
William G. Gossman, M.D.
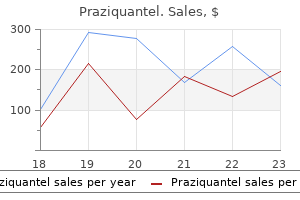
Praziquantel dosages: 600 mg
Praziquantel packs: 1 pills

Lymphatic drainage rom the abdominal wall merges with that rom the lower limbs treatment 7th march buy praziquantel 600 mg with visa, both pathways ollowing the arterial supply retrograde rom those parts. Ultimately, all lymphatic drainage rom structures inerior to the diaphragm, plus that draining rom the lower six intercostal spaces via the descending thoracic lymphatic trunks, enters the beginning o the thoracic duct at the T12 level, posterior to the aorta. Board-review questions, case studies, and additional resources are available at thePoint. Anatomically, the pelvis is the part o the body surrounded by the pelvic girdle (bony pelvis), part o the appendicular skeleton o the lower limb. The greater pelvis is occupied by inerior abdominal viscera, aording them protection similar to the way the superior abdominal viscera are protected by the inerior thoracic cage. The lesser pelvis is surrounded by the inerior pelvic girdle, which provides the skeletal ramework or both the pelvic cavity and the perineum-compartments o the trunk separated by the musculoascial pelvic diaphragm. Externally, the pelvis is covered or overlapped by the inerior anterolateral abdominal wall anteriorly, the gluteal region o the lower limb posterolaterally, and the perineum ineriorly. The term perineum1 reers both to the area o the surace o the trunk between the thighs and the buttocks, extending rom the coccyx to the pubis, and to the shallow compartment lying deep (superior) to this area but inerior to the pelvic diaphragm. The perineum includes the anus and external genitalia: the penis and scrotum o the male and the vulva o the emale. The primary unctions o the pelvic girdle are to bear the weight o the upper body when sitting and standing. Consequently, the pelvic girdle is strong and rigid, especially compared to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle. Other unctions o the pelvic girdle are to contain and protect the pelvic viscera (inerior parts o the urinary tracts and the internal reproductive organs) and the inerior abdominal viscera. Bones and Features o Pelvic Girdle In mature people, the pelvic girdle is ormed by three bones. In its most restricted sense, and in obstetrics, it has been used to reer to the area supercial to the perineal body, between the vulva or scrotum and the anus or to the perineal body itsel. In an intermediate sense, it has included only the perineal region, a supercial (surace) area bounded by the thighs laterally, the mons pubis anteriorly, and the coccyx posteriorly. In its widest sense, as used in Terminologia Anatomica (the international anatomical terminology), and in this book, it reers to the region o the body that includes all structures o the anal and urogenital triangles, supercial and deep, extending as ar superiorly as the inerior ascia o the pelvic diaphragm. Right and let hip bones (coxal or pelvic bones): large, irregularly shaped bones, each o which develops rom the usion o three bones (ilium, ischium, and pubis). The internal (medial or pelvic) aspects o the hip bones bound the pelvis, orming its lateral walls; these aspects o the bones are emphasized here. The pelvis (green) is the space within the pelvic girdle, overlapped externally by the abdominal and gluteal regions, perineum, and lower back. The greater pelvis (light green) is pelvic by virtue o its bony boundaries but is abdominal in terms o its contents. The lesser pelvis (dark green) provides the bony ramework (skeleton) or the pelvic cavity and deep perineum.
Epilobium spicatum (Fireweed). Praziquantel.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96440
Diagonal ractures are oten associated with limb shortening caused by overriding o the ractured ends 88 treatment essence purchase 600 mg praziquantel visa. Frequently during skiing, a racture results rom a highspeed orward all, which angles the leg over the rigid ski boot, producing a "boot-top racture". Tibial ractures in children are more serious i they involve the epiphysial plates because continued normal growth o the bone may be jeopardized. The tibial tuberosity usually orms by inerior bone growth rom the superior epiphysial center at approximately 10 years o age, but a separate center or the tibial tuberosity may appear at approximately 12 years o age. Disruption o the epiphysial plate at the tibial tuberosity may cause infammation o the tuberosity and chronic recurring pain during adolescence (Osgood-Schlatter disease), especially in young athletes. When a person slips and the oot is orced into an excessively inverted position, the ankle ligaments tear, orcibly tilting the talus against the lateral malleolus, and may shear it o. Even ater a segment o the shat has been removed, walking, running, and jumping can be normal. The remaining parts o the bula usually do not regenerate because the periosteum and nutrient artery are generally removed with the piece o bone, so that the grat will remain alive and grow when transplanted to another site. Secured in its new site, the bular segment restores the blood supply o the bone to which it is now attached. Awareness o the location o the nutrient oramen in the bula is important when perorming ree vascularized bular transers. Because the nutrient oramen is located in the middle third o the bula in most cases. Because o its extensive subcutaneous location, the anterior tibia is accessible or obtaining pieces o bone or grating in children; it is also used as a site or intraosseous inusion in dehydrated children or children with shock. The needle is inserted into the fat area o bone approximately 2 cm distal and slightly medial rom the tibial tuberosity. Special needles designed or manual insertion are used; battery-powered or impact-driven devices also are available to help aid insertion. Calcaneal Fractures A hard all onto the heel, rom a ladder, or example, may racture the calcaneus into several pieces, producing a comminuted racture. A calcaneal racture is usually disabling because it disrupts the subtalar (talocalcaneal) joint, where the talus articulates with the calcaneus. It is used primarily in cases o traumatic shock and in children with circulatory collapse.
The root o the penis medicine 93 5298 purchase 600mg praziquantel amex, the attached part, consists o the crura, bulb, and ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles. The root is located in the supercial perineal pouch, between the perineal membrane superiorly and the deep perineal ascia ineriorly. Each crus is attached to the inerior part o the internal surace o the corresponding ischial ramus. The enlarged posterior part o the bulb o the penis is penetrated superiorly by the urethra, continuing rom its intermediate part. The body o the penis is the ree pendulous part that is suspended rom the pubic symphysis. Except or a ew bers o the bulbospongiosus muscle near the root o the penis and the ischiocavernosus muscle that embrace the crura, the body o the penis has no muscles. The penis consists o thin skin, connective tissue, blood and lymphatic vessels, ascia, the corpora cavernosa, and corpus spongiosum containing the spongy urethra. Distally, the corpus spongiosum expands to orm the conical glans penis, or head o the penis. The margin o the glans projects beyond the ends o the corpora cavernosa to orm the corona o the glans. The corona overhangs an obliquely grooved constriction, the neck o the glans, which separates the glans rom the body o the penis. The slit-like opening o the spongy urethra, the external urethral orice (meatus), is near the tip o the glans penis. The anal canal is surrounded by the external anal sphincter, with an ischio-anal ossa on each side. The inerior anal (rectal) nerve branches rom the pudendal nerve at the entrance to the pudendal canal and, with the perineal branch o S4, supplies the external anal sphincter. The renulum o the prepuce is a median old that passes rom the deep layer o the prepuce to the urethral surace o the glans. The suspensory ligament o the penis is a condensation o deep ascia that arises rom the anterior surace o the pubic symphysis. The ligament passes ineriorly and splits to orm a sling that is attached to the deep ascia o the penis at the junction o its root and body. The bers o the suspensory ligament are short and taut, anchoring the erectile bodies o the penis to the pubic symphysis. When the penis is faccid, these arteries are coiled, restricting blood fow; they are called helicine arteries o the penis (G. Blood rom the cavernous spaces is drained by a venous plexus that joins the deep dorsal vein o the penis in the deep ascia.

The distal palmar crease begins at or near the clet between the index and middle ngers; it crosses the palm with a slight convexity treatment broken toe praziquantel 600mg buy with visa, supercial to the head o the 3rd metacarpal and then proximal to the heads o the 4th and 5th metacarpals. Each o the medial our ngers usually has three transverse digital fexion creases: Proximal digital crease: located at the root o the nger, approximately 2 cm distal to the metacarpophalangeal joint. The proximal digital crease o the thumb crosses obliquely, at or proximal to the 1st metacarpophalangeal joint. The skin ridges on the pulp (pads) o the digits, orming the ngerprints, are used or identication because o their unique patterns. The physiological unction o the skin ridges is to reduce slippage when grasping objects. The brous degeneration o the longitudinal bands o the palmar aponeurosis on the medial side o the hand pulls the 4th and 5th ngers into partial fexion at the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints. The disease rst maniests as painless nodular thickenings o the palmar aponeurosis that adhere to the skin. Treatment o Dupuytren contracture usually involves surgical excision o all brotic parts o the palmar ascia to ree the ngers (Salter, 1999). Hand Inections Because the palmar ascia is thick and strong, swellings resulting rom hand inections usually appear on the dorsum o the hand, where the ascia is thinner. The potential ascial spaces o the palm are important because they may become inected. The ascial spaces determine the extent and direction o the spread o pus ormed by these inections. Depending on the site o inection, pus will accumulate in the thenar, hypothenar, midpalmar, or adductor compartments. Antibiotic therapy has made inections that spread beyond one o these ascial compartments rare; however, an untreated inection can spread proximally rom the midpalmar space through the carpal tunnel into the orearm, anterior to the pronator quadratus and its ascia. Because the tendons o the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th ngers nearly always have separate synovial sheaths, the inection is usually conned to the inected nger. I the inection is untreated, however, the proximal ends o these sheaths may rupture, allowing the inection to spread to the midpalmar space. Because the synovial sheath o the little nger is usually continuous with the common fexor sheath. How ar an n inection spreads rom the ngers depends on variations in their connections with the common fexor sheath. Excessive riction o these tendons on their common sheath results in brous thickening o the sheath and stenosis o the osseobrous tunnel. The excessive riction is caused by repetitive orceul use o the hands during gripping and wringing.
The arch ascends anterior to the right pulmonary artery and the biurcation o the trachea treatment lead poisoning praziquantel 600 mg buy on-line, reaching its apex at the let side o the trachea and esophagus as it passes over the root o the let lung. The arch ends by becoming the thoracic (descending) aorta posterior to the 2nd let sternocostal joint. The arch o the azygos vein occupies a position corresponding to the aorta on the right side o the trachea (continued on p. In this superfcial dissection o the mediastinum, the sternum and ribs have been excised and the overlapping parietal pleurae removed. It is unusual to see such a distinct thymus in an adult; usually, it is impressive during puberty but subsequently regresses and becomes largely replaced by at and fbrous tissue. In this deep dissection o the root o the neck and superior mediastinum, the thymus has been removed. The let recurrent laryngeal nerve passes inerior and then posterior to the arch o the aorta and ascends between the trachea and esophagus to the larynx. The largest branch (brachiocephalic trunk) arises rom the beginning o the arch, the next artery (let common carotid artery) arises rom the superior part o the arch, and the third branch (let subclavian artery) arises rom the arch approximately 1 cm distal to the let common carotid. The ligamentum arteriosum, the remnant o the etal ductus arteriosus, passes rom the root o the let pulmonary artery to the inerior surace o the arch o the aorta. The usual branches o the arch are the brachiocephalic trunk, let common carotid artery, and let subclavian artery. The brachiocephalic trunk, the rst and largest branch o the arch o the aorta, arises posterior to the manubrium, where it is anterior to the trachea and posterior to the let brachiocephalic vein. The let common carotid artery, the second branch o the arch o the aorta, arises posterior to the manubrium, slightly posterior and to the let o the brachiocephalic trunk. It ascends anterior to the let subclavian artery and is at rst anterior to the trachea and then to its let. The let subclavian artery, the third branch o the arch o the aorta, arises rom the posterior part o the arch, just posterior to the let common carotid artery. It ascends lateral to the trachea and let common carotid artery through the superior mediastinum; it has no branches in the mediastinum. The vagus nerves exit the cranium and descend through the neck posterolateral to the common carotid arteries. The right recurrent laryngeal nerve hooks around the right subclavian artery and ascends between the trachea and esophagus to supply the larynx. It enters the mediastinum between the let common carotid artery and let subclavian artery. The let recurrent laryngeal nerve passes inerior to the arch o the aorta, immediately lateral to the ligamentum arteriosum, and ascends to the larynx in the groove between the trachea and the esophagus. The phrenic nerves also supply sensory bers to the pericardium and mediastinal pleura.
During this phase o lie schedule 6 medications praziquantel 600 mg buy line, the uterus undergoes monthly changes in size, weight, and density in relation to the menstrual cycle. Over the 9 months o pregnancy, the gravid uterus expands greatly to accommodate the etus, becoming larger and increasingly thin walled. The uterus becomes nearly membranous, with the undus dropping below its highest level (achieved in the 9th month), at which time it extends superiorly to the costal margin, occupying most o the abdominopelvic cavity. Immediately ater delivery o the etus, the large uterus becomes thick walled and edematous. The multiparous nongravid uterus has a large and nodular body and usually extends into the lower abdominal cavity, oten causing a slight protrusion o the inerior abdominal wall in lean women. Postmenopause, the uterus is involuted and regresses to a markedly smaller size, once again assuming childhood proportions. All these stages represent normal anatomy or the particular age and reproductive status o the woman. The decline in the incidence and number o women dying rom cervical cancer is related to the accessibility o the cervix to direct visualization and to cell and tissue study by means o cervical cytology (invented in 1946 by Dr. Cervical cytology allows detection and treatment o premalignant cervical conditions (Homan et al. The vagina can be distended with a vaginal speculum to enable inspection o the cervix. The spatula is rotated to scrape cellular material rom the mucosa o the vaginal cervix. Because no peritoneum intervenes between the anterior cervix and the base o the bladder, cervical cancer may spread by contiguity to the bladder. It may also spread by lymphogenous (lymph-borne) metastasis to external or internal iliac or sacral nodes. Hematogenous (bloodborne) metastasis may occur via iliac veins or via the internal vertebral venous plexus. The incidence o hysterectomy or noncancerous reasons has markedly declined in avor o exploring other options. The uterus may be surgically approached and removed through the anterior abdominal wall ("transabdominal approach") or through the vagina ("transvaginal approach"). When cervical or total hysterectomies are perormed, the vaginal ornices are incised, encircling the cervix, to separate the uterus rom the vagina. Ligation o the uterine artery is perormed distal to the vaginal artery and vaginal branches to enable maximal blood fow to the superior end o the vagina to acilitate healing.
Syndromes
The posterior compartment contains a three-headed extensor muscle treatment bronchitis cheap praziquantel 600 mg, the triceps, which is supplied by the radial nerve. One o the heads (the long head) acts at the shoulder, but mostly the heads work together to extend the elbow. Both compartments o the arm are supplied by the brachial artery, the posterior compartment primarily via its major branch, the prounda brachii artery. The primary neurovascular bundle is located on the medial side o the limb; thus, it is usually protected by the limb it serves. Cubital fossa: the triangular cubital ossa is bound by a line connecting the medial and lateral epicondyles o the humerus, and the pronator teres and brachioradialis muscles arising, respectively, rom the epicondyles. Medial to the tendon are the median nerve and terminal part o the brachial artery. Lateral to the tendon is the lateral cutaneous nerve o the orearm supercially and-at a deeper level-the terminal part o the radial nerve. In the subcutaneous tissue, most commonly, a median cubital vein runs obliquely across the ossa, connecting the cephalic vein o the orearm and basilic vein o the arm, providing an advantageous site or venipuncture. In about one th o the population, a median antebrachial vein biurcates into median cephalic and median basilic veins, which replace the diagonal median cubital vein. It extends rom the elbow to the wrist and contains two bones, the radius and ulna, which are joined by an interosseous membrane. In addition to rmly tying the orearm bones together while permitting pronation and supination, the interosseous membrane provides the proximal attachment or some deep orearm muscles. The head o the ulna is at the distal end o the orearm, whereas the head o the radius is at its proximal end. The role o orearm movement, occurring at the elbow and radioulnar joints, is to assist the shoulder in the application o orce and in controlling the placement o the hand in space. Compartments o Forearm As in the arm, the muscles o similar purpose and innervation are grouped within the same ascial compartments in the orearm. Although the proximal boundary o the orearm per se is dened by the joint plane o the elbow, unctionally the orearm includes the distal humerus. For the distal orearm, wrist, and hand to have minimal bulk to maximize their unctionality, they are operated by "remote control" by extrinsic muscles having their bulky, feshy, contractile parts located proximally in the orearm, distant rom the site o action. Furthermore, because the structures on which the muscles and tendons act (wrist and ngers) have an extensive range o motion, a long range o contraction is needed, requiring that the muscles have long contractile parts as well as a long tendon(s). The orearm proper is not, in act, long enough to provide the required length and sucient area or attachment proximally, so the proximal attachments (origins) o the muscles must occur proximal to the elbow-in the arm-and provided by the humerus. Generally, fexors lie anteriorly and extensors posteriorly; however, the anterior and posterior aspects o the distal humerus are occupied by the chie fexors and extensors o the elbow. To provide the required attachment sites or the fexors and extensors o the wrist and ngers, medial and lateral extensions (epicondyles and supraepicondylar ridges) have developed rom the distal humerus. The medial epicondyle and supra-epicondylar ridge provide attachment or the orearm fexors, and the lateral ormations provide attachment or the orearm extensors.

As a consequence treatment brown recluse bite purchase praziquantel 600mg otc, several parts o the gut come to lie against the posterior abdominal wall, and their posterior mesenteries become gradually reduced because o pressure rom overlying organs. Starting rom the primordial position, suspended rom the midline o the posterior abdominal wall (A), the mesocolon shits to the let (B) and gradually uses with the let posterior parietal peritoneum (C). The arrow indicates the let paracolic gutter, the site where an incision is made during mobilization o the colon during surgery. Sometimes, the descending colon retains a short mesentery, similar to the stage shown in (C), especially where the colon is in the iliac ossa. Peritoneum and Peritoneal Cavity 441 gut that will become the descending colon to the let side and presses its mesentery against the posterior abdominal wall. The mesentery is held there until the layer o peritoneum that ormed the let side o the mesentery and the part o the visceral peritoneum o the colon lying against the body wall use with the parietal peritoneum o the body wall. As a result, the colon becomes xed to the posterior abdominal wall on the let side with peritoneum covering only its anterior aspect. The descending colon (as well as the ascending colon on the right side) has thus become secondarily retroperitoneal, having once been intraperitoneal (Moore et al. Thus, the descending colon o the adult can be reed rom the posterior body wall (surgically mobilized) by incising the peritoneum along the lateral border o the descending colon and then bluntly dissecting along the plane o the usion ascia, elevating the neurovascular structures rom the posterior body wall until the midline is reached. Several parts o the gastrointestinal tract and associated organs become secondarily retroperitoneal. However, the roots o the short mesenteries do not arise rom the midline but shit to the let or right by a usion process like that described or the descending colon. A mesentery connects an intraperitoneal organ to the body wall-usually the posterior abdominal wall. The small intestine mesentery is usually reerred to simply as "the mesentery"; however, mesenteries related to other specic parts o the alimentary tract are named accordingly-or example, the transverse and sigmoid mesocolons. Mesenteries have a core o connective tissue containing blood and lymphatic vessels, nerves, lymph nodes, and at. An omentum is a double-layered extension or old o peritoneum that passes rom the stomach and proximal part o the duodenum to adjacent organs in the abdominal cavity. The greater omentum is a prominent, our-layered peritoneal old that hangs down like an apron rom the greater curvature o the stomach and the proximal part o the duodenum. Ater descending, it olds back and attaches to the anterior surace o the transverse colon and its mesentery. The lesser omentum is a much smaller, double-layered peritoneal old that connects the lesser curvature o the stomach and the proximal part o the duodenum to the liver. It also connects the stomach to a triad o structures that run between the duodenum and liver in the ree edge o the lesser omentum. The hepatogastric and hepatoduodenal ligaments are continuous parts o the lesser omentum and are separated only or descriptive convenience.
The transversus abdominis probably has no appreciable eect on the vertebral column (Standring symptoms liver disease 600mg praziquantel free shipping, 2016). The oblique and transverse muscles, acting together bilaterally, orm a muscular girdle that exerts rm pressure on the the map o dermatomes o the anterolateral abdominal wall is almost identical to the map o peripheral nerve distribution. The exception occurs at the L1 level, where the L1 anterior ramus biurcates into two named peripheral nerves. Each dermatome begins posteriorly overlying the intervertebral oramen by which the spinal nerve exits the vertebral column and ollows the slope o the ribs around the trunk. Dermatome T10 includes the umbilicus, whereas dermatome L1 includes the inguinal old. Iliohypogastric and ilio-inguinal nerves: terminal branches o the anterior ramus o spinal nerve L1. The thoraco-abdominal nerves pass inero-anteriorly rom the intercostal spaces and run in the neurovascular plane between the internal oblique and the transversus abdominis muscles to supply the abdominal skin and muscles. During their course through the anterolateral abdominal wall, the thoraco-abdominal, subcostal, and iliohypogastric nerves communicate with each other. The deeper veins o the anterolateral abdominal wall accompany the arteries, bearing the same name. A deeper, medial venous anastomosis may exist or develop between the inerior epigastric vein (an external iliac vein tributary) and the superior epigastric/internal thoracic veins (subclavian vein tributaries). The superfcial and deep anastomoses may aord collateral circulation during blockage o either vena cava. The primary blood vessels (arteries and veins) o the anterolateral abdominal wall are as ollows: Superior epigastric vessels and branches o the musculophrenic vessels rom the internal thoracic vessels. The distribution o the deep abdominal blood vessels reects the arrangement o the muscles: the vessels o the anterolateral abdominal wall have an oblique, circumerential pattern (similar to the intercostal vessels;. The superior epigastric artery is the direct continuation o the internal thoracic artery. It enters the rectus sheath superiorly through its posterior layer and supplies the superior part o the rectus abdominis and anastomoses with the inerior epigastric artery approximately in the umbilical region. The inferior epigastric artery arises rom the external iliac artery just superior to the inguinal ligament. It runs superiorly in the transversalis ascia to enter the rectus sheath below the arcuate line. Lymphatic drainage o the anterolateral abdominal wall ollows the ollowing patterns. Superfcial lymphatic vessels inerior to the transumbilical plane drain to the superfcial inguinal lymph nodes. For an overview o superfcial and deep lymphatic drainage, see Chapter 1, Overview and Basic Concepts. The skin and subcutaneous tissue o the abdominal wall are served by an intricate subcutaneous venous plexus, draining superiorly to the internal thoracic vein medially and the lateral thoracic vein laterally and ineriorly to the superfcial and inerior epigastric veins, tributaries o the emoral and external iliac veins, respectively.
During cooling medicine 8 discogs buy praziquantel 600mg cheap, the arch vessels are thoroughly mobilized, as well as the proximal descending aorta. Considerable care is taken to preserve the left recurrent laryngeal and vagus nerves, as well as the phrenic nerve. A fine neonatal vascular clamp is placed across the proximal aortic arch and a C-clamp is placed on the descending aorta. The left common carotid and left subclavian arteries are controlled with fine tourniquets. With bypass continuing, the coarctation area can be excised and an extended end-to-end anastomosis performed. In the very small baby, it is probably wise to cool to deep hypothermia because there is a risk that clamp manipulation may obstruct flow in the innominate artery although bypass flow is continued. Alternatively, if there is extensive hypoplasia of the aortic arch, either a radical extended end-to-end anastomosis can be fashioned or a patch plasty can be performed using glutaraldehyde-treated autologous pericardium. These procedures will necessitate the use of a period of hypothermic circulatory arrest which generally will not exceed 15 minutes. A patch of crimped Dacron has been sutured into the aortotomy using a continuous suture technique. CompliCatioNs oF CoarCtatioN surgery aNd how to miNimize them Early Complications Paraplegia By far the most devastating complication reported with coarctation surgery is paraplegia. In the current era, however, the risk of paraplegia is almost certainly much less. This may be because the risk of paraplegia is less when surgery is undertaken at a younger age when there is less likely to be major hemorrhage secondary to injury of the fragile collateral vessels which develop with age. In addition, the smaller aorta of the younger child necessitates a very much shorter suture line and therefore quicker cross-clamp time. Drawing on the adult experience with paraplegia after aneurysm surgery, it is very likely that an extended cross-clamp time, for example, more than 30 minutes, as well as hypotension, are important predisposing factors for the development of paraplegia. It is important to remember that the anterior spinal artery is supplied by branches from the right and left vertebral artery which arise from the subclavian arteries. Usually flow continues through the right subclavian and vertebral arteries, as well as the right internal mammary artery during the cross-clamp period. An aberrant right subclavian artery (which arises from the proximal descending aorta), however, is included within the clamped segment thereby increasing the risk of compromise of blood flow to the anterior spinal artery. In this setting, if multiple intercostal vessels and most particularly the artery of Adamkiewicz are occluded during the cross-clamp period, then the risk of paraplegia will be increased. Accordingly, it is important to preserve flow through as many collateral vessels as possible and to avoid division of collateral vessels unless absolutely necessary.
Quadir, 61 years: The pubic symphysis is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the bodies o the pubic bones. This allows the stretched elastic tissue o the lungs to recoil, expelling most o the air. The latter type o contraction is important in Equal resistance Isometric Skeletal muscles unction by contracting; they pull and never push.
Arokkh, 59 years: They are generally not performed in conjunction with the Ross procedure (see below). The primary role o the intercostal muscles in respiration is to support (increase the tonus or rigidity o) the intercostal space, resisting paradoxical movement especially during inspiration when internal thoracic pressures are lowest (most negative). Malabsorptive procedures involve rerouting o the connection o the stomach with the small intestine and/or o variable portions o the small intestine.
References