Rodrigo Martino, M.D., Ph.D.
Misoprostol dosages: 200 mcg, 100 mcg
Misoprostol packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills

At this point gastritis quiz order 100 mcg misoprostol visa, the vermillion is precisely reapproximated using the preplaced suture and the remainder of the lip is closed. Wound was closed with V wedge excision that extended through chin with mucosa left intact. Postoperative results shown intraoperatively at 1 week and 6 months, from left to right. Postoperative results shown intraoperatively at 1 week and 7 months, from left to right. Full-thickness defect with cutaneous and mucosal involvement was treated with Abbe flap. This can be utilized for even 90% nearly commissure-to-commissure defects of the lower lip, and it is essentially a circumoral innervated myocutaneous flap maintaining both the intact nerves and mucosa with advances bilaterally. The Abbe flap was then created from the right lower cutaneous lip and rotated medially to the upper lip. Patients are just given intraoperative antibiotics and routinely do not continue postoperative antibiotics. Mohs defect closed with layered closure and anatomic alignment of the commissure to the mid-pupillary line. Surgical correction with AlloDerm placement restored lower lip volume and corrected central incompetence. Commentary: use of porcine xenografts on partial-thickness vermilion border and mucosal lower lip Mohs defects. Second intention healing for intermediate and large postsurgical defects of the lip. Direct primary closure without undermining in the repair of vermilionectomy defects of the lower lip. V-Y advancement flap for the reconstruction of partial and full thickness defects of the upper lip. Repair of partial-thickness Mohs defects of the vermilion lip with a combination of full-thickness graft and mucosal advancement. Rehabilitation of speech and swallowing after burns reconstructive surgery of the lips and nose. The reconstruction of two large full-thickness wounds of the upper lip with different operative techniques: when possible, a local flap repair is preferable to reconstruction with free tissue transfer. Derderian Summary this article discusses the issues regarding soft-tissue reconstruction of the ear including the functional and anatomic considerations in ear reconstruction, the management of ear defects, as well as a spectrum of surgical repair options for ear defects including secondary healing, full-thickness skin grafting, wedge excision and closure, a two-stage folded postauricular flap (Dieffenbach flap), as well as the management of near-total auricular defects including prosthetic ears.
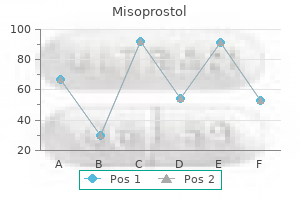
Scarlet Monarda (Oswego Tea). Misoprostol.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96206
Comparison of the diagnostic performance of the original and modified Wells score in inpatients and outpatients with suspected deep vein thrombosis gastritis diet vi buy 200 mcg misoprostol with visa. Exclusion of deep vein thrombosis using the Wells rule in clinically important subgroups: individual patient data meta-analysis. Safety and feasibility of a diagnostic algorithm combining clinical probability, D-dimer testing, and ultrasonography for suspected upper extremity deep venous thrombosis: a prospective management study. Articular disease characteristically causes swelling and tenderness that surrounds the entire joint and limits its entire repertoire of motion, during both active and passive movements. In a valgus deformity the distal part of the limb is directed away from the body midline. An attentive physical examination is fundamental to musculoskeletal diagnosis because, in contrast to other organ systems, the diagnostic standard for many musculoskeletal disorders is the bedside findings (Table 57. For example, in patients with symmetric arthritis of the wrists and hands, ulnar deviation of the metacarpophalangeal joints, and swan neck deformities of the fingers, the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis is almost certain whether or not the serologic rheumatoid factor is present (if absent, the patient has seronegative rheumatoid arthritis). Other chapters of this book review stance and gait (see Chapter 7), back pain (see Chapter 64), and hand pain (see Chapter 64). This anatomy grants the shoulder great flexibility but also renders the rotator cuff tendons and accompanying bursa susceptible to inflammation, degeneration, and tears. Using this classification, 5% to 12% of patients with shoulder pain have capsular syndromes, 17% acute bursitis, 5% to 11% acromioclavicular syndromes, 47% to 65% subacromial syndromes, and 5% to 10% referred shoulder pain. Nonetheless, the bedside examination continues to play an important role in patients with shoulder pain, especially in distinguishing intrinsic shoulder syndromes from disorders causing referred pain, and in identifying rotator cuff tears, a condition sometimes requiring surgical repair. The tendons of the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, subscapularis, and teres minor muscles make up the rotator cuff. Acute bursitis and subacromial disorders both represent disorders of the subacromial space, but bursitis causes inflammation and swelling that is more acute and severe, thus limiting motion. Both of these maneuvers were originally introduced to select patients for specific surgical procedures. The Neer maneuver forces the humerus (and overlying rotator cuff tendons) against the anterior acromion, which Neer proposed resecting. If patients develop pain during this maneuver and surgery is contemplated, Hawkins believed the coracoacromial ligament should be resected. The clinician then asks the patient to supinate the forearm against resistance. Pain indicates a positive test, implying inflammation of the long head of the biceps tendon (the main supinator of the forearm). Indeed, most tears of the biceps tendon are associated with advanced rotator cuff disease. The clinician detects atrophy of the supraspinatus or infraspinatus muscles by inspecting the posterior scapula on the symptomatic side and noting any increased prominence of the scapular spine when compared with the contralateral side.
Uneven swinging of the light may temporarily bleach the retina being illuminated more gastritis diet 91352 100 mcg misoprostol with mastercard, thus eventually producing a relative pupillary defect and erroneously confirming the initial suspicion. To avoid this and ensure equal illumination of both retinas, the clinician should silently count: "one, two, switch, one two, switch," and so on. If the patient has only one pupil that reacts to light (see the section on Anisocoria), the test is performed the same way, although the clinician focuses only on the normal iris to interpret the results. A relative afferent defect implies ipsilateral optic nerve disease or severe retinal disease. If the disease is asymmetric, the sensitivity of the finding is 92% to 98%, much higher than that for other tests of afferent function, including visual acuity, pupil cycle times, appearance of optic disc during funduscopy, and visual evoked potentials. During the swinging flashlight test, the pupils constrict when the normal eye is illuminated (rows 2 and 4) but dilate when the abnormal eye is illuminated (rows 3 and 5). Although both pupils constrict or dilate simultaneously, the clinician is usually focused on just the illuminated pupil. The pupil that dilates during the swinging flashlight test has the relative afferent pupillary defect and is labeled the Marcus Gunn pupil. In fact, during the time of Galen, the classical Roman physician, clinicians tested the pupillary light reaction of patients with cataracts to determine whether vision could be restored after couching (couching was an ancient treatment for cataracts that used a needle to displace the cataract posteriorly; a preserved light reaction indicated that the retina and optic nerve behind the cataract were intact). Originally described by Douglas Moray Cooper Lamb Argyll Robertson in 1868, this finding had great significance a century ago because it settled a long-standing debate whether general paresis and tabes dorsalis were the same disease. The pupillary abnormality was found in a high proportion of patients with both diseases and was limited to these diseases, arguing for a common syphilitic origin of both. The introduction of the Wasserman serologic test for syphilis in 1906 confirmed that the two diseases had the same cause. Either of these disorders may eliminate the light reaction when light is directed into the abnormal eye, although the pupils still constrict with the near synkinesis. However, in contrast to other causes of light-near dissociation, optic nerve and retinal disease severely impair vision. Dorsal Midbrain Syndrome (Parinaud syndrome, Sylvian Aqueduct Syndrome, Pretectal Syndrome). Common causes of the dorsal midbrain syndrome are pinealoma in younger patients and multiple sclerosis and basilar artery strokes in older patients. After damage to the third nerve (from trauma, aneurysms, or tumors, but not ischemia), regenerating fibers originally destined for the medial rectus muscle may instead reinnervate the pupillary constrictor, thus causing pupillary constriction during convergence but the absence of reaction to light. However, unlike Argyll Robertson pupils, this finding is unilateral, and most patients also have anisocoria, ptosis, and diplopia. Near-light dissociation was historically associated with von Economo encephalitis lethargica, although experts now believe it indicates that the patient is not trying hard enough to focus on the near object. These patients are invariably comatose from cerebral catastrophes causing elevated intracranial pressure.
Bleeding is inevitable during this part of the procedure but identifying the tonsillar capsule early and staying within the correct plane will minimize its extent gastritis blood test purchase misoprostol 100 mcg fast delivery. The tonsillar fossa is packed with a tonsil swab while dissection is performed on the opposite side. Once haemostasis has been achieved, the gag is relaxed for 30 seconds and the mouth reopened. If not removed, this clot may fall into and obstruct the airway, to be retrieved only later by the coroner. The endotracheal tube may on occasion herniate into the tongue blade and hence the patient may be inadvertently extubated. A survey of the teeth must be performed to document any dental trauma (or loss which will require retrieval of the tooth). Tonsillectomy using coblation has grown in popularity, particularly in paediatric cases where an intracapsular tonsillectomy can be performed, which decreases postoperative pain and can lead to a more rapid recovery. However, it does carry a greater risk of tonsil regrowth that may require further surgery in the future. Whilst tonsillectomy is routinely performed as a day case procedure, those with obstructive sleep apnoea require overnight observations as an inpatient. Patients will complain of odonophagia and otalgia, and require regular analgesia for the first postoperative week. It is essential that patients eat and drink normally as this reduces not only the likelihood of infection but also subsequent secondary bleeding. A tonsil swab or ribbon gauze soaked in 1:5000 adrenaline can be held over the bleeding point and may achieve haemostasis. If these measures fail, the patient is transferred to theatre for emergency surgical arrest of the haemorrhage. However, the tissue is generally friable in these situations; laying a strip of Surgicel within the tonsillar fossa and oversewing the anterior and posterior pillars together with a heavy stitch may be required. Adenoidectomy may decrease the risk of further persistent bilateral otitis media with effusion requiring grommets in the future. One should exclude a personal or familial bleeding tendency and discuss this with a senior colleague if necessary. There is an increase in the vascularity of the adenoidal pad following an upper aero-digestive tract infection, and many surgeons will postpone surgery if there has been a recent episode. Exclude a pulsatile adenoidal pad (this may actually be an angiofibroma, in which case adenoidectomy is ill advised). Exclude the presence of a cleft palate or submucous cleft (an adenoidectomy may result in a nasal voice and nasal regurgitation, and is a contra-indication for curette adenoidectomy).
Ondansetron gastritis diet ���� cheap misoprostol 100 mcg buy on line, a serotonergic receptor antagonist with minimal side effects, is widely used 30 minutes prior to arousal. After suctioning a patient with an endotracheal tube and little to no blood is in the airway, the endotracheal tube can also be removed with the gas on and the patient under deep anesthesia-a "deep extubation"-by an experienced anesthesia provider who is comfortable with deep extubations. The benefits to this are to avoid coughing and bucking during emergence causing hypertension in the face with added risks of additional bleeding or wound dehiscence. Hemodynamic changes intraoperatively are common and the anesthesia provider needs to be prepared to intervene pharmacologically to correct any hemodynamic instability such as blood pressure changes and dysrhythmias. Prompt recognition and treatment is vital to ensure organ blood flow, particularly to the brain, heart, and kidneys. Propofol produces vasodilation in both the arterial and venous circulation, producing a significant decrease in systemic blood pressure. Both sevoflurane and desflurane also reduce systemic vascular resistance and blood pressure, especially in the face of volume depletion due to fasting or bleeding. Boluses of ephedrine and phenylephrine are most commonly used to treat hypotension intraoperatively. Ephedrine is a sympathomimetic that has both alpha and beta activity and is used for treatment of vasodilatory hypotension. Phenylephrine exhibits potent vasoconstriction via alpha 1 receptors, which causes a rise in blood pressure as well as a reflex bradycardia. Treatment of hypotension should be swift because if left uncorrected, it can lead to stroke, myocardial infarction, and acute tubular necrosis. In facial surgeries, even slightly elevated blood pressure will cause bleeding at the surgical site, making the success for the desired result less likely. The most commonly used medications to lower intraoperative blood pressure are hydralazine and labetalol. Labetalol has a combined alpha and beta receptor antagonist effect and thus lowers blood pressure and heart rate. Changes in heart rate without significant blood pressure alterations can also occur. The most commonly uses local anesthetics are the amides (lidocaine and bupivacaine). Local anesthetics act by blocking sodium channels and may be used with or without epinephrine. Bupivacaine (Marcaine) can last up to 8 hours and it is longer acting than lidocaine, which lasts 1 to 2 hours (Table 2. The addition of epinephrine to all local anesthetics causes veins to constrict, helping with hemostasis, prolonging the anesthetic effect.
Because the carotid artery also pulsates in the neck definition akute gastritis misoprostol 100 mcg buy mastercard, the clinician must learn to distinguish the carotid artery from internal jugular vein, using the principles outlined in Table 36. Venous pulsations have a prominent inward or descending movement, the outward one being slower and more diffuse. In contrast, arterial pulsations have a prominent ascending or outward movement, the inward one being slow and diffuse. There are three positive waves (A, C, and V) and three negative waves (x, x, and y descents). The A wave represents right atrial contraction; the x descent, right atrial relaxation. The C wave-named "C" because Mackenzie originally thought it was a carotid artifact-probably instead represents right ventricular contraction and closure of the tricuspid valve, which then bulges upward toward the neck veins. The y descent begins the moment the tricuspid valve opens at the beginning of diastole, causing the atrium to empty into the ventricle and venous pressure to abruptly fall. Instead, the clinician sees two descents per cardiac cycle: the first represents merging of the x and x descents and is usually referred to as the x descent. The second is the y descent, which is smaller than the x descent in normal persons. The clinician identifies the descents by timing them with the heart tones or carotid pulsation (see text). The normal venous waveform has a prominent x descent and a small or absent y descent; there are no abrupt outward movements. This is the most common abnormal pattern, occurring both in atrial fibrillation (loss of A wave) and many different cardiomyopathies (more sluggish descent of the base), and (3) the absent y descent pattern. In patients with tricuspid regurgitation and pulmonary hypertension, the neck veins are elevated (more than 90% of patients) and consist of a single outward systolic movement that coincides with the carotid pulsation and collapses after S2. Instead of ejecting blood into the right ventricle, the contraction forces blood upward into the jugular veins. If the arterial pulse is regular but cannon A waves are intermittent, only one mechanism is possible: atrioventricular dissociation (see Chapter 16). The Study of the Pulse: Arterial, Venous, and Hepatic and of the Movements of the Heart. The venous and liver pulses, and the arrhythmic contraction of the cardiac cavities. The transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent-shunt procedure for variceal bleeding. Comparison of wedged hepatic vein pressure with portal vein pressure in human subjects with cirrhosis.
Syndromes
Finally gastritis diet ��������� misoprostol 100 mcg purchase overnight delivery, larger defects of the nasal dorsum or sidewall with exposed bone or cartilage or significant potential contour deformity can be managed with forehead flaps. Lower third nasal reconstruction is considerably more difficult than upper two-thirds nasal reconstruction. Alar retraction and asymmetry are common with poor local flap design and remarkably difficult to correct. For these reasons, very accurate planning, reconstructive method selection, and execution are required. Poorly executed full-thickness skin grafts, although simple in nature, can result in unmistakable long-term deformities. Although there is increasing reliance of wound healing agents to allow the body to heal in secondarily without surgical repair, often resulting in equivalent or superior aesthetic results, the usefulness of these agents for nasal reconstruction is currently limited. The requirements for a functional reconstruction with accurate airway flow patterns and the aesthetic intolerance of alar retraction do not permit a wide range of secondary healing. It is useful to break down the nose into upper two-thirds and lower third anatomic regions. Invariably, the upper third can be treated by non-subunit, that is, defect-only full-thickness grafting, for the vast majority of defects. Our selection of donor site is based almost entirely on the size of the defect, as well as the thickness of the defect. Additionally, a special category of a combined cheek and nasal defect with exposed nasal cartilage deserves special management. Additionally, there are instances, particularly in young patients, that such large defects in the upper two-thirds require forehead flap reconstruction to adequately fill in or recreate soft-tissue contour defects, but these are relatively infrequent. The use of full-thickness skin grafts on lower third defects has long been an issue in plastic surgery. Traditional plastic surgery teaching has often derided lower third skin grafting as an unacceptable operative choice with unacceptable final aesthetic results. In fact, with meticulous and disciplined approach to patient selection and graft selection, full-thickness grafting for lower third soft-tissue defects can yield superior aesthetic results. As discussed earlier, proper patient donor-site selection is essential to achieving optimal results. The criteria for selecting nasal defects that can be appropriately treated with full-thickness skin grafts include defect location and this would include 1. Banner flap, most useful for nasal dorsum taking advantage of adjacent cheek laxity. Note flap, also most useful for defects of nasal dorsum and side walls to recruit adjacent tissue laxity.
Organs have definite anatomical boundaries and are visibly distinguishable from adjacent structures gastritis que debo comer order misoprostol 100 mcg overnight delivery. They include not only what people traditionally think of as the "internal organs," such as the heart and kidneys, but less obvious examples such as the skin, muscles, and bones. However, there are organs within organs- the large organs visible to the naked eye contain smaller organs, some of which are visible only with the microscope. Included within it are thousands of smaller organs: hair follicles, nails, sweat glands, nerves, and blood vessels. A tissue is a mass of similar cells and cell products that forms a discrete region of an organ and performs a specific function. The body is composed of only four primary classes of tissue- epithelial, connective, nervous, and muscular tissues. Cells are the smallest units of an organism that carry out all the basic functions of life; nothing simpler than a cell is considered alive. A cell is a microscopic compartment enclosed in a film called the plasma membrane. Frontal plane AnatomicalPosition In describing the human body, anatomists assume that it is in anatomical position (fig. Without such a frame of reference, to say that a structure such as the sternum, thymus, or aorta is "above the heart" would be vague, since it would depend on whether the subject was standing, lying face down (prone), or lying face up (supine). From the perspective of anatomical position, however, we can describe the thymus as superior to the heart, the sternum as anterior (ventral) to it, and the aorta as posterior (dorsal) to it. Unless stated otherwise, assume that all anatomical descriptions refer to anatomical position. In most anatomical illustrations, for example, the appendix appears on the left side of the page, though it is located on the right side of the abdomen. Transverse plane Sagittal plane AnatomicalPlanes Many views of the body are based on real or imaginary "slices" called sections or planes. The median (midsagittal) plane passes through the midline of the body and divides it into equal right and left halves. Other planes parallel to this but off center are called parasagittal15 planes and divide the body into unequal right and left portions. A frontal (coronal16) plane also extends vertically, but it is perpendicular to the sagittal plane and divides the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions. A frontal section of the head, for example, would divide it into one portion bearing the face and another bearing the back of the head.
This article explains how to distinguish these lesions in patients with nerve complaints of the arms or legs diet makanan gastritis order 100 mcg misoprostol overnight delivery. This figure indicates those spinal levels that usually (dark blue shade) and sometimes (light blue shade) contribute to the corresponding muscle; based on references 4, 5, and 8 to 14. The motor examination of radiculopathy has two characteristics: (1) Weakness affects two or more muscles from the same spinal segment but different peripheral nerves. For example, a C6 radiculopathy may simultaneously weaken elbow flexion (biceps muscle, musculocutaneous nerve) and wrist extension (radial and ulnar wrist extensors, radial nerve). Proximal nerves originate from the nerve roots but then promptly innervate muscles of the shoulder, thus moving away from the course of the peripheral nerves of the arm. Therefore if a muscle innervated by one of these nerves is weak in a patient with nerve complaints of the arm or hand, the lesion must be a proximal one near the nerve roots. Involvement of the serratus anterior points to the C7 root and away from the radial nerve or brachial plexus. Brachial plexus lesions usually affect either the upper plexus (C5 to C6) as a group, causing weakness of the shoulder and upper arm but sparing all muscles of the hand, or the lower plexus (C7 to T1) as a group, affecting all muscles of the hand but sparing those of the shoulder and upper arm. For example, a complete radial nerve injury weakens the brachioradialis muscle (C5-C6),* elbow extension (triceps, C7), wrist extension (wrist extensors, C6-C7), and finger extension (finger extensors, C8). Therefore a proximal lesion of the radial nerve in the axilla would cause the findings described in the previous paragraph, but a lesion of the radial nerve at the elbow, after the branch to the brachioradialis muscle, spares the triceps and brachioradialis but weakens more distal muscles. A callus over the hypothenar eminence in a patient with ulnar muscle weakness suggests damage to the deep branch of the ulnar nerve caused by chronic pressure on the heel of the hand from bicycling or using a walker. All metacarpophalangeal joints are hyperextended because of paralysis of all interossei and unopposed action of finger extensors (radial nerve). The hyperextension is less prominent in the index and middle fingers because the lumbricals of these digits, innervated by the median nerve, act to flex the joint. One pure sensory syndrome of the arm is cheiralgia paresthetica, from injury to the superficial branch of the radial nerve, usually because of too tight a wristband or handcuffs. Therefore the finding of abnormal reflexes excludes both median and ulnar neuropathies (nerves lacking reflexes) and instead increases the probability of radiculopathy or plexopathy. Radial nerve lesions usually spare the brachioradialis and triceps reflexes because the branches to these muscles diverge from the main trunk proximally in the axilla, and most injuries to this nerve occur at a more distal point. The three figures on the left depict the volar surface of the arm; the three on the right, the dorsal surface. Proximal lesions of the radial nerve (upper right), near the axilla (and above the origin of the posterior cutaneous nerves of the arm and forearm) affect sensation of the posterior arm, forearm, and hand; more distal lesions in the radial nerve. Proximal lesions of the median nerve affect both palm and fingers; more distal ones. The sensory innervation of the medial arm and forearm derives from cutaneous nerves that branch directly off the brachial plexus. The Tinel sign and Phalen sign are provocative tests traditionally used to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome.
Combined use of pretest clinical probability score and latex agglutination D-dimer testing for excluding acute deep vein thrombosis gastritis university of maryland order misoprostol 100 mcg online. Atrophy of these muscles may appear as soon as 2 to 3 weeks after a rotator cuff tear. The most important muscles to test in suspected tears of the rotator cuff are the supraspinatus muscle (involved in most rotator cuff tears) and the infraspinatus muscle (involved in 11% to 45% of tears). The patient flexes the shoulder forward to 60 to 90 degrees, with his or her elbow extended and arm fully supinated. The patient is asked to hold this position and resist attempts to lower the arms to the side. Some investigators propose testing the supraspinatus muscle in a slightly different way, with the arms externally rotated and thumbs pointing up. In patients with a positive test, indicating rotator cuff tear, the patient lowers the arm smoothly until approximately 100 degrees, after which the smooth movements become irregular and the arm may fall suddenly to the side. In patients with tears of the supraspinatus tendon (which inserts on the greater tuberosity), the clinician detects both an abnormal eminence and an abnormal sulcus posterior to this eminence. The abnormal eminence is the greater tuberosity with attached remnant of tendon, and the sulcus just behind it is the actual rent in the supraspinatus tendon. Comparison with the contralateral shoulder helps to determine whether the suspected tear is real or not. The diagnostic accuracy of Yergason sign and Speed test emphasizes again the association between biceps tendon pain and rotator cuff disease (see the section on Yergason sign). Nonetheless, these studies did not repeat the impingement signs after lidocaine injection as Neer originally proposed, a maneuver that might improve specificity). Murrell22 combined (1) impingement signs, (2) supraspinatus weakness, and (3) infraspinatus weakness, and Park27 combined (1) Hawkins sign, (2) painful arc, and (3) infraspinatus weakness. Consequently, some patients with hip arthritis develop groin pain, but many experience pain at distant sites in the cutaneous distribution of nerves innervating the hip joint capsule, such as the thigh and knee (obturator and femoral nerves) or buttock (sciatic nerve). If there is excessive laxity of movement or a "soft" or "mushy" endpoint, the ligament is damaged. Blunt trauma to the outside of the knee is associated with injury of the medial collateral ligament; trauma to the inside of the knee suggests injury of the lateral collateral ligament. The patient lies supine with hip flexed at 45 degrees, knee flexed at 90 degrees, and foot flat on the table. Abnormal anterior subluxation of the tibia (arrow) with a soft end point is a positive test. What specifically is responsible for the sudden reduction at 40 to 50 degrees is controversial, but most experts believe it is the pull of the iliotibial tract (whose action abruptly changes from a knee extensor to knee flexor beyond 40 degrees of flexion)56,58,59 and the geometric peculiarities of the convex tibial surface. The clinician grasps the lower thigh with one hand and the upper calf with the other, pulling forward on the tibia to stress the ligament and reveal the abnormal anterior subluxation of the tibia (arrow).
Mazin, 63 years: Auras are related to depression of visual cortical function or retinal function and persist for minutes to hours before the headache. No Yes Suspect 3rd nerve palsy or myasthenia gravis Yes Suspect thyroid myopathy Yes Suspect orbital fracture Are there associated neurologic signs These capillaries surround the tubules of the nephron, where they provide them with oxygen and nutrients and also take substances reabsorbed by the tubules back into the blood.
Ugrasal, 45 years: Paramidline forehead flaps should be considered the gold standard for the majority of nasal reconstruction and the only flap suitable for nasal reconstruction with lining deficits. For example, if one of the clinicians in our hypothetical study heard a third heart sound in 10 of the 100 dyspneic patients and the other heard it in 20 of the patients (even though they agreed about the presence of the heart sound in only 5 patients), simple agreement by chance alone would be 74%. These substances form one of the groups of recreational drugs now referred to as novel psychoactive substances (see below).
References