces in shaping colonization. Many studies over the past several decades have been undertaken to examine this process in detail, with genomicbased technology taking center stage more recently.

Rhizobium radiobacter wound infection in a patient with diabetes-fact gastritis migraine 20 mg rabeprazole purchase free shipping, factitious or just plain unlucky Three cases of post-cataract surgery endophthalmitis due to Rhizobium (Agrobacterium) radiobacter. Bacteriologic characterization of 36 strains of Roseomonas species and proposal of Roseomonas mucosa sp nov and Roseomonas gilardii subsp rosea subsp nov. An initial appraisal of the clinical significance of Roseomonas species associated with human infections. Catheter-related bacteremia caused by Roseomonas gilardii in an immunocompromised patient. Infections with Roseomonas gilardii and review of characteristics used for biochemical identification and molecular typing. Peritonitis caused by Roseomonas in a patient undergoing automated peritoneal dialysis: case report and literature review. Vertebral osteomyelitis due to Roseomonas species: case report and review of the evaluation of vertebral osteomyelitis. Nosocomial ventriculitis due to Roseomonas gilardii complicating subarachnoid haemorrhage. Clinical significance of Roseomonas species isolated from catheter and blood samples: analysis of 36 cases in patients with cancer. Peritonitis due to Roseomonas fauriae in a patient undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. A pseudo-outbreak of Methylobacterium mesophilica isolated from patients undergoing bronchoscopy. Shewanella algae and Shewanella putrefaciens: clinical and microbiological characteristics. Epidemiology and clinical features of Shewanella infection over an eight-year period. Outbreak of Shewanella algae and Shewanella putrefaciens infections caused by a shared measuring cup in a general surgery unit in Korea. Purulent pericarditis with greenish pericardial effusion caused by Shewanella algae. A plasmid-borne Shewanella algae gene, qnrA3, and its possible transfer in vivo between Kluyvera ascorbata and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Identification and susceptibility to multipurpose disinfectant solutions of bacteria isolated from contact lens storage cases of patients with corneal infiltrative events. Necrotizing fasciitis and septic shock related to the uncommon gram-negative pathogen Sphingobacterium multivorum. Extrinsic allergic alveolitis (hypersensitivity pneumonitis) caused by Sphingobacterium spiritivorum from the water reservoir of a steam iron. Hydrolysis of imipenem, meropenem, ceftazidime, and cefepime by multiresistant nosocomial strains of Sphingobacterium multivorum. Sphingomonas paucimobilis bacteremia related to intravenous human immunoglobulin injections. Sphingomonas paucimobilis: a persistent gram-negative nosocomial infectious organism.
However gastritis no appetite cheap rabeprazole 10 mg on-line, there is less published experience using these agents in the United States or for infections caused by the more virulent F. Among tularemia cases reported in Missouri between 2000 and 2007, 9 of 10 patients given ciprofloxacin alone or combined with ineffective agents were cured. It was used successfully to treat a child with chronic granulomatous disease and F. The effectiveness of these drugs in treating tularemia is not fully established, and ceftriaxone has failed in several patients treated as outpatients. Dienst102 reported two pregnant patients with tularemia; one was successfully treated with streptomycin in the fifth month of pregnancy and had a normal birth, and the other spontaneously aborted a 6-week-old fetus after 35 days of illness. Four recently reported pregnant patients with tularemia and suppurative adenopathy were treated successfully with gentamicin followed by oral ciprofloxacin and lymph node drainage; all the patients had otherwise normal pregnancies, and the infants were normal at 18 months of follow-up. Immunotherapy TherapyforTularemiaafter aBioterrorismEvent PregnantandImmunosuppressed Patients Tularemia cases occurring during pregnancy or in immunosuppressed patients have been reported only rarely, but they may be more frequently encountered during a bioterrorism event, affecting large numbers of people without the usual risk factors. Treatment of pregnant or immunocompromised patients with tularemia is challenging, and optimal antibiotic regimens are unknown. Aminoglycosides, tetracyclines, and fluoroquinolones have potential risks to the fetus when used during pregnancy; immunocompromised patients with tularemia may have an increased risk for relapse or treatment failure. Prior to the availability of effective antibiotics, Pullen and Stuart159 reported three Recommendations for therapy for tularemia in the context of a bioterrorism event were presented in the Working Group for Civilian Biodefense Consensus Statement. Thus, treatment options for contained casualties are similar to those listed in Table 229-2 and as discussed earlier; in addition, the Working Group also included chloramphenicol alone as an option for both adults and children and ciprofloxacin as an option for children. For contained casualties, the Working Group recommended that streptomycin, gentamicin, and ciprofloxacin be given for 10 days and that doxycycline and chloramphenicol be given for 14 to 21 days. Molecular assays capable of rapidly and reliably detecting ciprofloxacin resistance in F. Wild animals should not be skinned or dressed using bare hands, and bare hands should not be used to handle an animal that appears ill. Gloves, masks, and protective eye covers should be worn when 2601 performing such tasks and when disposing of dead animals brought home by household pets. Treatment of community water supplies with standard chlorination protects against waterborne tularemia. Frequent checks should be made for attached ticks so that they may be removed promptly; this must not be done with bare hands, and care should be taken not to crush the tick. Hospitalized patients with tularemia do not need special isolation because person-to-person spread does not occur, and even in the preantibiotic era, secondary cases were not found. Standard universal precautions for contaminated secretions are adequate when handling drainage from wounds or eyes. This vaccine does not spread from the inoculation site, induces cellmediated and humoral immunity, is effective in preventing typhoidal disease, and reduces the severity of ulceroglandular disease but does not prevent it.
The isolation of Pasteurella multocida from an infection occurring after a cat bite was first described in 1930 gastritis xarelto 20 mg rabeprazole with amex. Subsequently, as additional isolates were recovered and characterized, related species were grouped together, first as Pasteurella septica and then by the late 1930s as the P. Organisms grow in culture on a variety of commercial media, including sheep blood and chocolate agar, but not usually on MacConkey agar media. They are fastidious and can be difficult to isolate and identify from nonsterile specimens such as sputum. Most strains are catalase, oxidase, and indole positive and produce acid from sucrose. Of the remaining strains (A, D), group A strains have been more frequently isolated as respiratory tract colonizers or pathogens, whereas non-A strains have been isolated more frequently from nonrespiratory tract specimens including blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and abscess fluid. In most cases, carriage is asymptomatic, although both upper and lower respiratory tract infections and septicemia are well known to occur in animals. Antibodies to somatic and capsular antigenic determinants develop within 2 weeks after clinical infection. Although both subspecies multocida and septica cause skin and soft tissue infections as a result of animal bites and scratches, subspecies multocida has also been found to cause respiratory tract infections and systemic infection. Infections of skin and soft tissues most commonly develop after an animal bite or scratch. Inflammation, swelling, and tenderness develop at the site of injury, usually within 24 hours from the time of exposure. Wound discharge, ranging from serosanguineous to frankly purulent, has been noted in 20% to 40% of cases; fever develops in approximately 20%. Anatomically, more than 50% of cases of infection from both dog and cat bites occur in the upper extremities, followed by the lower extremities, head, face, and neck; multiple sites of infection are sometimes evident. Weber and colleagues13 noted an overall complication rate of 39% among 23 patients studied. In a large study analyzing bacterial species isolated from wounds inflicted by dog and cat bites, P. Infection after animal bites is the most commonly reported clinical setting for the organism (see Chapter 320). Approximately 15% to 20% of dog bite wounds and more than 50% of cat bite wounds become infected. For dog bite infections, Staphylococcus aureus and streptococcal species are the most commonly isolated pathogens, with Pasteurella and other organisms next in frequency. Pasteurella infections have also been reported after bites from a variety of other animals, including pigs, rats, lions, opossums, and rabbits. These include skin and soft tissue infections, bone and joint infections, pneumonia, meningitis, endocarditis, and septicemia.
A multi-omic systems-based approach reveals metabolic markers of bacterial vaginosis and insight into the disease gastritis symptoms dizziness purchase rabeprazole 10 mg with mastercard. Gardnerella vaginalis septicemia with pyelonephritis, infective endocarditis and septic emboli in the kidney and brain of an adult male. Reservoir of four organisms associated with bacterial vaginosis suggests lack of sexual transmission. Susceptibility of Mobiluncus species to 23 antimicrobial agents and 15 other compounds. Syphilis is a complex systemic illness caused by the highly invasive, noncultivable spirochete Treponema pallidum. It holds a special place in the history of Western medicine because of its prevalence in modern times, the many historical personages who had or are presumed to have had the disease, and its protean clinical manifestations, for which it came to be known as "the great imitator" or "the great impostor. Special clinics were established in Europe and North America to care for the enormous number of persons afflicted with this disorder, and its ubiquity spawned one of the first specialized medical journals, the American Journal of Syphilis, Gonorrhea and Venereal Disease. The identification of the causative agent, initially named Spirochaeta pallida, in 1906 was a milestone in biomedical research. As one example, at the turn of the 20th century, syphilis was the leading cause of neurologic and cardiovascular disease among middle-aged persons. In an exhaustive evaluation of all extant data, Harper and colleagues12 concluded that no case of Old World treponemal disease has a radiocarbon date that places it firmly in the pre-Columbian period. These same investigators have used sequence analysis of multiple loci in modern T. Universally agreed upon is that an epidemic known as the Great Pox (as distinguished from smallpox) ravaged Europe shortly after the return of Columbus from his first voyage of discovery. In his treatise, Fracastoro provided a detailed description of the clinical features of syphilis along with recommendations for treatment, ending with the allegory of Syphilus, a shepherd who contracted an illness as punishment for offending the sun god Apollo. Whether the comparatively mild nature of the present-day ailment reflects a change in the virulence of T. One of the difficulties in sorting through medical writings from the 17th and 18th centuries is that unequivocal clinical distinctions between syphilis, gonorrhea, and other venereal diseases did not emerge until the late 18th century. One prominent example is the dogma of Ricord, the greatest syphilologist of the 19th century, that material from secondary syphilis lesions is noncontagious. Two years later, Schaudinn and Hoffmann discovered Spirochaeta pallida in chancre exudates and adjacent lymph node aspirates. By 1906, Wassermann had developed his complement fixation test using an extract from the liver of a syphilitic stillborn baby. Subsequently, it was shown that extracts from uninfected beef livers and hearts were equally sensitive and that a phospholipid extracted from beef heart (cardiolipin) reproduced the Wassermann reaction when mixed with lecithin and cholesterol.
Cruz, 53 years: Other risk factors include trauma, use of hearing devices, and presence of eczema. Epidemic outbreaks of acute pyelonephritis caused by nosocomial spread of P fimbriated Escherichia coli in children. Almost exclusively associated with injection drug use of "black-tar" heroin, wound botulism was first reported in the United States in the 1990s. Tissue lesions are usually localized and appear grossly as well-circumscribed nodules.
Brant, 56 years: Ninety percent of cases were from the Southeast Asia region, with 79% of those from India. Resource consumption in the infection control management of pertussis exposure among healthcare workers in pediatrics. The impact of maternal intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis on the incidence of early-onset group B streptococcal disease was first assessed by active, population-based surveillance in selected counties of eight states and reported in 2000. Like all gram-negative bacteria, the gonococcus possesses a cell envelope composed of three distinct layers: an inner cytoplasmic membrane, a middle peptidoglycan cell wall, and an outer membrane.
Onatas, 63 years: Since then, further work has been done to analyze these groups and define species. Infants are most vulnerable to severe pertussis disease, so specific strategies have been examined to protect neonates from pertussis transmission. Early recognition by parents and health care professionals of the importance of fever and headache with a rash, prehospital antibiotic treatment, rapid transportation to a local hospital, early effective antibiotics, and stabilization in an intensive care unit can reduce the casefatality rate. In contrast to the overt inflammatory response generated with gonococcal infection of the male urethra, 50% to 80% of women with lower genital tract N.
References