
Elizabeth Jones, MT, ABHI (CHT), ASPT (CPT)
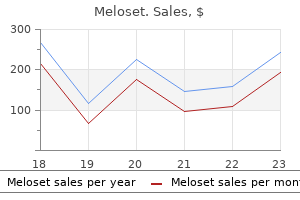
Meloset dosages: 3 mg
Meloset packs: 100 pills, 200 pills, 300 pills

Four transient fetal carotid basilar connections exist medicine lyrics generic meloset 3mg buy on line, which include (from superior to inferior) the trigeminal, otic, hypoglossal, and proatlantal intersegmental arteries. Aside from the proatlantal intersegmental artery, they are named for the cranial nerves they follow. The purpose of these transient connections is to supply blood to the hindbrain, diverting blood from the carotids to the posterior circulation while the developing vertebrobasilar systems begins to form. The posterior communicating arteries begin to develop when the embryo is 5 mm in size, which is approximately the same time the carotid basilar connections begin to disappear and the vertebrobasilar system begins to develop (with fusion of the paired dorsal longitudinal arteries, forming the basilar artery, and the longitudinal connections between the cervical intersegmental arteries, forming the vertebral arteries). The otic artery regresses first, followed by the hypoglossal, trigeminal, and proatlantal intersegmental arteries. In a small percentage of people, the carotid basilar connections fail to regress and persist into adulthood. These anastomoses are usually clinically insignificant; however, they have been associated with other neurovascular abnormalities, such as aneurysms, and sometimes can alter the management of neurointerventional and neurosurgical procedures. The trigeminal artery, which is the most common of these fetal connections to persist into adulthood, represents 85% of all persistent fetal anastomoses. When present, this vessel may have a parasellar course around the posterior clinoid process or may run through a canal through the bony dorsum sella (as described in the Spectrum of Disease section). The importance of the trigeminal artery lies in its association with other vascular anomalies. Aneurysms may arise from the trigeminal artery itself (in 2% of cases), but more commonly aneurysms may arise elsewhere within the cerebral circulation (reported in 14% to 32% of cases). This large percentage, however, is probably exaggerated because it was derived from a number of biased case studies that favored the inclusion of cerebral aneurysms in association with a trigeminal artery. Case reports also exist that link trigeminal arteries with the presence of arteriovenous malformations, brain tumors, moyamoya disease, facial hemangiomas, Dandy-Walker syndrome, Sturge-Weber syndrome, carotid-cavernous fistulas, cranial nerve symptoms such as tic douloureux, Congenital Arterial Anastomosis 419 and vascular anomalies such as hypoplastic/ aplastic posterior communicating arteries and vertebral arteries. The presence of an intrasellar trigeminal artery is crucial for presurgical planning of any transsphenoidal pituitary surgery. The remaining persistent fetal connections are less common than the persistent trigeminal artery. The hypoglossal artery, which is the next most prevalent, is seen in approximately 0. The proatlantal intersegmental artery arises more inferiorly than the hypoglossal artery, roughly around the C2-C3 level. The proatlantal intersegmental artery is classically differentiated from the hypoglossal artery because it passes much more posteriorly and horizontally than normally would be seen for a hypoglossal artery. It enters the skull base via the foramen magnum and typically anastomoses more proximally than the hypoglossal artery, around the horizontal portion of the vertebral artery. Although the proatlantal intersegmental artery is rare, with only about 40 cases reported in the literature since 1999, it is important to take note of this particular fetal connection for preinterventional and presurgical planning purposes and because of its reported association with aneurysms. The otic artery is the most rare fetal connection to persist into adulthood, with only a handful of cases reported in the literature.
Brain abscesses are usually of hematogenic origin and located in the deep white matter treatment ind buy meloset 3mg on line. The role of diffusion-weighted imaging in the differential diagnosis of intracranial cystic mass lesions: a report of 147 lesions. Cerebral abscesses and necrotic cerebral tumours: differential diagnosis by perfusionweighted magnetic resonance imaging. Role of diffusion weighted imaging in differentiation of intracranial tuberculoma and tuberculous abscess from cysticercus granulomas-a report of more than 100 lesions. Importance Prompt diagnosis of brain abscess allows prompt treatment, which can be life-saving and negates expensive and timeconsuming work-up for metastatic and primary tumors. Typical clinical scenario Acute-onset seizure or focal neurologic deficits are the most common presenting symptoms. Recent history of dental procedures, endocarditis, sinonasal and otologic infections may be present. Solitary lesions may also occur, and these require a broader differential diagnosis. Imaging description the imaging spectrum of neurocysticercosis is broad, which may create challenges in differential diagnosis. Enhancement becomes more nodular, and cysts get smaller or transform into small nodules, which may start showing calcification. Extraparenchymal neurocysticercosis may present as (1) intraventricular cysts or (2) subarachnoid cysts. Cysts are most commonly found in the fourth ventricle but they may move within the ventricles. Subarachnoid cysts usually present with a completely degenerated and therefore invisible scolex and form clusters of poorly visible cysts (racemose form), typically in the basilar cisterns. Typically there are multiple parenchymal lesions found in cortical locations, but basal ganglia and cerebellar lesions may occur as well. Lesions may be in the same or Importance Cysticercosis is the most common parasitic disease worldwide, and it continues to be a significant problem in developed countries, partly because of immigration and travel, although approximately one-third of neurocysticercosis cases seen in developed countries occur in individuals with no history of travel. Typical clinical scenario the most common clinical manifestation of neurocysticercosis is seizure. Obstructive hydrocephalus, intracranial hypertension, focal neurologic signs, and cerebral infarction may also occur. An acute encephalitis-like presentation has been described in the pediatric population. Differential diagnosis When multiple lesions in different stages of evolution are found the diagnosis is straightforward. Multiple or single ring-enhancing lesions of the colloidal vesicular stage and nodular enhancing lesions of the granular nodular stage require differential diagnosis from abscesses and metastases. Teaching points Neurocysticercosis may be parenchymal and/or extraparenchymal, and multiple lesions may present at the same or different stages of disease.
Sunburned shoulders are an example of normal symptoms neck pain buy meloset 3 mg lowest price, adaptive central sensitization not due to direct nerve injury, and anyone experiencing this will recall features of warm and pressure allodynia as they stood in a shower, for example. Under normal circumstances, this is a temporary phenomenon that may resolve as tissues heal. In some circumstances, however, either affected tissues fail to heal or the mechanisms evolve and, despite tissue healing, neuronal hyperexcitability persists, thus pain is no longer coupled to ongoing tissue damage. Documentation of this phenomenon is clinically important to provide (to patients, their family, insurance companies, and the courts), in the differential diagnosis, a physiological basis that may explain some of their symptoms. Diagnosis of peripheral sensitization relies on a history that has features consistent with neuropathic pain. Research has demonstrated some clinical findings that characterize plasticity at different levels or by different mechanisms but it can be difficult to impossible to separate peripheral from central mechanisms. In some cases this is because both mechanisms contribute to a particular clinical finding. For example, abnormally increased pain following a noxious cold stimulus (cold hyperalgesia) is mediated by peripheral sensitization in addition to reduced inhibition and central sensitization. In other cases peripheral input may be driving central sensitization so both will be present. Clinically, especially in the setting of a brief bedside examination, it can be difficult to document findings that would allow distinction between these two mechanisms. The bedside examination should focus on simply documenting signs consistent with the presence of sensitization. Interpretation of these signs must take into account caveats described at the end of this chapter. Repeated brush strokes (tested as one per second for 10 seconds) that produce increasing pain with each stroke is a simple test to perform. Repeated brush strokes or pinpricks (tested as 1 per second for 10 seconds) that produce increasing pain with each stroke is a simple test to perform. Have the patient rate the pain intensity at the beginning and end of the ten strokes/pinpricks and compare to the normal side. Repeated painful stimuli, like a pinprick, normally results in a progressively facilitated discharge by neurons in the spinal cord and results in an augmented pain response so that following repetitive pinpricks the intensity of the pain rating at the end is graded higher than a single stimulus. An exaggerated response to this test, compared to the normal side, is consistent with sensitization.
Rapid synaptic remodeling in the adult somatosensory cortex following peripheral nerve injury and its association with neuropathic pain moroccanoil treatment order meloset 3mg visa. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: amelioration of pain with transcutaneous electrostimulation. Acupuncture for the treatment of chronic painful peripheral diabetic neuropathy: a long-term study. Relief of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy with pregabalin: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Pregabalin for the treatment of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Sodium valproate for painful diabetic neuropathy: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study. Efficacy of pregabalin for peripheral neuropathic pain: results of an 8-week, flexible-dose, double-blind, placebo-controlled study conducted in China. Efficacy and safety of pregabalin for treating neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a 14 week, randomized, double-blind, 116 Chapter 9: Diabetic and other peripheral neuropathies placebo-controlled trial. Amitriptyline relieves diabetic neuropathy pain in patients with normal or depressed mood. A double-blind, randomized multicenter trial comparing duloxetine with placebo in the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Duloxetine for patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain: a 6-month open-label safety study. Mechanisms of neuropathic pain and their implications for the design of clinical trials. A comparative evaluation of amitriptyline and duloxetine in painful diabetic neuropathy: a randomized, double-blind, crossover clinical trial. Superiority of duloxetine to placebo in improving diabetic neuropathic pain: results of a randomized controlled trial in Japan. Advances in neuropathic pain: diagnosis, mechanisms, and treatment recommendations. A comparison of amitriptyline and nortriptyline in neuropathic pain due to peripheral neuropathy. An openlabel, non-randomized comparison of venlafaxine and gabapentin as monotherapy or adjuvant therapy in the management of neuropathic pain in patients with peripheral neuropathy. Venlafaxine extendedrelease in patients older than 80 years with depressive syndrome. Oxcarbazepine in painful diabetic neuropathy: a randomized, placebo-controlled study.

Diseases
Common feeding vessels at angiography include the internal maxillary artery and ascending pharyngeal artery symptoms upper respiratory infection purchase 3 mg meloset, with variable internal carotid artery supply. InvertingPapilloma An inverting papilloma arises in either the nasal cavity (~20% isolated) or maxillary 356 Head and Neck sinus (from which it may extend into the nasal cavity). It may exhibit calcifications (up to 50%), with up to two thirds of these relating to entrapped fragments of conchal bone. SquamousCellCarcinoma information and imaging characteristics are virtually pathognomonic. Biopsies of these lesions should be performed with caution because of the high risk of hemorrhage. OlfactoryNeuroblastoma Inverting papillomas tend to appear in middle-aged to elderly men (~20% female) with nonspecific sinonasal symptoms. SquamousCellCarcinoma Olfactory neuroblastoma is also known as esthesioneuroblastoma. Location in the upper nasal cavity is a helpful diagnostic feature because this tumor arises from olfactory epithelium. A more locally advanced tumor typically demonstrates a dumbbell shape, with an intracranial component and a "waist" at the cribriform plate. Marginal cysts within the intracranial component are highly suggestive of this diagnosis. OlfactoryNeuroblastoma Imaging features of a nasal septal perforation are nonspecific, although an enhancing soft tissue component raises suspicion for malignancy. Olfactory neuroblastoma appears in persons with a broad age range, with bimodal distribution (second and sixth decades). Lesions affecting the gland often arise from salivary, lymphoid, or neural tissue within the gland. Pleomorphic adenomas, also known as benign mixed tumors, are the most common neoplasms of the parotid, accounting for approximately 70% of lesions. Lesions are twice as common in women and occur most commonly in the superficial lobe of the parotid gland. Tumors are composed of solid, glandular, or ductal elements and often have a hyperintense signal on T2-weighted images as a result of an internal myxoid matrix. The border can have a slightly undulating margin, which has been referred to as "bosselated. Care must be taken during surgical removal because inadvertent tumor spillage from a tear of the pseudocapsule can result in a multinodular recurrence. Perineural spread along the auriculotemporal nerve toward V3 and foramen ovale or along the facial nerve toward or into the temporal bone indicates malignancy. However, a smoothly marginated solitary mass also can be malignant, particularly a low-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma. Warthin tumors are the second most common benign parotid tumor, representing 10% to 25% of lesions.
Chronic invasive fungal sinusitis is common in patients with diabetes and is associated with adjoining soft tissue invasion symptoms hypothyroidism buy cheap meloset 3mg on-line. Radiologically, benign paranasal sinus masses such as inverted papilloma, sinonasal polyposis, mucoceles, and ossifying fibroma should be ruled out. An expansile mass with osseous periphery and soft tissue fibrous center is seen in ossifying fibroma. Inverted papilloma arises in the middle meatus with secondary involvement of maxillary sinus, is usually non-calcified, and results in bony remodeling. In allergic fungal sinusitis, central highdensity material is surrounded by a low-attenuating rim of thickened mucosa. Invasion of the retroantral fat, maxillary ridge, and adjoining orbital structures can also be seen and may mimic more aggressive disease processes. Imaging description the spectrum of chronic sinusitis is wide and includes diverse etiologies such as pyogenic, allergic, and fungal. This is generally seen in immunocompetent, non-diabetic, and otherwise healthy populations. Importance the clinical spectrum of chronic rhinosinusitis represents diverse etiologies. Making the correct diagnosis of allergic fungal sinusitis allows for more accurate treatment options for this condition, including surgical resection and debridement. Typical clinical scenario the presence of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal discharge and congestion, headaches, fever, and facial pain and pressure is common. Involvement of frontal sinus results in headache of forehead and supraorbital region. In severe cases with bony remodeling and orbital complications, facial deformity, proptosis, and diplopia can be seen. Differential diagnosis the clinical spectrum of rhinosinusitis includes acute sinusitis, chronic purulent sinusitis, aspergilloma, and invasive fungal sinusitis. There is remodeling of the posterior wall of the right maxillary sinus, extending into the retroantral pad of fat (short arrow). There is erosion of right lamina papyracea with extension of the mass into the medial orbital cavity (short arrow). The signal intensities of right maxillary fungal infection (arrow) and left maxillary air appear almost similar. Soft tissue density with polypoid outline contains areas of high attenuation that likely represents inspissated mucus.
Agents that block the action of Ach at muscarinic receptors anticholinergic have more therapeutic applicasyndrome medicine vile order 3 mg meloset, 219 tions than those that block nicobelladonna, 218 tinic receptors. These drugs are curare, 226 known by a number of names, ganglionic including anticholinergics, choblockers, 218 linergic blockers, muscarinic malignant antagonists, and parasympathohyperthermia, 225 lytics. Although the term anticholinergic is commonly used in motor end plate, 223 clinical practice, the most accumuscarinic rate term for this group of drugs antagonists, 217 is muscarinic antagonists. This is neuromuscular because these drugs are selective blockers, 218 for Ach muscarinic receptors at nicotinic therapeutic doses and have little antagonists, 217 effect on nicotinic receptors. Because Ach is prevented from binding to its receptors, parasympathetic responses are diminished at the neuroeffector organs. Muscarinic antagonists block cholinergic receptors in the parasympathetic nervous system. Nicotinic antagonists block cholinergic receptors at ganglia, or in the somatic nervous system at the neuromuscular junction. Most therapeutic uses of the muscarinic antagonists are predictable extensions of their parasympathetic-blocking actions: dilation of the pupil, increase in heart rate, drying of secretions, and bronchodilation. Note that these are the same symptoms as fight-or-flight sympathetic activation; thus blocking the parasympathetic division causes actions similar to those that result when activating the sympathetic division. Their actions are also opposite those of the cholinergic agonists discussed in Chapter 17. Ganglionic blockers inhibit transmission at the ganglia in the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, thus affecting both autonomic divisions. Neuromuscular blockers do not act on the autonomic nervous system at all but instead inhibit transmission at the neuromuscular junctions on skeletal muscles in the somatic nervous system. The therapeutic uses of nicotinic antagonists are more limited than those of muscarinic antagonists due to their widespread and diverse actions on body function. Anticholinergics are very old drugs that have been used for a large number of disorders over many centuries. The deadly nightshade plant, Atropa belladonna, grows throughout the world and has been a natural source of alkaloids with anticholinergic activity. References to the use of belladonna date back to the ancient Hindus, the Roman Empire, and the Middle Ages. Because of its extreme toxicity, extracts of belladonna were sometimes used for intentional poisoning, including suicide. Although once widely prescribed, the development of safer and more effective medications has greatly decreased the current usage of muscarinic antagonists. Muscarinic antagonists suppress the secretion of gastric acid and can be used to treat peptic ulcer disease (see Chapter 62). Topical application of muscarinic antagonists to the eye causes pupil dilation (mydriasis) and paralysis of accommodation (cycloplegia), actions that are beneficial during ophthalmic examinations (see Chapter 77).
However treatment 6 month old cough meloset 3 mg low price, if the patient has signs of nerve root compression on exam, or severe radicular pain, further imaging is indicated. Magnetic resonance imaging is the preferred imaging modality but is not always easily accessible. Therefore, the imaging findings must be correlated with the history and examination findings. Nerve block A diagnostic block is used when clinical and radiographic studies are equivocal; a good response to nerve root block indicates that a particular nerve root is the source of the symptoms. Nerve conduction studies Nerve conduction studies are used to localize the lesion, for example, an ulnar neuropathy vs. Spontaneous resolution of herniated disc material has been well documented in serial imaging studies [13]. Patients should be counseled that a pain reduction of 30% represents a meaningful benefit. Patients should be advised to avoid positions and activities (for example, neck extension, high impact activity) that increase the symptoms. Physical therapy, and a gentle stretching and strengthening program commenced once the symptoms begin to improve can be beneficial. Mechanical traction may provide temporary symptom relief but has not been demonstrated to provide durable benefit. However, there is little good quality evidence showing benefit of spinal manipulation for radiculopathy; spinal manipulation is not recommended in patients with neurologic deficit, due to risk of further disc herniation [16]. An ergonomic assessment and education regarding correct lifting techniques may help prevent recurrent episodes of radicular pain. Studies show mixed results for nerve root blocks, but in some cases pain relief lasts for 6 weeks to several months [17,18]. Steroids with or without local anesthetic are injected under fluoroscopic guidance. Contraindications to epidural or selective nerve root blocks include coagulopathy, local or systemic infection, and allergy to injected material. The use of fluoroscopy allows accurate needle placement and may minimize complications. Complications include direct trauma to the nerve or damage to the neural vasculature, infection, or allergic reactions [19]. Significant or progressive motor deficit Intractable pain that has not responded to conservative measures Signs of an associated myelopathy on exam (spasticity, hyper-reflexia, upgoing toes) Signs/symptoms of cauda equina syndrome (numbness over the buttocks, bowel or bladder involvement, bilateral limb findings in the legs) (Table 11. Surgical treatment consists of nerve decompression with or without fusion of the disc space segment. Discectomy and laminectomy are common surgical procedures but the efficacy of surgical intervention relative to non-operative care remains controversial in mild/moderate cases. Limited evidence from both epidemiologic studies and several prospective studies on operative compared with nonoperative management of lumbar and cervical disc disease, suggests that pain and neurologic symptoms resolve faster with surgery, but that over time most patients improve and have a good prognosis regardless of treatment.
Lisk, 51 years: It is composed of basisphenoid and basiocciput and thus forms an important boundary of the posterior skull base, but is easily accessible from the middle skull base.
Yespas, 58 years: The health care provider prescribes epinephrine (adrenalin) to a client who was stung by several wasps 30 minutes ago.
Navaras, 22 years: In an adult, metastases and infection are the two most common causes of vertebra plana.
Denpok, 60 years: Clearly, from the standpoint of mechanism of action, we are in a better position to explain how cannabinoid drugs work, and therefore the reason for their beneficial as well as their adverse effects.
Ismael, 53 years: Meningiomas generally present in the fifth and sixth decades and are seen more often in female patients.
References