
Alison Suzanne Clay, MD

https://medicine.duke.edu/faculty/alison-suzanne-clay-md
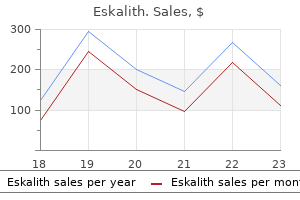
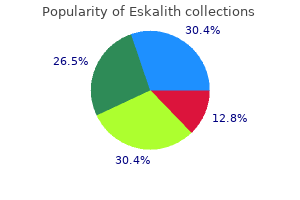
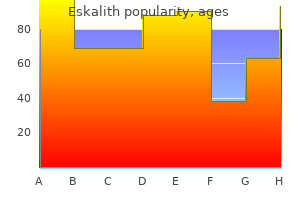
Eskalith dosages: 300 mg
Eskalith packs: 90 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills
Medial compartment of femoral sheath is the femoral canal occupied by a lymph node while the lateral compartment is occupied by the femoral artery depression symptoms hallucinations cheap eskalith 300 mg online. Give a vertical incision in the deep fascia of thigh from tubercle of iliac crest till the lateral condyle of femur and remove the deep fascia or fascia lata in lateral part of thigh. This will expose the tensor fasciae latae muscle and gluteus maximus muscle getting attached to iliotibial tract. Identify the sartorius muscle stretching gently across the thigh from lateral to medial side and the adductor longus muscle extending from medial side of thigh towards lateral side into the femur, being crossed by the sartorius. This triangular depression in the upper one-third of thigh is the femoral triangle. The medial border of sartorius forms lateral boundary and medial border of adductor longus forms medial boundary. Expose the sartorius muscle till its insertion into the upper medial surface of shaft of tibia. The apex, which is directed downwards, is formed by the point where the medial and lateral boundaries cross. Superficial fascia containing the superficial inguinal lymph nodes, the femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve, branches of the ilioinguinal nerve, superficial branches of the femoral artery with accompanying veins, and the upper part of the great saphenous vein. The vein is medial to the artery at base of triangle, but posteromedial to artery at the apex. The femoral vein receives the great saphenous vein, circumflex veins and veins corresponding to the branches of femoral artery. The femoral nerve lies lateral to the femoral artery, outside the femoral sheath, in the groove between the iliacus and the psoas major muscles. The nerve to the pectineus arises from the femoral nerve just above the inguinal ligament. The femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve occupies the lateral compartment of the femoral sheath along with the femoral artery. The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh crosses the lateral angle of the triangle. Runs on the lateral side of thigh and ends by dividing into anterior and posterior branches. These supply anterolateral aspect of front of thigh and lateral aspect of gluteal region respectively. The sheath is formed by downward extension of two layers of the fascia of the abdomen. Section 1 Femoral Canal Lower Limb and receive lymph from superficial inguinal lymph nodes, from glans penis or clitoris and deep lymphatics of lower limb.
Syndromes
In most cases of sympathetic terminals depression vs bipolar discount 300mg eskalith, these vesicles contain adrenaline or noradrenaline. The whole of nervous system develops from ectoderm except the blood vessels and the microglia (neuroglial tissue). At the beginning of 3rd week of development, the ectodermal germ layer has the shape of a flat disc that is broader in cephalic region than in the caudal region. With the appearance of the notochord and its inductive influence, ectoderm overlying the notochord thickens to form a slipper-shaped plate, called neural plate. Cells of the plate make-up neuroectoderm and with induction, the process of neurulation starts. With further development, the neural groove between the two folds on either side becomes deeper. Eventually, the neural folds approach each other in midline and finally fuse, thus forming the neural tube. At the most cranial and caudal ends of the embryo, fusion is delayed and the cranial and caudal neuropores temporarily form open connections between the base of neural tube and the amniotic cavity. Final closure of cranial neuropore occurs on 25th day and caudal neuropore two days later of the embryonic life, and eventually neuropores disappear leading to a closed tube. Before the neural tube is completely closed, it is divisible into an enlarged cranial part with three divisions which forms brain and a caudal tubular part which forms spinal cord. Further Development of the Brain Prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon are first arranged cephalocaudally. Cephalic or mesencephalic flexure: this flexure is located in the region of midbrain. Pontine flexure: When the embryo is 5 weeks old, the prosencephalon consists of two lateral outpocketings-the primitive cerebral hemispheres. This is called pontine flexure, and it divides rhombencephalon into metencephalon and myelencephalon. The lumen of the spinal cord, the central canal is continuous with that of primitive brain vesicles. The cavity of rhombencephalon is known as fourth ventricle, those of cerebral hemisphere are lateral ventricles and cavity of diencephalon is third ventricle. Cavity of lateral ventricles communicates with that of third ventricle through interventricular foramen of Monro. Neural Crest Cells and their Derivatives During folding of the neural tube, a group of cells are formed along each side of neural groove and after the formation of neural tube, lie between the surface ectoderm and neural tube. These cells (ectodermal in origin) migrate laterally, and are called neural crest cells.
The majority are free-living organisms growing on dead or decaying matter whose prime function is the turnover of organic materials in the environment bipolar depression symptoms in women eskalith 300 mg buy. Pharmaceutical microbiology, however, is concerned with the relatively small group of biological agents that cause human disease, spoil prepared medicines or can be used to produce compounds of medical interest. In order to understand microorganisms more fully, living organisms of similar characteristics have been grouped together into taxonomic units. The most fundamental division is between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, which differ in a number of respects (Table 13. Eukaryotic cells contain chromosomes, which are separate from the cytoplasm and contained within a limiting nuclear membrane, i. Possess a true nucleus Present More than 1 Present Absent 80S is free within the cytoplasm, although it may be aggregated into discrete areas called nuclear bodies. Prokaryotic organisms make up the lower forms of life and include Eubacteria and Archaeobacteria. Eukaryotic cell types embrace all the higher forms of life, of which only the fungi will be dealt with in this chapter. One characteristic shared by all microorganisms is the fact that they are small; however, it is a philosophical argument whether all infectious agents can be regarded as living. Some are little more than simple chemical entities incapable of any free-living existence. One particularly well-studied viroid has only 359 nucleotides (1/10 the size of the smallest known virus) and yet causes a disease in potatoes. Viruses are more complex than viroids or prions, possessing both protein and nucleic acid. Despite being among the most dangerous infectious agents known, they are still not regarded as living. They are thus incapable of leading an independent existence and cannot be cultivated on cell-free media, no matter how nutritious. The size of human viruses ranges from the largest poxviruses, measuring approximately 300 nm, to the picornaviruses, such as poliovirus, which is approximately 20 nm. When one considers that a bacterial coccus measures 1000 nm in diameter, it can be appreciated that only the very largest virus particles may be seen under the light microscope, and electron microscopy is required for visualizing the majority. It will also be apparent that few of these viruses are large enough to be retained on the 200 nm (0. The protein capsid constitutes 50% to 90% of the weight of the virus and, as nucleic acid can only synthesize approximately 10% its own weight of protein, the capsid must be made up of a number of identical protein molecules. These individual protein units are called capsomeres and are not in themselves symmetrical but are arranged around the nucleic acid core in characteristic symmetrical patterns. Additionally, many of the larger viruses possess a lipoprotein envelope surrounding the capsid arising from the membranes within the host cell.
If the obstruction is in the third ventricle anxiety 029 cheap eskalith 300 mg mastercard, both the lateral ventricles are dilated symmetrically. Obstruction at an interventricular foramen causes unilateral dilatation of the lateral ventricle of that side. Now try to separate the frontal lobe from the temporal lobe, and open up the stem of the lateral sulcus. Put the knife in the anterior part of stem of the lateral sulcus and extend the incision medially to the inferior part of stem of the lateral sulcus. Keep on opening the cut while making it and identify the choroid plexus entering the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle from its medial side. Now brain is easily separable into an upper frontal part and a lower occipitotemporal part. Identify structures in all horns of lateral ventricle with the help of the two parts, i. Expose the anterior column of fornix by scraping the ependyma of anterior part of third ventricle. Trace another bundle, the mammillothalamic tract till the anterior nucleus of the thalamus. It starts at the interventricular foramen (above and in front) and passes around the thalamus and cerebral peduncle to the uncus (in the temporal lobe). Thus, it is present only in relation to the central part and inferior horn of the lateral ventricle. At the fissure, the pia mater and ependyma come into contact with each other and both are invaginated into the ventricle by the choroid plexus. Medial 1 Septum pellucidum 2 Column of fornix Posterior Horn this is the part of the lateral ventricle which lies in front of the interventricular foramen and extends into the frontal lobe. This is the part of the lateral ventricle which lies behind the splenium of the corpus callosum and extends into the occipital lobe. Boundaries Floor and medial wall 1 Bulb of the posterior horn raised by the forceps major. These parts represent the phylogenetically older areas of the cortex (archipallium and paleopallium) which have been grouped in the past with the rhinencephalon and were earlier considered to be predominantly olfactory in function. However, their important role in controlling the behaviour patterns is now increasingly realized. Structures comprising limbic system form a ring along medial wall of cerebral hemisphere. Limbic structures process and monitor emotional aspects of experience and direct emotional responses. These aid in understanding the behavioural consequences of our deeds with the help of frontal lobe. Lesions of limbic system cause disturbances of motivation, memory and emotions as occur in schizophrenia. In the inferior horn, the line of ependymal invagination by the choroid plexus.
Once removed mood disorder undiagnosed 300mg eskalith order with amex, the surfactant can be adsorbed at the particle surface, creating charge and hydration barriers which prevent deposition. Solubilization and drug stability Solubilization has been shown to have a modifying effect on the rate of hydrolysis of drugs. Nonpolar compounds solubilized deep in the hydrocarbon core of a micelle are likely to be better protected against attack by hydrolysing species than more polar compounds located closer to the micellar surface. For example, the alkaline hydrolysis of benzocaine and homatropine in the presence of several nonionic surfactants is retarded, the less polar benzocaine showing a greater increase in stability compared to homatropine because of its deeper penetration into the micelle. The large surface area of the dispersed drug ensures a high availability for dissolution and hence absorption. Aqueous suspensions may also be used for parenteral and ophthalmic use and provide a suitable form for the application of dermatological materials to the skin. Suspensions are used similarly in veterinary practice, and a closely allied field is that of pest control. Pesticides are frequently presented as suspensions for use as fungicides, insecticides, ascaricides and herbicides. An acceptable suspension possesses certain desirable qualities, amongst which are the following: the suspended material should not settle too rapidly; the particles which do settle to the bottom of the container must not form a hard mass but should be readily dispersed into a uniform mixture when the container is shaken; and the suspension must not be too viscous to pour freely from the orifice of the bottle or to flow through a syringe needle. Physical stability of a pharmaceutical suspension may be defined as the condition in which the particles do not aggregate and in which they remain uniformly distributed throughout the dispersion. Since this ideal situation is seldom realized, it is appropriate to add that if the particles do settle, they should be easily resuspended by a moderate amount of agitation. The major difference between a pharmaceutical suspension and a colloidal dispersion is one of the size of the dispersed particles, with the relatively large particles of a suspension liable to sedimentation due to gravitational forces. The reader is referred to Chapter 26 for an account of the formulation of suspensions. However, with pharmaceutical suspensions, in which the solid particles are very much coarser, such a system would sediment because of the size of the particles. The electrical repulsive forces between the particles allow the particles to slip past one another to form a close-packed arrangement at the bottom of the container, with the small particles filling the voids between the larger ones. The supernatant liquid may remain cloudy after sedimentation due to the presence of colloidal particles that will remain dispersed. Those particles lowermost in the sediment are gradually pressed together by the weight of the ones above. The repulsive barrier is thus overcome, allowing the particles to pack closely together.
Argousier (Sea Buckthorn). Eskalith.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96747
At the anterior superior iliac spine depression symptoms not sleeping buy eskalith 300mg otc, it anastomoses with the superior gluteal, the lateral circumflex femoral and superficial circumflex iliac arteries. Just behind the anterior superior iliac spine, it gives off an ascending branch which runs upwards in the neurovascular plane. Posterior wall: It is deficient; the rectus muscle rests directly on the 5th, 6th and 7th costal cartilages. Between the costal margin and the arcuate line Anterior wall: External oblique aponeurosis and anterior lamina of the aponeurosis of the internal oblique. Midway between the umbilicus and the pubic symphysis, the posterior wall of the rectus sheath ends in the arcuate line or linea semicircularis or fold of Douglas. Below the arcuate line Anterior wall: Aponeuroses of all the three flat muscles of the abdomen. Abdomen and Pelvis Section Features Anterior Wall 1 It is complete, covering the muscle from end to end. Posterior Wall 1 It is incomplete, being deficient above the costal margin and below the arcuate line. Laterally, the anterior and posterior walls extend till linea semilunaris, which extends from tip of 9th costal cartilage to pubic tubercle. Contents Muscles Functions 1 It checks bowing of rectus muscle during its contraction and thus increases the efficiency of the muscle. Arteries Both leaves of external oblique aponeurosis and anterior leaf of internal oblique aponeurosis. Posterior Sheath 2 the inferior epigastric artery enters the sheath by passing in front of the arcuate line. Veins 1 the superior epigastric venae comitantes accompany its artery and join the vena comitantes of internal thoracic vein. Posterior leaf of aponeurosis of internal oblique and both leaves of aponeurosis of transversus abdominis. The three lateral abdominal muscles may be said to be digastric with a central tendon in the form of linea alba. Linea alba is a tendinous raphe between xiphoid process above to symphysis pubis and pubic crest below. Superficial fibres of linea alba are attached to symphysis pubis, while deep fibres are attached behind rectus abdominis to posterior surface of pubic crest. Section 2 Abdomen and Pelvis 1 the superior epigastric artery enters the sheath by passing between the costal and xiphoid origins of the diaphragm. It crosses the upper border of the transversus abdominis behind the seventh costal cartilage. Rectus sheath is formed by decussating fibres from three abdominal muscles of each side.
The fibres cross to the opposite side thus forming dorsal tegmental decussation in midbrain depression on period discount eskalith 300 mg on line. The tract descends through pons, medulla and anterior white column of spinal cord. These facilitate/inhibit flexor/ extensor reflexes Injury leads to increased muscle tone with clasp knife rigidity central process of the neurons in the dorsal root ganglia enter the spinal cord through dorsal nerve root and terminate either by synapsing with cells in posterior grey column of spinal cord or at higher level in the medulla oblongata with the cells of nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus. After relay in the nuclei, second neuron fibres start and ascend to either thalamus or cerebellum. The cerebellum finally receives second neurons fibres, whereas from the thalamus relayed third neuron fibres are projected to the sensory areas in the cerebral cortex (Table 3. The peripheral process of these cells form the sensory fibres of peripheral nerves. These lie in continuity with each other in the anterolateral white column of spinal cord showing somatotopic lamination. The sensations of pressure, touch, temperature and pain are lying medial to lateral. Proprioceptive Sensations the sensations like deep touch, pressure, tactile localisation (the ability to locate exactly the proprioceptive part touched), tactile discrimination (the ability to localise two separate points on the skin that is touched), stereognosis (ability to recognise shape of object held in hand) and sense of vibration are carried by fasciculus gracilis and fasciculus cuneatus. These run directly upwards (without relaying in the spinal grey matter) in the posterior column of white matter of spinal cord. The fibres which enter in the coccygeal and lower sacral region are thrust medially by fibres which enter at higher levels. These ascend in the lateral white column of spinal cord anterior to the the reflex proprioceptive sensations are carried by dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar tracts. They convey to the cerebellum both exteroceptive (touch) and unconscious proprioceptive impulses arising in Golgi tendon organ and muscle spindle and are essential for the control of posture (Table 3. This relay gives rise to second neuron fibres which form dorsal spinocerebellar tract. This uncrossed tract ascends in the lateral column of white matter of spinal cord. Here it is situated as a flattened band at the posterior region of lateral column, medially in contact with lateral corticospinal tract. Functionally, both spinocerebellar tracts control the coordination and movements of muscles controlling posture of the body. The ventral tract conveys muscle and joint information from the entire lower limb, while the dorsal tract receives information from individual muscles of lower limb (Table 3. These are present in anterior, posterior and lateral columns of white matter adjacent to the grey matter of spinal cord. The clinical features involve weakness, atrophy of muscles of hands and arms and later extending to the lower limb. Subacute combined degeneration: the posterior and lateral funiculi are degenerated bilaterally and it is caused due to deficiency of intrinsic factor which helps in absorption of vitamin B12.
Connections of Corpus Striatum 4 these do not receive any sensory input from spinal cord unlike the cerebellum depression test doctor best eskalith 300mg. Functions of Corpus Striatum 1 the corpus striatum regulates muscle tone and thus helps in smoothening voluntary movements. Similarly, it controls the coordinated movements of different parts of the body for emotional expression. This is a nuclear mass in the temporal lobe, lying anterosuperior to the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle. Topographically, it is continuous with the tail of the caudate nucleus, but functionally, it is related to the stria terminalis. It is continuous with the cortex of the uncus, the limen insulae and the anterior perforated substance. Efferents: It gives rise to the stria terminalis which ends in the anterior commissure, the anterior perforated substance and in hypothalamic nuclei. Substantia nigra Efferents Chiefly to globus pallidus, but also to substantia nigra and thalamus Efferents form three bundles, namely: 1. Subthalamic fasciculus from the middle part of the globus pallidus these bundles terminate in the following: 1. Chorea is form of involuntary movement characterised by fine random movements of hands and feet. The nigrostriate fibres are considered important in the genesis of parkinsonism tremor, since its neurons utilize dopamine in the neurotransmission. Neurosurgically, pallidectomy and thalamodectomy have been used with success to control the contralateral tremors in different types of disease of corpus striatum. The fibres are classified into three groups- association fibres, and commissural fibres and projection fibres. Some examples are: 1 the uncinate fasciculus, connecting the temporal pole to the motor speech area and to the orbital cortex. Scrape the grey matter of this gyrus till a band of white matter-the cingulum is exposed. Similarly scrape the cortex between temporal pole, motor speech area and the orbital cortex to expose uncinate fasciculus. Also expose superior longitudinal fasciculus joining the frontal lobe to the occipital and temporal lobes.
Thickened bands of superficial fascia stretch across the roots of the toes forming the superficial transverse metatarsal ligaments depression symptoms vision cheap 300 mg eskalith fast delivery. Identify the cutaneous branches from medial and lateral plantar arteries and nerves on the respective sides of plantar aponeurosis. Medial plantar nerve and vessels are easily visualised close to the medial border of sole. Stems of lateral plantar nerve and vessels including its superficial division are also seen. Plantar Aponeurosis Plantar aponeurosis represents the distal part of the plantaris which has become separated from the rest of the muscle during evolution because of the enlargement of the heel. It is attached to the medial tubercle of the calcaneum, proximal to the attachment of the flexor digitorum brevis. Each process splits, opposite the metatarsophalangeal joints, into a superficial and a deep slip. The deep slip divides into two parts which embrace the flexor tendons, and blend with the fibrous flexor sheaths and with the deep transverse metatarsal ligaments. From the margins of the aponeurosis, lateral and medial vertical intermuscular septa pass deeply, and divide the sole into three compartments. Thinner transverse septa arise from the vertical septa and divide the muscles of the sole into four layers. Functions 1 Lower Limb the deep fascia covering the sole is thick in the centre and thin at the sides. The plantar aponeurosis differs from the palmar aponeurosis in giving off an additional process to the great toe, which restricts the movements of the latter. Deep Transverse Metatarsal Ligaments these are four short, flat bands which connect the plantar ligaments of the adjoining metatarsophalangeal joints. They are related dorsally to the interossei, and ventrally to the lumbricals and the digital vessels and nerves. Muscles of Second Layer Section the contents of second layer are the tendons of the flexor digitorum longus, and of the flexor hallucis longus; and the flexor digitorum accessorius and lumbrical muscles. Identify and detach the abductor digiti minimi and identify the lateral head of the flexor digitorum accessorius till its insertion into the tendon of flexor digitorum longus. Trace the long flexor tendons through the fibrous flexor sheath into the base of distal phalanges of toes. Cut through both the long flexor tendons (flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus) and flexor digitorum accessorius where all the three are united to each other.
In superficial extravasation depression dsm 5 buy eskalith 300 mg low price, the urine spreads downwards deep to the membranous layer of the superficial fascia. It first fills the superficial perineal space; and then the scrotum, the penis and the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. Their outer surfaces are covered with hair, and the inner surfaces are studded with large sebaceous glands. The larger anterior ends are connected to each other below the mons pubis to form the anterior commissure. Labia Minora Labia minora are two thin folds of skin, which lie within the pudendal cleft. Anteriorly, each labium minus splits into two layers; the upper layer joins the corresponding layer of the opposite side to form the prepuce of the clitoris. Similarly, the lower layers of the two sides join to form the frenulum of the clitoris. Clitoris 3 Vaginal orifice or introitus lies in the posterior part of the vestibule, and is partly closed, in the virgin, by a thin membrane called the hymen. In married women, the hymen is represented by rounded tags of tissue called the carunculae hymenales. Bulbs of the Vestibule the clitoris is an erectile organ, homologous with the penis. The body of clitoris is made up of two corpora cavernosa enclosed in a fibrous sheath and partly separated by an incomplete pectiniform septum. The down-turned free end of clitoris is formed by a rounded tubercle, glans clitoridis, which caps the free ends of corpora. The glans is made up of erectile tissue continuous posteriorly with the commissural venous plexus uniting right and left bulbs of vestibule called bulbar commissure. The surface of glans is highly sensitive and plays an important role in sexual responses. The bulbs lie on either side of the vaginal and urethral orifices, superficial to the perineal membrane. The tapering anterior ends of the bulbs are united in front of the urethra by a venous plexus, called the bulbar commissure. The expanded posterior ends of the bulbs partly overlap the greater vestibular glands. Greater Vestibular Glands of Bartholin Greater vestibular glands are homologous with the bulbourethral glands of Cowper in the male. Each gland has a long duct about 2 cm long which opens at the side of the hymen, between the hymen and the labium minus. The superficial fatty layer is continuous with the superficial fascia of the surrounding regions. Anteriorly, it is continuous with the membranous layer of the superficial fascia of the anterior abdominal wall or fascia of Scarpa. Section the urogenital region is bounded by the interischial line which usually overlies the posterior border of the transverse perinei muscles.
Aila, 38 years: Identify and detach the abductor digiti minimi and identify the lateral head of the flexor digitorum accessorius till its insertion into the tendon of flexor digitorum longus. Other attractive forces contributing to interparticulate adhesion and cohesion may be produced by surface tension forces between adsorbed liquid layers at the particle surfaces and by electrostatic forces arising from contact or frictional charging. Trace the large grey rami communicantes from the ganglia to the ventral rami of the sacral nerves.
Lars, 31 years: Rotation � a small amount of rotation may be produced by the hamstrings when the knee is flexed. They drain the skin and fasciae of the lateral part of infraumbilical part of anterior abdominal wall, the buttock, the flank and the back below the umbilical plane. The dura is pierced by the ventral and dorsal nerve roots of the spinal nerves, but it ensheaths the nerves as far as the intervertebral foramina.
Vasco, 43 years: Section 2 Abdomen and Pelvis 1 the superior or pelvic surface is covered with pelvic fascia which separates it from the bladder, prostate, rectum and the peritoneum. Neck � Iliac crest is used for taking bone marrow biopsy in cases of anemia or leukemia. The aorticorenal ganglion gives off the renal plexus which accompanies the renal vessels.
Anktos, 46 years: The tendons of peroneus (fibularis) longus and brevis cross the joint posterolaterally. Within the medial angle of each eyelid is a pink elevation, the lacrimal caruncle. Sperms are present in the ejaculations after vasectomy for 2�3 months as it is an emptying process.
Runak, 40 years: The arcuate fasciculus connects the language areas in the frontal Superior fronto-occipital Short longitudinal fasciculus association bres and temporal lobes and is in close proximity to the superior longitudinal fasciculus. Examples of the importance of polymorphism with respect to the bioavailability of drugs are given in Chapter 20. In general, for poorly soluble materials there will be a correlation between the melting point of the different polymorphs and the rate of dissolution, because the one with the lowest melting point will most easily give up molecules to dissolve, whereas the most stable form (highest melting point) will not give up molecules to the solvent so readily.
Olivier, 34 years: So both the venous blood in the capillaries and air in the alveoli come close by in the lung tissue, separated by the lining of the alveoli. Bachofen, Muttenz, Switzerland) is a more sophisticated form of tumbling mixer which utilizes inversional motion in addition to the rotational and translational motion of traditional tumbling mixers. Sensory Fibres of Cerebellum the afferent connections of cerebellum are through mossy and climbing fibres.
Innostian, 39 years: One day after having a partial thyroidectomy, a patient is noted to have a weak, hoarse voice. In order to carry out measurements of critical orifice diameter, powder is filled into a shallow tray to a uniform depth with near-uniform packing. In the vast majority of cases, several ingredients are needed to ensure that the dosage form functions as required.
References