
J. Jason West, MD
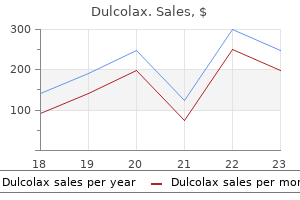
Dulcolax dosages: 5 mg
Dulcolax packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

A pressure of about 25 cm H2O is necessary to overcome the surface tension of the airways and the alveoli medications images discount dulcolax 5 mg amex. Viscosity of the lung fluid is a major factor for normal neonatal lung expansion and aeration. Diaphragmatic contraction and chest wall expansion create a negative intrathoracic pressure. Increased fluid absorption and less fluid secretion perfusion and subsequent normal pattern of breathing. This also is sufficient to overcome the surface tension and is helped immensely 3. This fluid is derived from the In a normal birth the process is completed within ultrafiltration of pulmonary capillary blood, secretion of 2 hours. Continuation of intrauterine hypoxia (placental insufficiency) the placenta, as a respiratory organ of the fetus, fails functionally either due to anatomical changes or due to inadequacy of uteroplacental circulation (such as premature placental separation, circumvallate placenta, hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, abnormal labor, cord compression, vascular anomalies in cord, etc. Maternal hypoxic states: the maternal diseases such as anemia, eclampsia, cyanotic cardiovascular disorders, status asthmaticus, dehydration and hypotension. Prenatal and intranatal medication to the mother Morphine, pethidine and anesthetic agents depress the respiratory centers directly and the chance of development of asphyxia is increased. Birth trauma to the neonate Malpresentation such as breech, oblique lie, occipitoposterior often requires manipulative and operative vaginal delivery (forceps or ventouse). Increased intracranial tension cerebral edema and congestion increased intracranial pressure asphyxia. Postnatal factors Postnatal asphyxia is secondary to pulmonary, cardiovascular and neurological abnormalities of the neonate. In response to asphyxia, a mature fetus redistributes the blood flow to the heart, brain and adrenals to ensure adequate oxygen and substrate delivery to these vital organs. Long-term Signs neurological correlation is obtained at the Respiratory Absent Slow, Good, irregular crying 5-minute score which is of more value. In cases effort where the score remains significantly depressed Heart rate Absent < 100 bpm > 100 bpm at 5 minutes, it should be evaluated again after 15 Muscle Flaccid Flexion of Active body minutes. This scoring is done in a newborn baby tone extremities movements at 1 minute, 5 minutes and 15 minutes and can be Reflex No response Grimace Cough or tabulated as in follows (Table 33. But it must be emphasized that in certain circumstances, it is inappropriate to delay resuscitative efforts until the 1 minute Apgar score is obtained. Heart rate, skin color and respiratory activity provide the most accurate evaluation and the need of resuscitation.
The transport is a slow process and is controlled by muscular contraction and movement of the cilia medicine used for pink eye cheap dulcolax 5 mg buy online. The central cell of the morula is known as inner cell mass which forms the embryo proper and the peripheral cells are called outer cell mass which will form protective and nutritive membranes of the embryo. The fluid passes through the canaliculi of the zona pellucida which separates the cells of the morula and is now termed blastocyst. Zona hatching is the next step so that trophectoderm cells interact with endometrial cells and implantation occurs. The cells on the outer side of the morula (polar) become trophectoderm and the inner cells (apolar) become inner cell mass by the mediation of epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin) (protein). Trophectoderm differentiates into chorion (placenta) and the inner cell mass into the embryo. Pinopods are long finger like projections (microvilli) from the endometrial cell surface. These pinopods absorb the endometrial fluid which is secreted by the endometrial gland cells. This fluid, rich in glycogen and mucin provides nutrition to the blastocyst initially. Adhesion of blastocyst to the endometrium occurs through the adhesion molecules like integrin, selectin and cadherin (glycoproteins). With increasing lysis of the stromal cells, the blastocyst 26 Textbook of Obstetrics. Concurrently, the syncytial cells penetrate deeper into the stroma and erode the endothelium of the maternal capillaries. The syncytium by penetrating the vessels, not only becomes continuous with the endothelial lining but permits the maternal blood to enter into the lacunar system. Ultimately erosion of few maternal arteries with formation of blood space (lacunae) occurs. Further penetration is stopped probably by the maternal immunological factor and the original point of entry is sealed by fibrin clot and later by epithelium. This type of deeper penetration of the human blastocyst is called interstitial implantation and the blastocyst is covered on all sides by the endometrium (decidua). Occasionally, there may be increased blood flow into the lacunar spaces at the abembryonic pole. This results in disruption of the lacunae and extravasation of blood into the endometrial cavity. This corresponds approximately to 13th day after fertilization (at about the expected day of the following period).
It is synthesized in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus symptoms 10 dpo dulcolax 5 mg buy mastercard. By nerve axons it is transported from the hypothalamus to the posterior pituitary where it is stored and eventually released. Oxytocin acts through receptor and voltage-mediated calcium channels to initiate myometrial contractions. Bound intracellular calcium is eventually mobilized from the sarcoplasmic reticulum to activate the contractile protein. In the second trimester, relative refractoriness persists, and, as such, oxytocin can only supplement other abortifacient agents in induction of abortion. In later months of pregnancy and during labor in particular, it is highly sensitive to oxytocin even in small doses. Pregnancy grand multipara All the contraHypovolemic - Augmentation of labor indication in state - Uterine inertia pregnancy Labor: - Inactive management of third stage contracted pelvis Obstructed labor Cardiac of labor disease - Following expulsion of placenta as history of Incoordinate uterine cesarean section an alternative to ergometrine. Maternal Fetal maTeRnal Uterine hyperstimulation (overactivity)-is a frequently observed side effect. There may be excessive duration of uterine contraction (hypertonia) or increased frequency (> 6 in 10 min time) of contractions (polysystole). High-risk cases are: grand multipara, malpresentation, contracted pelvis, prior uterine scar (hysterotomy) and excessive oxytocin use. Water intoxication is manifested by hyponatremia, confusion, coma, convulsions, congestive cardiac failure and death. It is prevented by strict fluid intake and output record, use of salt solution and by avoiding high dose oxytocin for a long time. FeTal: Fetal distress, fetal hypoxia or even fetal death may occur due to uterine hyperstimulation. Calculation of the infused dose: Nowadays the infusion is expressed in terms of milliunits per minute. This can give an accurate idea about the exact amount administered per minute irrespective of the concentration of the solution.
The ventral part of the medulla is occupied symptoms 10 days before period purchase dulcolax 5 mg free shipping, on either side of the middle line, by a prominent bundle of fibres: these fibres form the pyramid. The fibres of the pyramids are corticospinal fibres on their way from the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord. At this level in the medulla, many of these fibres run backwards and medially to cross in the middle line. Having crossed the middle line, the corticospinal fibres turn downwards to enter the lateral white column of the spinal cord. The anterolateral region of the medulla is continuous with the anterior and lateral funiculi of the spinal cord. The central canal surrounded by central grey matter, the nucleus gracilis, the nucleus cuneatus, the spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve, and the pyramids occupy the same positions as at lower levels. The nucleus gracilis and the nucleus cuneatus are, however, much larger and are no longer continuous with the central grey matter. The region just behind the pyramids is occupied by a prominent bundle of fibres, the medial lemniscus, on either side of the middle line. The medial lemniscus is formed by fibres arising in the nucleus gracilis and the nucleus cuneatus. These fibres cross the middle line and turn upwards in the lemniscus of the opposite side. The region lateral to the medial lemniscus contains scattered neurons mixed with nerve fibres. The pyramids, the medial lemniscus, the spinal nucleus and tract of the trigeminal nerve, and the reticular formation are present in the same relative position as at lower levels. The medial lemniscus is, however, much more prominent and is somewhat expanded anteriorly. Lateral to the spinal nucleus (and tract) of the trigeminal nerve, we see a large compact bundle of fibres. This is the inferior cerebellar peduncle that connects the medulla to the cerebellum. Here, it is lined by a layer of grey matter in which are located several important cranial nerve nuclei. The inferior olivary nucleus forms a prominent feature in the anterolateral part of the medulla at this level. It is made-up of a thin lamina of grey matter that is folded on itself like a crumpled purse. Others are corticospinal fibres that descend through the pons into the medulla where they form the pyramids.
The common causes are: (1) injudicious administration of oxytocics medications ending in pam 5 mg dulcolax buy, (2) premature rupture of the membranes, and (3) premature attempt at instrumental delivery. It is revealed during cesarean section in the first stage, during forceps application in the second stage and during manual removal in the third. Maternal condition is not much affected but the fetus is in jeopardy because of the hypertonic state. The ring usually passes off by deepening the plane of anesthesia otherwise the ring may have to be cut vertically to deliver the baby. The difficulties faced during forceps delivery (second stage) or during normal removal of placenta (third stage) can be overcome by using deep anesthesia that relaxes the constriction ring. Failure of cervical dilatation may be due to-(a) Inefficient uterine contractions (see p. Primary: Commonly observed during the (i) First birth where the external os fails to dilate, (ii) Rigid cervix, (iii) Inefficient uterine contractions and the others (as mentioned earlier). Treatment: In presence of associated complications (malpresentation, malposition), cesarean section is preferred. If the head is sufficiently low down with only thin rim of cervix left behind, the rim may be pushed up manually during contraction or traction is given by ventouse. Thus, there is no physiological differentiation of the active upper segment and the passive lower segment of the uterus. The whole uterus undergoes a sort of tonic muscular spasm holding the fetus inside (active retention of the fetus). Causes: (i) Cephalopelvic disproportion (ii) Obstruction (iii) Injudicious use of oxytocics. Abdominal examination reveals the uterus to be somewhat smaller in size, tense and tender. Hypercontractility (tachysystole) may be induced by oxytocics (>5 contractions in 10 min). Cesarean delivery is done in majority of the cases, especially when obstruction is suspected. Short labors may be associated with: placental abruption and uterine tachysystole. Rapid expulsion is due to the combined effect of hyperactive uterine contractions associated with diminished soft tissue resistance. Labor is short as the rate of cervical dilatation is 5 cm/hr or more for the nulliparous women. The fetal risks include-intracranial stress and hemorrhage because of rapid expulsion without time for molding of the head. The baby may sustain serious injuries if delivery occurs in standing position; bleeding from the torn cord and direct hit on the skull, brachial plexus injury are real hazards.
Persistent hypotension leads to acute tubular necrosis and ultimately renal failure treatment ulcerative colitis discount 5 mg dulcolax amex. Congestion, hemorrhage and ulceration are responsible for hematemesis (d) Lungs-Congestion or atelectasis leads to tachypnea or dyspnea, progressive hypoxemia and reduced pulmonary compliance. Endotoxins have got special affinity for kidneys and lungs for reasons which are not very clear. Hypovolemic shock: Circulating blood volume is inadequate resulting from acute depletion. Hemorrhagic shock: Associated with postpartum or postabortal hemorrhage, ectopic pregnancy, placenta previa, abruptio placenta, rupture of the uterus and obstetric surgery: Shock associated with disseminated intravascular coagulation, Intrauterine dead fetus syndrome and amniotic fluid embolism (Table 39. Nonhemorrhagic shock: Fluid loss shock - Associated with excessive vomiting, diarrhea, diuresis or too rapid removal of amniotic fluid. Supine hypotensive syndrome-Due to compression of inferior vena cava by the pregnant uterus (see p. Associated typically with septic abortion, chorioamnionitis, pyelonephritis, and rarely postpartum endometritis 3. Cardiogenic shock: Myocardial infarction Cardiac arrest (asystole or ventricular fibrillation) Cardiac tamponade Characterized by systolic pressure (< 80 mm Hg), cardiac index (< 1. Extracardiac shock: Massive pulmonary embolism, amniotic fluid embolism, anaphylaxis, drug overdose, neurogenic. In the irreversible (late) phase, the clinical features are the same as the final pathology is multiple organ failure. Intermediate phase (Reversible phase): If the early phase remains untreated, the patient passes into the state of hypotension. Patient progressively becomes pale; tachycardia persists and due to intense vasoconstriction, the periphery becomes cold and there may be sweating. Due to diversion of blood to vital organs, the patient remains conscious and the urine output is within normal limits. Extremities become cold and clammy because of vasoconstriction due to sympathetic stimulation. Practically imperceptible low volume pulse, oliguria, mental confusion is observed. Treatment of any kind is practically useless in this phase and mortality varies between 3% and 100%. In the reversible phase, unlike hypovolemic shock, pallor is absent; on the contrary, the face may be flushed. Prompt diagnosis and immediate resuscitation is essential failing which multiple organ failure develops.

But when a fetal or neonatal death occurs medications that cause pancreatitis buy cheap dulcolax 5 mg online, special attention must be given to the grieving patient and her family. Perinatal grieving may also be due to unexpected hysterectomy, birth of a malformed or critically ill infant. Prolonged separation from a critically ill newborn can also provoke grief reaction. The common maternal somatic symptoms are: insomnia, fatigue and sighing respirations, feeling of guilt, hostility and anger. Management of perinatal grieving: Facilitating the grieving process with consolation, support and sympathy is important. Others are: supporting the couple in seeing or holding or taking photographs of the infant; autopsy requests, planning investigations, follow-up visit and plan for subsequent pregnancy. This includes: (i) Endometritis, (ii) Endomyometritis, or (iii) Episiotomy wound infection. Pathogens commonly responsible for female genital infections are: (A) Aerobes (Gram-positive-Streptococci and Staphylococci, Gram-negative-E. Common causes of subinvolution are: (a) Excess enlargement of the uterus (twins), (b) Anemia, (c) Retained bits of tissues, (d) Endometritis (see p. Common breast complications in the puerperium are: (a) Breast engorgement (b) Cracked and retracted nipple, (c) Mastitis and breast abscess (see p. There may be some complications that are relatively delayed but acute and alarming. Before the actual examination, the important maternal and perinatal history should be reviewed (p. May need screening with pulse oximetry (>95% and 3% difference between right hand and foot). General examination: Skin color: It is the single most important parameter of cardiorespiratory function. Cyanosis: Central cyanosis (bluish skin, including the tongue and lips) is caused by low oxygen saturation. Peripheral cyanosis (bluish skin with pink lips and tongue) may be due to drugs (nitrates or nitrites) or hereditary. It is often associated with methemoglobinemia (hemoglobin oxidizes from ferrous to ferric form) Acrocyanosis (bluish hands and feet only) may be normal immediately following birth. Mongolian spots are bluish, often large, commonly seen on the back, buttocks or thighs. Large fontanels are associated with hypothyroidism, osteogenesis imperfecta or chromosomal anomalies (Down syndrome). Bulging fontanel may be due to increased intracranial pressure, meningitis or hydrocephalus.
Betamethasone (24 mg in three divided doses) should be administered to the mother 24 hours before transfusion from 26 weeks onwards to enhance pulmonary maturity treatment 8 cm ovarian cyst 5 mg dulcolax buy fast delivery, in case delivery becomes necessary during transfusion. With the advent of wider use of prophylactic anti-D immunoglobulin, less and less problem babies are born and through exchange transfusion, the incidence of kernicterus has also been reduced. Thereafter, the baby is quite capable to get rid of the maternal antibodies by producing sufficiently his own Rh-positive blood. A plastic catheter of 1 mm diameter is passed about 7 cm beyond the umbilicus so as to place it in the inferior vena cava. Entire set should be air tight and to be periodically flushed with heparinized saline (1,000 units in 100 mL) to prevent clotting. For every 100 mL of blood transfused, one milliequivalent of sodium bicarbonate is given to combat metabolic acidosis and 1 mL of 10% calcium gluconate to prevent tetany due to transfusion of citrated blood. To estimate the hemoglobin and bilirubin concentration prior to and after the exchange transfusion. Occasionally, the level of conjugated bilirubin may remain higher and phototherapy should be continued and (4) hypoglycemia (due to increased insulin secretion) is to be checked by blood glucose estimation posttransfusion 4 hourly. Immediate complications: (1) Cardiac failure due to raised venous pressure and overloading of the heart; (2) air embolism; (3) clotting and massive embolism; (4) hyperkalemia; (5) tetany; (6) acidosis; (7) sepsis; (8) hypocalcemia; (9) hypoglycemia and (10) coagulopathies due to thrombocytopenia. Delayed complications: (1) Necrotizing enterocolitis; (2) extrahepatic portal hypertension due to thrombosis of portal vein and (3) other complications are mostly attributed to prematurity, hyperbilirubinemia and hypoxia. These products are water soluble and therefore readily excreted in the bile and urine. Phenobarbitone increases the glucuronyl transferase enzyme activity in the fetal and neonatal liver to conjugate the bilirubin which hastens its clearance. With alloimmunization of the mother, the prognosis of the baby depends on: (1) Genotype of the father; (2) genotype of the fetus; (3) maternal antibody level; (4) history of previous affection of the baby due to hemolytic disease and (5) availability of sophisticated diagnostic and therapeutic facilities for the affected babies (specialist fetal medicine care unit). The age limit is arbitrary and is based on the fact that the outcome of the pregnancy is adversely affected beyond the specified age limit. There are two groups of patients: (1) one with high fecundity-a women married late but conceives soon after and (2) one with low fecundity-woman married early but conceives long after marriage. The latter one is prognostically more unfavorable so far as the obstetric outcome is concerned after conception occurs following treatment of infertility (ovulation induction or assisted reproductive technology). During labor: There is increased incidence of: (1) preterm labor; (2) prolonged labor due to (a) uterine inertia caused by anxiety or malposition (occipito-posterior); (b) impaired joint mobility and (c) inelasticity of the soft tissues of the birth canal; (3) maternal and fetal distress appears early; (4) increased cesarean delivery and (5) retained placenta due to uterine atony and increased association of fibroid. Puerperium: (1) Increased morbidity due to operative interference and (2) failing lactation. The perinatal mortality is increased due to prematurity, increased congenital malformation (trisomy 21) and operative interference.
Hogar, 46 years: An oval gap in the chorion with torn ends of blood vessels running up to the margin of the gap indicates a missing succenturiate lobe.
Urkrass, 44 years: The central canal surrounded by central grey matter, the nucleus gracilis, the nucleus cuneatus, the spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve, and the pyramids occupy the same positions as at lower levels.
Osko, 63 years: The glottis has an anterior (membranous) part placed between the two vocal folds, and a posterior (cartilaginous) part placed between the medial surfaces of the two arytenoid cartilages (45.
Sulfock, 43 years: Abdominal examination reveals the cystic swelling felt separated from the gravid uterus.
Porgan, 53 years: Mechanism: There is compression of the engaging diameter of the head with corresponding elongation of the diameter at right angle to it.
Konrad, 45 years: The antigen-binding regions of antibody molecules are highly variable, and any one individual has the potential to produce millions of different antibodies, each with distinct antigen specificity.
References