Jamie Kisgen, PharmD
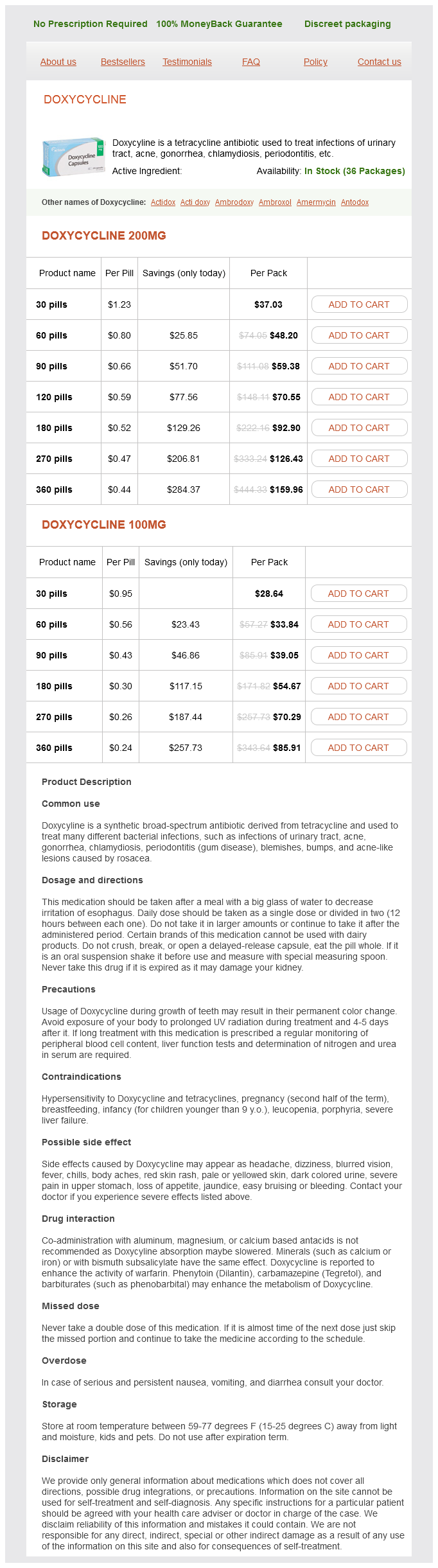
Amermycin dosages: 200 mg, 100 mg
Amermycin packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Increase in cerebral aerobic metabolism by normobaric hyperoxia after traumatic brain injury best antibiotics for acne treatment purchase amermycin 100 mg with mastercard. A Review of Red Cell Transfusion in the Neurological A Review of Red Cell Transfusion in the Neurological Intensive Care Unit. Longitudinal Changes in the Corpus Callosum following Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury Dev. Effect of cerebral perfusion pressure augmentation with dopamine and norepinephrine on global and focal brain oxygenation after traumatic brain injury. Is there an upper limit of intracranial pressure in patients with severe head injury if cerebral perfusion pressure is maintained Effects of catecholamines on cerebral blood vessels in patients with traumatic brain injury. What is the optimal threshold for cerebral perfusion pressure following traumatic brain injury Limits of intermittent jugular bulb oxygen saturation monitoring in the management of severe head trauma patients Neurosurgery 2000; 46: 1131-8 107. Factors affecting changes produced in electroencephalogram by standardized hyperventilation. Cerebral blood flow an metabolism, in comatose patients with acute head injury: Relationship to intracranial hypertension. Hyperventilation at referring hospitals is common before transport in intubated children with neurological diseases. Effect of hyperventilation on cerebral blood flow in traumatic head injury: Clinical relevance and monitoring correlates. Bedside Microdialysis for Early Detection of Cerebral Hypoxia in Traumatic Brain Injury Neurosurgical Focus. The Time Course of Photosynthesis as Shown by a Rapid Electrode Method for Oxygen Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1938; 24: 420-7 117. Continuous recordings of oxygen pressure in the cerebrospinal fluid of cat, dog and man. Tissue pO2, monitoring of cerebral oxygenation: Experimental studies and preliminary clinical results of continuous monitoring of cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue oxygen tension. Determination of the ischemic threshold for the brain tissue oxygenation in the severely head injured patient. Traystman by Society of Critical Care Medicine 1993; 4: 239-74 219 Intensive Care in Neurology and Neurosurgery 125. A comparison of pO histograms from rabbit hind-limb muscles obtained by simultaneous measurements with hypodermic needle electrodes and with surface electrodes. Heterogeneities and profiles of oxygen pressure in brain and kidney as examples of the pO distribution in the living tissue. Brain oxygen tension, oxygen supply, and oxygen consumption during arterial hyperoxia in a model of progressive cerebral ischemia.
Functions of Retinaculum It fixes the peroneus longus and brevis tendons in place medicine for lower uti cheap 100 mg amermycin fast delivery. Muscle Arises from Flexor Retinaculum Origin of abductor hallucis from the lower part. Function It maintains the position of tendons of the deep flexor muscles of the back of the leg. After its origin it descends downwards and laterally in the femoral triangle, which lies lateral to the femoral artery. Then it turns posterior to the femoral artery and passes between the pectineus and the adductor longus where it leaves the femoral triangle. Then the artery passes between adductor longus and brevis muscle of which adductor longus anteriorly. After that the artery lies on the adductor longus and magnus, reaching the lower onethird of the thigh, finally pierces adductor magnus. End It ends by forming anastomosis with the superior muscular branches of the popliteal artery. Then the artery anastomoses with the superior muscular branches of the popliteal artery. It passes medially and also forwards along the dorsum of the proximal part of the first intermetatarsal space iii. Then the artery turns in to the sole between the two heads of the fitst dorsal interosseous muscle iv. Lastly the artery ends by anastomosing with the lateral plantar artery to complete the plantar arterial arch. Lateral circumflex femoral artery Medial circumflex femoral artery Perforating arteries-(4 in number) Muscular branches. It is the direct continuation of the anterior tibial artery distal to the ankle ii. End It ends by anastomosing with the lateral plantar artery to complete the plantar arterial arch. After its origin it just passes distal to the ankle opposite the midpoint between the lateral and medial malleoli. This artery may be palpated on the dorsum of the foot with slightly dorsiflexed ankle just lateral to the tendon of extensor hallucis longus ii. Absent or diminished pulse in arteria dorsalis pedis usually indicates vascular insufficiency due to arterial disease. The plantar digital veins drain in to dorsal digital veins in the cleft between the toes. The dorsal metatarsal veins join across the proximal parts of the metatarsal bones to form the dorsal venous arch. On the medial and lateral side of the foot presents medial and lateral marginal veins respectively.
Diseases
Appearance of blastopore: A depression medial corners of the eyes) appears in the center of the primitive node bacteria 5 kingdoms 100 mg amermycin with amex. Formation of notochordal process: It is the cranially extended part up to the prochordal plate by the multiplication of the cells of the primitive knot. Formation of notochordal canal: the blastopore extends in to the notochordal process and converts in to a canal called notochordal canal. Appearance of neuroenteric canal: the floor of the notochordal canal break forming small openings and communicate between the yolk sac and amniotic cavity. Formation of notochordal plate: the opening rapidly becomes confluent and the floor of the notochordal canal closed, flattened to notochordal plate. Formation of notochord: Finally, the cells of the notochordal plate life prorate and thickened forming in to a solid rod of cells called notochord. Posterior or inferior: On its free margin usually presents two clefts, which subdivides the cusp in to three scallops Fate 1. Free margin: Connected with the chordae tendineae, on the free margin of the post leaflet usually presents two clefts. The cusps are closed during ventricular systole by the apposition of the ventricular surfaces with the zones of the adjacent cusps. The rough zone: It is thick and provides attachments to the chordae tendineae on its ventricular surface. The basal zone: It is thick and vascular about 2 to 3 mm in extent and provides attachments of to the basal chordae on its ventricular surface. These are connecting the apical one-third part of the papillary muscles to the free margins and ventricular surface of the cusps. The chordae tendineae are help in the valve closure during ventricular systole and prevent eversion of the cusps towards the atrium. Commissural and Cleft Chordae: They are fan shaped, and attached to the commisssures and free margins of the adjacent cusps or scallops. Free Marginal: these are attached to the margins of the cusps and dividing in to branches: Rough zone chordae, deep chordae and basal chordae. Rough Zone Chordae: these are consists of three strands, one is attached to the free margin, one to the junction of rough and clear zones and the other to the rough zone midulary between former two. Blood supply is only present in the collagenous ring and in the basal one-third of the cusps.
Despite these figures antibiotic resistant bacterial infection order amermycin 100 mg amex, there is reluctance to use pharmacological prophylaxis therapy in these patients because of the fear of an increased risk of bleeding. Two recently published surveys reported that only 32 to 33% of such patients receive pharmacological prophylaxis, although it is not definitively established whether therapy actually increases the risk of intracranial hemorrhage to any significant degree. Comparing study results is difficult because most studies are non-randomized and because spontaneous re-bleeding after elective neurosurgery has been reported to occur in more than 25% of cases. In 2003, Gerlach published a study of a series of 2823 neurosurgical patients who received 0. The incidence of post-operative bleeding associated with clinical deterioration or which required a new operation was 1. Also, Chibaro, in a 2008 study involving a series of 746 neurosurgical patients who received Tinzaparine, reported post-surgical intracranial bleeding in less than 1% of cases. In 1998 Agnelli published a randomized study of 307 patients undergoing elective neurosurgery (90% involving the brain, 97% of which brain tumours) who received 40 mg enoxaparin once daily + graduated compression stockings versus graduated compression stockings + placebo. Guidelines for Management of Acute Cervical Spine Injuries- Deep Venous Thrombosis and Thromboembolism in Patients with Cervical Spine Cord Injuries. Guidelines for the Early Management of Adults With Ischemic Stroke from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. J Neurotrauma 2007; 24 (Suppl 1): S32-S36 Broderick J, Connolly S, Feldmann E, et al. American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, High Blood Pressure Research Council, and the Quality of Care and Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Group. Safety of deep venous thrombosis prophylaxis with lowmolecular-weight heparin in brain surgery. Utility of Once-Daily Dose of Low-MolecularWeight Heparin to Prevent Venous Thromboembolism in Multisystem Trauma Patients. Risk of postoperative hemorrhage after intracranial surgery after early nadroparin administration: results of a prospective study. Major bleeding during anticoagulation after cerebral ischemia: patterns and risk factors. Low-Molecular-Weight and Unfractionated Heparin for Prevention of Venous Thromboembolism in Neurosurgery. What is the optimal pharmacological prophylaxis for the prevention of deep-vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients with acute ischemic stroke Low-molecular-weight heparins or heparinoids versus standard unfractioned heparin for acute ischaemic stroke. Leukoaraiosis is associated with warfarin-related hemorrhage following ischemic stroke. Safety of low-dose subcutaneous enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after primary intracerebral haemorrhage.
The hematoma may also expand in to the adventitia (subadventitial dissection) treatment for uti when pregnant amermycin 100 mg buy with visa, weakening the vessel wall and allowing the development of pseudoaneurysms or dissecting aneurysms. The micrograph of the extracranial portion of the right internal carotid artery (panels A, B and C) shows a dissection between the outer layer and the tunica media causing stenosis of the arterial lumen (L). Intramural hemorrhage (asterisk) extends almost completely around the artery (panel A) (van Gieson stain, 4x). At higher magnification, the internal carotid artery shows fragmentation of the elastic lamina (panel b) (van Gieson stain, 25x) with accumulation of a pale substance in the tunica media shown by the blue staining of mucopolysaccharides (panel C) (Alcian Blue, x25). These changes are consistent with the diagnosis of cystic necrosis of the tunica media [Schievink, 2001]. Compression on the true lumen decreases blood flow, with the consequent risk of cerebral hypoperfusion. Imaging studies obtained by nuclear magnetic resonance suggests that the pathophysiological mechanism that causes ischemia is, in most cases, thromboembolism. It has been postulated that arterial dissection is a result of structural instability of the vessel wall. In addition, arterial dissection has been linked to other arterial diseases such as cystic necrosis of the lamina media and Moyamoya disease. Other risk factors are migraine, recent infection, pregnancy, hyperhomocysteinemia, smoking, hypertension, and use of oral contraceptives. The clinical presentation is variable but is most often accompanied by ipsilateral or widespread neck pain, facial pain or headache which may precede the occurrence of stroke for days or weeks. Subintimal dissections usually cause transient ischemic attack or stroke; the clinical presentation depends on the infarcted area but most patients present with amaurosis fugax, hemiparesis, or hemiparesthesia. Vertebral dissections usually present with pain located in the neck, occipital region, or trapezius muscle; the pain can also radiate down the arm simulating a radicular neuralgia. The most common presentation is Wallenberg syndrome, which is caused by ischemia in the posterior inferior cerebellar artery territory. The latter is rarely transient and evolves in to infarction more often than in extracranial dissections. The diagnosis of arterial dissection has historically been based on radiographic findings obtained from digital cerebral angiography. Other typical angiographic findings are arterial dilation in the proximal or distal to the dissection, double lumen, intramural or intraluminal clot formation, and dissecting aneurysm. Conventional catheter angiography showing carotid dissection with reduction of the calibre of the internal carotid artery with its distal end forming a "scarf" (A), followed by a long, thin column of contrast material forming the "string sign" (B). The intensity of the hematoma on T1- and T2-weighted sequences depends on the age of the dissection. In comparison, vertebral artery dissections most commonly affect the poserioinferior cerebellar artery territory. Finally, Doppler ultrasound of the carotid and transcranial Doppler ultrasound are useful in evaluating patients with suspected arterial dissection. Doppler ultrasound image of the retrograde flow and bidirectional flow in carotid artery in a patient with arterial dissection.
The neurons transmit information through a dense and articulated network across synapses where the impulse is mediated by neurotransmitters virus hunters of the cdc amermycin 200 mg buy cheap. The glia is a heterogeneous tissue that primarily provides physical support for neurons. Unlike neurons, glial cells can divide and reproduce, so that they can take its place when a neuron dies. There are four types of neuroglial cells: oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, microglia, and ependymal cells. Oligodendrocytes have a small number of prolongations and a small cellular body (the nucleus occupies the greatest part). Satellite oligodendrocytes are other types of oligodendrocytes and are mainly found in the sensory and autonomic ganglia. Ependymal cells line the ventricular cavities of the brain and the central canal of the spinal cord. Their functions include biochemical support of the endothelial cells forming the blood-brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of the extracellular ion balance, and repair and scarring processes of the brain and spinal cord following traumatic injury. They have many ramifications and prolongations, known as podocytes, that surround the capillaries. They are vey important because they are thought to aid in the maintenance of the blood-brain barrier, forming high specialised regions that control the transport of glucose, oxygen, hormones and other substances essential for the nervous tissue. The former are found in the grey matter, possess a larger quantity of organelles, and exhibit short and highly branched cellular processes. The latter are predominantly located within the white matter, have relatively few organelles, and exhibit long unbranched cellular processes. Astrocytes also envelope the neuronal synapses, forming a sort of network, thus regulating the ion concentration in the extracellular space. They play a key role during embryonic development and in the secretion of growth factors which contribute to neuronal maturation and the survival of glial cells as a whole. When activated (like macrophages), they generate free oxygen radicals, proinflammatory proteins and cytokines such as interleukin 1 and tumour-like necrosis factor which can become detrimental for the nervous system. It is formed by specialized endothelial cells that cover the cerebral vascular system. The cells of the endothelium are united to each other through narrow junctions similar to those that can be found between the endothelium and astrocytes.
Plant Protease Concentrate (Bromelain). Amermycin.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96862
Anterior: Superior mesenteric vessels bacteria chlamydia trachomatis cheap 200 mg amermycin with visa, where vein lies on the right side and artery on the left side. Sometimes, a piece of pancreatic tissue may encircle the 2nd part of duodenum, called annulus pancreas. At the right end of superior border of body of pancreas, there is presence of an elevation called tuber omentale. The main pancreatic duct receives in its course a number of smaller ducts open at right angles resembling herring bone pattern. Due to the hemopoietic activity of liver in fetal life and it occupies about 2/5th of the abdomen. On the inferior border of right lobe of liver, right to the fundus of gallbladder. Fossa for gallbladder (sometimes gall bladder has a mesentery in between the two layers of mesentery of gallbladder there is a bare area) vii. Pressure within the abdomen and which is maintained by the abdominal muscles tone c. It is a nonperitoneal triangular rough area on the posterior surface of the right lobe of the liver, which is directly contact with the inferior surface of the right dome of the diaphragm. What is the demarcating line between right and left lobe of liver physiologically On which lobe caudate and quadrate lobes occupies anatomically and physiologically Since the right lobe get more nutritious blood through the superior mesenteric vein, via the right branch of portal vein, so right lobe is greater than the left lobe. It is a transverse, nonperitoneal cleft or fissure on the inferior surface of the right lobe of the liver through which some structures are going in and coming out from the liver. What are the structures which passes through the porta hepatis with their arrangements Right and left branches of portal vein- going in (lymphatics run along with vein). Between inferior surface of right lobe of liver and anterior surface of right kidney there is a peritoneal pouch known as hepatorenal pouch of Morison. What is the amount of blood which passes through the portal vein and hepatic artery Total 1500 ml/minute of which 1200 ml/ minute by the portal vein and 300 ml/ minute by the hepatic artery. As the cecum with appendix belongs to the midgut and the common habitat of Entamoeba histolytica is in the cecum and their amoebulae may enters in to the right lobe through the superior mesenteric vein, via the right branch of portal vein and lodges in the right lobe, which causes amoebic liver abscess. It occupies whole of the right hypo chondrium, upper part of the epigastrium and left hypochondrium (up to the left midclavicular line). On the superior surface of the liver, there is an impression due to the weight of the heart. In fetal life, the left umbilical vein connects the umbilicus to the left branch of portal vein.
The central canal may continue in to the proximal part of the filum terminale of about 4 to 5 mm c antibiotic viruses discount 100 mg amermycin overnight delivery. Nuclei in Spinal Cord Nuclei in Anterior (Ventral) Gray Column or Horn the nuclei of anterior (ventral) column or horn are arranged in the following groups: 1. Medial group: It is present in whole length of the spinal cord and innervates the axial musculature of the body. Lateral group: Present only in the region of cervical and lumbar enlargements of the spinal cord. Anterolateral/ventrolateral: Supply in case of upper limbs to the muscles of the shoulder and arm and in case of lower limbs to the muscles of the gluteal region and thigh ii. Posterolateral/dorsolateral: Supply in case of upper limbs to the muscles of the forearm and in case of lower limbs to the muscles of the leg iii. Postposterolateral/retrodorsolateral: Supply in case of upper limbs the muscles of the hand and in case of lower limbs the muscles of the foot. Central group: It is present only in the upper cervical segments which are represented by the phrenic and accessory nuclei. Nuclei in Posterior (Dorsal) Gray Column or Horn Nuclei in posterior (dorsal) gray column or horn are arranged in the following groups: 1. Consists of thin layer of cells (neurons) present superficial to the substantia gelatinosa b. Nucleus proprius: It lies just deep to the substantia gelatinosa in whole extent of the spinal cord. It is also called the thoracic nucleus, situated on the medial side of the base b. They are divided in to ten laminae and numbered from the tip of the posterior horn to the ventral horn. Sensory receptors the peripheral ends of the afferent nerve fibers receive impulses called receptors. The white matter lies in the medial and ventral to the anterior gray columns forms the anterior funiculus. The white matter lies lateral to the anterior and posterior gray columns forms the lateral funiculus. The white matter medial to the dorsal gray columns some important descending tracts in the spinal cord. Pyramidal tracts Reticulospinal tract Tectospinal tract Vestibulospinal tract Olivospinal tract Rubrospinal tract Lateral corticospinal tract.
The difference was mainly due to the high number of perioperative strokes antimicrobial cleaner discount amermycin 200 mg overnight delivery, while during later follow-up there were no significant differences. The main criticism raised against this trial was the lack of experience of many of the operators, the use of different classes of stents and protective devices. It includes: a) risk factor assessment; b) cessation of harmful habits and unhealthy lifestyle (smoking, excessive alcohol intake, recreational drug use, sedentarism); c) diet (risk-profile specific) and weight loss; d) use of antiplatelet therapy; e) antihypertensives; and f) statins [144]. An important feature of medical treatment for carotid artery disease is that, exceptions aside, it helps prevent general vascular risk. Not only does it prevent stroke but also acute myocardial infarction, heart failure and peripheral vascular disease. Moreover, unlike endarterectomy or angioplasty (which are aimed to prevent mainly hemodynamic and arterio-arterial mechanisms), medical treatment reduces the risk of stroke across the entire spectrum of stroke subtypes and, apart from preventing carotid artery events, it also reduces small vessel and cardioembolic strokes. These studies proved that surgery plus best medical treatment initiated at randomization time and maintained during the follow-up period is superior to best medical treatment alone. Nonetheless, in the last 25 years medical treatment has evolved spectacularly with development of new drugs and the discovery of new properties for old ones. The relevance of this article, with its exceptional analysis of evolution and impact of best medical treatment on stroke rates in patients with asymptomatic carotid disease over the last 25 years justifies a detailed discussion of its results and most interesting findings. The most significant finding was evidence for a progressive reduction in the rate of cerebrovascular events in patients under best medical treatment included in hospital observational studies between 1985 and 2007: ipsilateral stroke -1. This occurred despite an increase in the prevalence of arterial hypertension (5%) and average patient age (5. If we also consider that best medical treatment is 3 to 8 times less expensive (another conclusion of this study) for stroke prevention, the balance certainly shifts toward the use of the first option. A randomized trial for this purpose would require a very large number of patients due to effectiveness parity between both therapeutic interventions. Therefore, the cost would be hard to justify, even more so when considering applicability obstacles or external validity. One way to shed light on this matter would be to create large multicentre registries. What we can certainly suggest is that the introduction of health policies aimed to optimize vascular prevention programs may have an enormous impact. Whatever the conclusion regarding this question, patients with symptomatic or asymptomatic carotid artery disease should be treated with the currently available best medical treatment. This phenomenon may be boosted by a reduction in the antiaggregant effect of aspirin during surgery [149].
J of Trauma 2008; 64: 872-5 584 A Different Point of View in Intracranial Hypertension Management: the Lund Therapy 18 solanum xanthocarpum antimicrobial activity 200 mg amermycin amex. Brain energy metabolism during controlled reduction of cerebral perfusion pressure in severe head injuries. A large, prospectively collected database study published in 1991 by Marmarou et al. After trauma, the traumatised brain is characterised by a marked pathophysiological heterogeneity: ischemic areas (cytotoxic edema) coexists with areas with blood-brain barrier disruptions (vasogenic edema), contusions, and normal brain parenchyma. Benzodiazepines, especially midazolam, are administered in combination with morphine or derivatives such as sufentanil. While they are particularly suitable in the neurological intensive care unit, they are unable to depress brain electrical activity even at high doses, present a long duration of action and a plateau effect. However, the potential risk with using propofol is the feared propofol infusion syndrome. This syndrome, characterized by multiorgan failure, has a high incidence in sepsis or septic shock, which are therefore contraindications to propofol administration. It is mandatory to stop propofol in case of metabolic acidosis (with or without lactates), hyperkalemia, renal insufficiency, rhabdomyolysis or triglyceride level >5 mmol/l [10]. The occurrence of refractory brain hypertension during the first days following the onset of head trauma often requires therapeutic escalation with such therapeutics as neuromuscular blockers, hypothermia and thiopental, all of which have a high potential to deteriorate lung status further through mechanical effects or direct immunosuppressive effects. The authors concluded that barbiturate therapy significantly improved clinical outcome on the assumption that their patients would have otherwise died. Continuous barbiturate infusion is also known to produce immunosuppression by inhibiting lymphocyte function [14], affecting neutrophil function and depressing humoral immune response through a decrease in immunoglobulin production [15]. The use of barbiturates is, by itself, a statistical predictor of an increased risk of pneumonia [11]. Such a decrease in cerebral blood volume also occurs when the mean arterial pressure is increased. It is likely that local pH rather than local carbon dioxide is the mediator of tone regulation. The mediator cascade that links extracellular pH to cerebral vascular tone is complex and interrelated, the final mediator being intracellular calcium. Acute hypocapnia significantly decreased PbrO2, indicating the risk of secondary ischemic damage during hyperventilation in severely head-injured patients. The most recent guidelines of the Joint Committee on Trauma and Critical Care of the American Association of Neurologic Surgeons indicate that aggressive or prophylactic hyperventilation must be avoided in patients with severe head trauma [19].
Peer, 48 years: It is a very heterogeneous disease; therefore, knowledge of its triggering mechanisms will aid in interpreting the manifestations of stroke correctly and to properly plan therapy and secondary prevention.
Falk, 62 years: It will also document the most common complications of three treatment options, i.
Dennis, 29 years: Due to the hemopoietic activity of liver in fetal life and it occupies about 2/5th of the abdomen.
Grim, 44 years: The outward proliferation of endodermal cells forms as solid buds, which are subsequently canalized to form tonsillar pits and crypts iii.
Rocko, 31 years: Injury to the centre can lead to thermoregulatory dysfunction and is generally associated with poor prognosis.
Wenzel, 37 years: Take a point 5 cm above the transpyloric plane and 2 cm right to the median plane ii.
References