Carl Bouchard, DMD, MSc, FRCD (C)
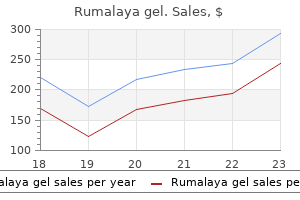
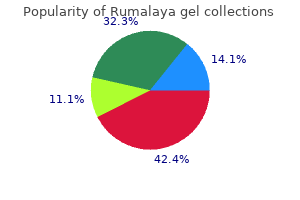
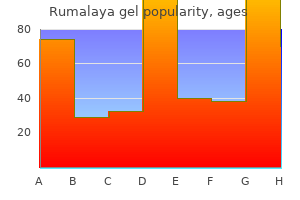
Rumalaya gel dosages: 30 gr
Rumalaya gel packs: 1 tubes, 2 tubes, 3 tubes, 4 tubes, 5 tubes, 6 tubes, 7 tubes, 8 tubes, 9 tubes, 10 tubes

Patients with serious eye infections may have worse vision than can be measured by use of the Snellen eye chart: the "big E" at the top of the chart is 20/400 vision muscle relaxant youtube buy rumalaya gel 30 gr on-line. In addition, there are many factors that affect vision in the setting of an acute eye infection, and some of these are reversible. To illustrate the interpretation of an ophthalmology note, the following are examples of eye infection cases referred for infectious disease con sultation. Case Example 1 A 65yearold woman with multiple medical problems presented with 5 weeks of painless decrease in vision in her right eye. There is no hypopyon, meaning no layer of white blood cells in the anterior chamber. Very low pressure may occur in a kera titis case, for example, if the corneal infection has led to a corneal perforation and aqueous humor leak. This eye therefore has marked vitritis and this produces a hazy view of the fundus, so details such as a retinal infiltrate are difficult to see. Case Example 2 A 19yearold otherwise healthy man presented to his college infir mary with a 1day history of right eye redness but no drainage. He was initially misdiagnosed with conjunctivitis and prescribed a topical antibiotic. Over the next 3 days, he developed blurring in his peripheral vision and eye pain. D, View of periphery of retina, showing the peripheral necrotizing retinitis and vasculitis (whitening and hemorrhage). The ophthalmologist correctly diagnosed acute retinal necrosis, a visionthreatening viral retinitis usually due to either herpes simplex or herpes zoster and discussed further in Chapter 117. This infection often occurs in other wise healthy patients, as in this case, and is due to reactivation of latent virus. This shows a new active lesion (creamy yellow) adjacent to a black "scar" from a prior episode. Ophthalmologists treat most eye infections without consulting an infectious disease specialist. This case would be readily diagnosed by the retina specialist as ocular toxoplasmosis because the appearance of the fundus is classic for that disease. However, ophthalmologists will refer patients in whom a diagnosis is in question or in whom the usual treatment for a presumed diagnosis is failing. In this chapter we describe the anatomy and physiology of the conjunctiva and the clinical presentation and laboratory testing of microbial conjunctivitis, and we discuss viral conjunctivitis, bacterial conjunctivitis, and neonatal conjunctivitis. This membrane lining the lids (palpebral conjunctiva) is reflected on itself, forming an inferior and superior cul-desac, or fornix, as it then covers the surface of the globe (bulbar conjunctiva) and extends to the edge of the cornea (limbus).
A diffuse hyperemia spasms in legs 30 gr rumalaya gel buy mastercard, minimal mucopurulent discharge, and conjunctival thickening with either a follicular or papillary reaction are common. Eyelid involvement may manifest as redness, telangiectasia, loss of lashes, thickening, or recurrent hordeola ("stye"), and ulceration at the base of the eyelashes may be seen. Maceration and ulceration of the inner and outer canthal angles may be seen in chronic blepharoconjunctivitis caused by Moraxella species. Chronic staphylococcal blepharoconjunctivitis may lead to marginal corneal ulceration, most likely as the result of an immune-mediated hypersensitivity reaction. The acute conjunctivitis is marked by unilateral hyperemia, tearing, mucopurulent discharge, and matting of the eyelids. Viridans streptococci and Streptococcus pyogenes can produce an acute conjunctivitis, often with an associated membranous reaction. Gram-negative rods, other than Haemophilus species, rarely cause acute conjunctivitis in the immunocompetent patient. Acute(Mucopurulent)Bacterial Conjunctivitis Appropriate laboratory confirmation of bacterial conjunctivitis should be attained to guide treatment. Although many mild conjunctival infections resolve on their own, topical antibiotic treatment may speed resolution and reduce severity and morbidity. In one study it was reported that the upper eyelid may have tarsoconjunctival crypts, and these may be a reservoir for the organisms. TreatmentofAcuteBacterial Conjunctivitis TreatmentofChronicBacterial Conjunctivitis Treatment of this type of bacterial conjunctivitis demands appropriate antibiotic therapy combined with aggressive lid hygiene and possible evaluation of the lacrimal system. Laboratory evaluation may guide appropriate antibiotic treatment, often with erythromycin or bacitracin ointment. Lid hygiene involves the use of warm compresses, eyelid scrubs with nontearing shampoo, and gentle lid massage because the meibomian (sebaceous gland) orifices at the base of the eyelashes may harbor the inciting agents. The lacrimal canaliculus or sac may also serve as a bacterial reservoir requiring antibiotic irrigation and oral 1399 antibiotics. The staphylococcal hypersensitivity reaction in the cornea may require mild topical corticosteroid treatment to reduce the associated inflammation. Any conjunctivitis occurring within the first 4 weeks of life is classified as neonatal conjunctivitis (ophthalmia neonatorum). Specific identification of the cause is particularly important because there is often a potentially serious systemic infection associated with the localized ocular condition. Neonatal conjunctivitis is more commonly found if babies are delivered vaginally compared with cesarean, and this may be a risk factor for this disease.
Lymphadenopathy in certain anatomic areas (preauricular muscle relaxants kidney failure order rumalaya gel 30 gr visa, posterior auricular, supraclavicular, deltoideopectoral, and pectoral) should always be viewed with greater suspicion because these nodes are not frequently enlarged as a result 1226 1226. Enlargement of superficial lymph nodes along the external jugular vein, as well as of nodes that drain the earlobe and the floor of the external acoustic meatus, may be associated with superficial infection accompanying recent ear piercing. Rarely, a firm mass in the tail or lateral aspect of the breast, suggestive of carcinoma, proves to be an enlarged lymph node in an unusual location caused by toxoplasmosis. In the past 4 decades, Staphylococcus aureus (both methicillin-susceptible and methicillin-resistant strains8,9) has superseded group A streptococci as the most frequent etiologic agent. The most common sites of involvement are, in descending order, submandibular (submaxillary), anterior and posterior cervical, inguinal, and axillary lymph nodes. The portal of entry for infection is frequently difficult to determine in children when cervical lymph nodes are involved. The recovery of a variety of anaerobic pathogens and/or -hemolytic streptococci, including Streptococcus intermedius10 in cervical lymph node aspirates from some patients, suggests that in addition to cutaneous foci, primary dental or pharyngeal infections may lead to suppurative lymphadenitis. Lymphatics from this area do not pass through the epitrochlear nodes but drain directly into the axillary nodes, which in turn communicate with the subpectoral nodes. If infection is not contained in the axillary nodes, subpectoral lymphadenitis develops and may progress to frank suppuration. Infection in this area may dissect downward and manifest as cellulitis over the lower chest and upper abdomen, suggesting an intraabdominal infection. Occasionally, large subpectoral abscesses may suggest a tumor because the overlying pectoralis major obscures the local warmth and erythema commonly associated with infection. Rarely, contraction of the pectoral muscle (as on arm elevation) causes movement of the pectoral area swelling, suggesting avulsion of the inferior attachments of this muscle. Acute unilateral adenitis of pyogenic origin occurs most often in preschool-aged children; bilateral disease occurs in less than 10% of cases. Although in only a minority of cases is there a history of sore throat, group A streptococci historically have been the most common cause of suppurative cervical lymphadenitis in children. Improved anaerobic culture techniques have demonstrated a variety of oral anaerobes in percutaneous needle aspirates in up to 40% of patients, as either pure anaerobic infections or mixed infections with conventional gram-positive aerobes. The mass is typically exquisitely tender and firm at presentation but may be fluctuant initially or develop fluctuance during the course of therapy. Acute bilateral cervical adenitis usually involves multiple nodes that are enlarged and somewhat tender in association with viral pharyngitis, infectious mononucleosis and related syndromes, human herpesvirus 6,7 streptococcal pharyngitis, or periodontal infection. Such lymphadenopathy may progress to suppuration if the primary pyogenic process is untreated. Bilateral suppurative lymphadenitis may occur at increased frequency in immunocompromised hosts.
Accidental self-inoculation spasms early pregnancy discount rumalaya gel 30 gr overnight delivery, which most commonly occurs on the face, mouth, lips, or genitalia, is usually not serious and requires no specific treatment. Inoculation of the conjunctiva, cornea, or eyelid is more serious and can be sight threatening if not evaluated and treated appropriately. In the 5 years between 1963 and 1968, ocular vaccinia was observed in 348 persons: 259 vaccinees and 66 contacts. Myocarditis had been reported after vaccination with the vaccine strains used in Europe and Australia,91,92 and in the U. On a clinical basis alone, distinguishing among generalized vaccinia is often difficult, which represents virus presumably spread hematogenously, a form of erythema multiforme, or erythematous urticaria eruptions that may be immunologically mediated. Laboratory identification of virus within the disseminated rash may differentiate these conditions. Studies of recent vaccination efforts have also identified focal and generalized folliculitis associated with vaccination. Vaccinia immunoglobulin is available to treat possible postvaccination complications, which can be severe. Sporadic outbreaks of infection caused by the vaccinia virus subspecies buffalopox virus, which involve transmission between milking buffalo, cattle, and people, have been reported, mainly in India but also in Egypt, Bangladesh, Pakistan, and Indonesia. Ordinary smallpox (90% of cases) produced viremia, fever, prostration, and rash; mortality rates were generally proportionate to the extent of rash. Flat smallpox (5% of cases) produced slowly developing focal lesions with generalized infection and an approximate 50% fatality rate. Variola major strains produced a disease with a severe prodrome, fever, and prostration. The virus was most often transmitted between humans via large-droplet respiratory particles inhaled by susceptible persons who had prolonged close faceto-face contact with an infectious person; it was spread less commonly via aerosol or direct contact with the rash lesion or sloughed crust material from the scab. Secondary attack rates among unvaccinated contacts within households ranged from 30% to 80%. Variola minor strains (alastrim, amass, or kaffir viruses) produced less severe infection and case-fatality rates of less than 1%, although secondary attack rates among unvaccinated contacts within households also ranged from 30% to 80%. The last naturally occurring smallpox case was in Somalia in October 1977, although a fatal laboratoryassociated infection with variola major virus occurred at the University of Birmingham, England in August 1978. Associated constitutional symptoms included backache, headache, vomiting, and prostration. Within 1 or 2 days after incubation, a systemic rash appeared that was characteristically centrifugally distributed.
Orthopedic devices are used to stabilize bone fractures muscle relaxant new zealand 30 gr rumalaya gel purchase otc, fuse the vertebral column, correct deformities such as scoliosis, and replace damaged joints. The presence of an implant increases the risk for an infection because its local susceptibility for bacterial adherence is high. Empirical antibiotic treatment without diagnostic workup should be avoided in the absence of life-threatening sepsis. These include an abscess or a sinus tract that communicates with the joint or the presence of purulence in the affected joint. Swabs from the operative site or from a draining sinus are difficult to interpret, particularly if Staphylococcus epidermidis or other skin flora are isolated. However, growth in a single specimen must always consider other criteria and take into account the constellation of diagnostic procedures. Prosthetic joints are made of metal and plastic, most commonly polyethylene inlay between metal shell and metal head. Materials for implantation that do not cause inflammation in the absence of infection are selected. This process is called "frustrated phagocytosis" and results in impaired granulocyte function. The latter route is rare and implicates spread from an adjacent focus of infection. Implant-associated microorganisms growing as a biofilm are protected from not only phagocytosis but also the action of antimicrobial agents. The traditional classification differentiates among early (those developing within <3 months after implantation), delayed (3 to 24 months after surgery), and late (>24 months after implantation) infection. However, most hematogenous infections occur late after surgery because the risk for hematogenous seeding persists lifelong. In these cases, early detection by a high degree of suspicion, rapid diagnostic workup, and prompt surgical treatment is required for retention of the implant. Some of the proposed risk factors have to be interpreted with caution because the corresponding studies used different statistical methods or focused on only one particular anatomic site. These factors influence wound healing and predispose for many other infectious diseases as well.
Zidovudine should never be co-administered with stavudine (d4T) because of antagonism spasms back rumalaya gel 30 gr order with amex, demonstrated both in vitro and in vivo. Drugs from this class were the first antiretrovirals to enter clinical use but, because of drug-associated toxicities, these early agents have largely been replaced in clinical practice by newer drugs with improved therapeutic, toxicity, and dosing profiles. The structural exception is tenofovir, which causes chain termination because of the lack of an intact ribose moiety. Virions bud from the infected cellular surface and are released, continuingthecycle. Zidovudine can also cause dose-limiting toxicities of anemia and granulocytopenia. Lactic acidosis, hepatic steatosis, peripheral neuropathy, lipodystrophic/ lipoatrophic changes, and myopathy all appear to be related to the mitochondrial toxicities associated with zidovudine. Stavudine Stavudine (2,3-didehydro-2,3-dideoxythymidine, d4T) is a thymidine analogue dosed at 40 mg twice daily for patients weighing more than 60 kg; a dose reduction to 30 mg twice daily is recommended for 1625 patients weighing less than 60 kg. Stavudine has similar antiretroviral activity as zidovudine but has significant toxicities that limit its clinical use. These include peripheral neuropathy, hyperlactatemia, lactic acidosis, hepatic steatosis, lipoatrophy, and pancreatitis. Stavudine is antagonistic to zidovudine, and should also not be co-administered with didanosine because of concerns for possibly fatal lactic acidosis that appears to have a female predominance. Didanosine (2,3-dideoxyinosine, ddI) is functionally an adenosine analogue that is administered in a delayed release enteric-coated form. Dosing is weight-based; 400 mg daily is recommended for patients weighing more than or equal to 60 kg, 250 mg for patients less than 60 kg. In the setting of renal insufficiency, didanosine dosing should be reduced commensurate with creatinine clearance. There is no specific recommendation for dosing in the setting of hepatic impairment, although the potential for toxicities in this situation should be closely monitored. Didanosine absorption is decreased in the presence of food, and the drug should be taken 30 minutes before or 2 hours after a meal. Most commonly, didanosine can cause peripheral neuropathy and pancreatitis and should not be co-administered with drugs having similar toxicity profiles. In one observational study, current didanosine use was associated with a reversible 1. Mild hepatic dysfunction necessitates a decrease in dose to 200 mg twice daily; the use of abacavir in patients with moderate-tosevere hepatic dysfunction is contraindicated. The use of abacavir with ribavirin or ganciclovir can increase the likelihood of mitochondrial, hepatic, and pancreatic toxicities. Abacavir is available as fixed-dose combinations with lamivudine, and with lamivudine and zidovudine.
Cognitive behavior therapy for chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomized controlled trial infantile spasms 9 months cheap rumalaya gel 30 gr on line. Cognitive behaviour therapy for the chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Cognitive behavioural therapy for chronic fatigue syndrome: a multicenter randomised controlled trial. Efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy for chronic fatigue syndrome: a meta-analysis. Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled treatment trial of fluoxetine and graded exercise for chronic fatigue syndrome. Randomised control trial of patient education to encourage graded exercise in chronic fatigue syndrome. Adaptive pacing, cognitive behaviour therapy, graded exercise, and specialist medical care for chronic fatigue syndrome: a costeffectiveness analysis. Chronic fatigue in general practice: is counselling as good as cognitive behaviour therapy Chronic fatigue in general practice: economic evaluation of counseling versus cognitive behaviour therapy. Detection of Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus in patients with chronic fatigue. Markers of viral infection in monozygotic twins discordant for chronic fatigue syndrome. New cardiomyopathy: pilot study of intravenous ganciclovir in a subset of the chronic fatigue syndrome. Prevalence of IgM antibodies to human herpesvirus 6 early antigen (p41/38) in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Activation of human herpesviruses 6 and 7 in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Investigation by polymerase chain reaction of enteroviral infection in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Persistent parvovirus-associated chronic fatigue treated with high dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Severe stealth virus encephalopathy following chronic-fatigue-syndrome-like illness: clinical and histopathological features. Possible correlation between Borna disease virus infection and Japanese patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. No serologic evidence of Borna disease virus in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Lack of evidence for infection with known human and animal retroviruses in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Assessment of a retrovirus sequence and other possible risk factors for the chronic fatigue syndrome in adults.
Some physicians base their diagnosis on how patients respond to an empirical trial of acyclovir stomach spasms 6 weeks pregnant rumalaya gel 30 gr buy on-line. Often, a prodrome of tingling and pain precedes the appearance of painful vesicles and ulcers. Lesions may be found on the lips, buccal mucosa, gingiva, soft palate, uvula, and tongue. Recurrent episodes at the same or different sites, chronic (nonremitting) zoster, and dissemination are often seen. Lesions are often extremely pruritic, and excoriation with secondary bacterial infection commonly occurs. Over a period of 4 to 7 days, lesions form bullae and crusts and begin to heal, although some patients have zoster chronically. Outbreaks along the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve may result in corneal involvement and lead to scarring and opacification that impair vision. A substantial proportion of patients may experience postherpetic scarring and pain. Vesicles, bullae, and hyperpigmented indurated plaques have all been described, however. In addition to genital lesions (see Chapter 146), warts are often seen in periungual locations, on the feet (plantar warts), and in bearded areas of the face. The agent is transmitted by sexual or other close contact; reactivation of remote infection may cause outbreaks in immunosuppressed hosts. Molluscum lesions are small firm papules with a pearly white umbilicated surface distributed on the face, trunk, or genital areas. The lesions are usually painless and can be differentiated from herpetic lesions by the absence of erythema, smaller size, and resolution of lesions without ulcerating or crusting. Biopsy may be necessary to exclude more serious causes of cutaneous lesions, such as cryptococcosis, pyogenic granuloma, and basal cell carcinoma. The typical skin lesions are purple-red nodules or plaques that can ulcerate and crust. Lesions may be mistaken for cutaneous Kaposi sarcoma, skin tags, or basal cell carcinoma. Visceral disease may include hepatitis (bacillary peliosis), splenic or osseous lesions, bacillemia, pneumonitis or, less often, involvement of other organs. Hematoxylin and eosin stains of biopsy specimens from skin lesions show proliferation of small blood vessels in the dermis or cutis, enlarged endothelial cells with abundant cytoplasm, and necrotic and granulomatous changes. Warthin-Starry stains show perivascular accumulations of bacilli; these findings may be confirmed by electron microscopy, although this is not usually necessary. Fluoroquinolones, other macrolides, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole also have activity against Bartonella.
Gamal, 37 years: The membrane is incubated with patient sera, and the immobilized antibody is detected typically using an antihuman IgG conjugated to a conveniently measured detection system (direct conjugation to alkaline phosphatase, conjugated with biotin or detected with avidin-horseradish peroxidase), or both. The precise nature of the infection that leads to development of tropical sprue is less clear. Various poxvirus-encoded proteins are predicted to bind and interfere with the function of host cytokines, chemokines, interferon, and complement.
Jack, 29 years: The standard commercial genotypic assays cannot reliably detect resistance mutations present at less than 20% of the viral population. In 2001, it became widely known that in a number of Chinese provinces, but mostly in Henan in central China, paid blood donation for plasmapheresis did not respect basic practices of infection control. Overall mortality is approximately 30%, although higher mortality rates are reported in older individuals.
Marius, 38 years: Symptomatic patients with negative examination results should have urethral or urine specimens tested for urethral pathogens and be asked to return in several days, by which time the symptoms may have resolved or examination may provide a diagnosis. Bacillary angiomatosis and bacillary peliosis in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus: clinical characteristics in a case-control study. Three types of cutaneous lesions have been described in cutaneous diphtheria: (1) wound diphtheria- secondary C.
References