
Anthony J. Guarascio, PharmD, BCPS
https://www.duq.edu/assets/Documents/pharmacy/Faculty%20CVs/2017-18/Guarascio.pdf
Imitrex dosages: 100 mg, 50 mg, 25 mg
Imitrex packs: 10 pills, 20 pills, 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills

Grasp the lateral edges of the incision with Allis clamps and carefully dissect 1 to 2 cm laterally; you should be in a plane between the vaginal wall and the sling muscle relaxant equipment cheap imitrex 50 mg on-line. If there is no sign of the sling, one may have to extend the incision proximally or distally in case the sling has migrated. If one is still unable to identify the sling, then dissect further laterally under the pubis and attempt to palpate/identify the sling in that area. Some prefer to do this dissection lateral to the urethra to decrease the risk of urethral injury. In either case, it is important that the tip of the clamp be parallel to the urethra and the sling, and that the dissection by performed slowly and carefully to avoid inadvertent urethral injury. Once behind the sling, completely spread the right angle to expose a few centimeters of the sling. If the ends of the mesh seem as though they may interfere with closure of the vaginal wall, you can trim them. After direct visualization of the urethra, back the tip of the scope out to just proximal to the meatus and compress the meatus to examine the area of dissection and ensure there is no fluid leak. Postoperative Assuming there is no urethral injury, the patient should be asked to void in the recovery room and if successful can be discharged without a catheter. Intraoperative: Urethrolysis after Retropubic Colposuspension this can be done transvaginally as a urethrolysis- breaking through the endopelvic fascia and blindly trying to identify and cut the suspension suture- or retropubically. We will focus on the retropubic approach since there is literature to suggest that the retropubic approach may be more effective. Careful attention is paid to the location of the Foley catheter and balloon to avoid inadvertent bladder or urethral injury. In some cases, there is so much scarring that the bladder may be entered accidentally-if that occurs, place a finger in the bladder to help guide the rest of the dissection and repair the bladder injury after the urethrolysis is complete. It may also be useful to place a finger in the vagina to help guide the retropubic dissection. At the end of the dissection, the urethra, bladder neck, and anterior vaginal wall should be mobilized and freed from the pubic bone. Postoperative Anesthesia and Patient Positioning the patient is placed in a low lithotomy position so one can have access to both the lower abdomen and vagina. Incision-A Pfannenstiel or lower midline incision is made and the retropubic space is entered. Cut sutures and incise scar-Outlet obstruction is typically due to hypersuspension of the proximal urethra.
The profunda femoris vein (deep vein of thigh) spasms compilation cheap imitrex 100 mg without a prescription, formed by the union of three or four perforating veins, enters the femoral vein inferior to the inguinal ligament and inferior to the termination of the great saphenous vein. In approximately 20% of people, an enlarged pubic branch of the inferior epigastric artery either takes the place of the obturator artery (replaced obturator artery) or joins it as an accessory obturator artery. The obturator artery passes through the obturator foramen, enters the medial compartment of the thigh, and divides into anterior and posterior branches, which straddle the adductor brevis muscle. The obturator artery supplies the obturator externus, pectineus, adductors of thigh, and gracilis. Its posterior branch gives off an acetabular branch that supplies the head of the femur. It divides into anterior and posterior branches, which, like the vessels, straddle the adductor brevis. The anterior branch supplies the adductor longus, adductor brevis, gracilis, and pectineus; the posterior branch supplies the obturator externus and adductor magnus. It is helpful to think of the greater sciatic foramen as the "door" through which arteries and nerves leave the pelvis and enter the gluteal region, with veins coursing in the opposite direction. The parts of the bony pelvis-hip bones, sacrum, and coccyx-are bound together by gluteal ligaments. A femoral hernia is more common in women than in men (in whom inguinal hernias are more common). The hernial sac displaces the contents of the femoral canal and distends its wall. Initially, the hernia is relatively small because it is contained within the femoral canal, but it can enlarge by passing through the saphenous opening into the subcutaneous tissue of the thigh. Strangulation of a femoral hernia may occur and interfere with the blood supply to the herniated intestine, and vascular impairment may result in death of the tissues. Femoral Pulse and Cannulation of Femoral Artery the pulse of the femoral artery is usually palpable just inferior to the midpoint of the inguinal ligament. Normally, the pulse is strong; however, if the common or external iliac arteries are partially occluded, the pulse may be diminished. The femoral artery may be cannulated just inferior to the midpoint of the inguinal ligament. For left cardiac angiography, a long slender catheter is inserted percutaneously into the femoral artery and passed superiorly in the aorta to the openings of the coronary arteries (see Chapter 1). Femoral artery Pubic ramus Cannulation of Femoral Vein the femoral vein usually is not palpable; however, its position can be located by feeling the pulsations of the femoral artery, which lies just lateral to it. In thin people, the femoral vein may be close to the surface and may be mistaken for the great saphenous vein.
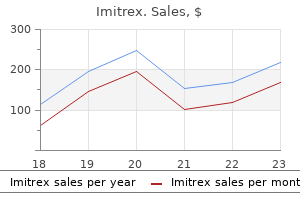
There are no longitudinal studies of patients with untreated primary bladder neck obstruction upon which to make an evidence-based recommendation about watchful waiting spasms 14 year old beagle order 50 mg imitrex free shipping. This was initially based on a study of 24 women with obstructive voiding symptoms or retention who were all initially placed on clean intermittent catheterization and -blocker therapy. After 8 weeks of treatment, patients also had an improvement in maximum flow rate (10. The principles of treatment are to maintain or restore low storage pressures and facilitate emptying. Antimuscarinic agents are the first-line therapy to treat neurogenic detrusor overactivity and/or impaired compliance. Because the most important outcome is lower storage pressures, this is actually a desired outcome and often ultimately results in resolution of incontinence with appropriate emptying. In cases where antimuscarinic agents fail to lower bladder pressure, consideration can be given to intradetrusor injection of botulinum toxin or even lower urinary tract reconstruction with bladder augmentation or urinary diversion. Indications may include severe detrusor overactivity, poor bladder compliance, or continued upper urinary tract deterioration despite aggressive conservative therapy. The duration of the effect of this therapy in this skeletal muscle is reported to range between 50 and 90 days. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Risk factors for developing voiding dysfunction after abdominoperineal resection for adenocarcinoma of the rectum. Vesical dysfunctions after radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer: a critical review. Lower urinary tract dysfunction as persistent complication of radical hysterectomy. Recent advances in understanding the biology of diabetesassociated bladder complications and novel therapy. Myogenic bladder decompensation in boys with a history of posterior urethral valves is caused by secondary bladder neck obstruction A comparison of spontaneous and nerve-mediated activity in bladder muscle from man, pig and rabbit. Effect of tamsulosin on spontaneous bladder contraction in conscious rats with bladder outlet obstruction: Comparison with effect on intraurethral pressure. Are female lower urinary tract symptoms alleviated by -adrenoreceptor antagonists An experimental study of urodynamic effects of epidural morphine and of naloxone reversal. Drug effects on urinary bladder tone during spinal morphine-induced inhibition of the micturition reflex in unanesthetized rats.
Large tears that involve more than 50% of the bowel wall spasms piriformis imitrex 100 mg buy, particularly when intraperitoneal or when associated with devascularization or significant thermal injury, will require rectosigmoid resection and primary anastomosis. Diverting colostomy should be considered in the presence of shock or sepsis, previous radiation, delayed recognition, and/or significant fecal contamination. Intraoperative If one is in doubt about the appropriate approach or one does not feel comfortable repairing a rectal injury, then the surgeon should obtain an intraoperative general surgery or colorectal surgery consult. Primary Repair of Proctotomy Most extraperitoneal injuries and intraperitoneal injuries that involve less than 50% of the bowel wall and are not devascularized or involve thermal injury or significant peritonitis can also be managed with primary closure. Isolate the site of injury with atraumatic clamps to prevent further spillage of bowel contents. Repair in proctotomy-Although single-layer closure has been described, we prefer a two-layered closure. The first layer of closure can be performed with simple interrupted sutures or a running suture of 3-0 absorbable suture material incorporating all layers. With rectum or colon injuries, the direction of closure is less critical than with small bowel injuries as narrowing of the rectal lumen is unlikely. A second layer consisting of interrupted longitudinal mattress stitches through the seromuscular layer using 2-0 or 3-0 delayed absorbable suture is performed. The integrity of the repair may be assessed via digital rectal examination, proctoscopy, or a "bubble test" as described above. Preoperative Consent Bowel injury is an uncommon but well-described complication of a wide range of gynecologic and pelvic reconstructive procedures. The possibility of an injury to the rectum should be reviewed with the patient and documented in the informed consent. Rectosigmoid Resection with Primary Anastomosis Large intraperitoneal rectal injuries that involve more than 50% of the bowel wall or a rectal injury associated with significant devascularization or thermal injury should be repaired with rectosigmoid resection and primary anastomosis. For intraperitoneal lesions, the mesentery should be inspected for any vascular compromise. Rectosigmoid resection-Proximal to the area of injury, a small mesenteric window is made adjacent to the sigmoid colon. The sigmoid mesentery is transected parallel to the rectum to below the area of injury, ligating the vascular pedicles with sutures, hemoclips, and/or the harmonic scalpel. If possible, the left colonic branch of the inferior mesenteric artery should be preserved. The perirectal, rectovaginal, and rectorectal spaces are developed mobilizing the rectosigmoid until normal rectum is encountered distally. Care should be taken to avoid ureteral injury and injury to presacral vessels during this dissection. The stapler is locked in the proper position and fired to place a staple line across the distal rectum.
Patient Preparation Intravenous antibiotic prophylaxis is recommended to prevent infection for most pelvic reconstructive surgery muscle relaxant used by anesthesiologist generic imitrex 25 mg with mastercard. Historically, mechanical bowel preparation has often been recommended prior to laparoscopic or open pelvic reconstructive procedures. Intraoperative recognition and repair is essential in order to avoid the potentially devastating sequelae of peritonitis, abscess, and sepsis that can be associated with delayed recognition. Other potential sequelae of small bowel injury include fistula, prolonged ileus, and bowel obstruction. Potential mechanisms of injury include laceration, perforation, thermal or burn injury, crush with associated ischemic injury, and mesenteric/vascular injury. It is important to be cognizant of the mechanisms of injury as they will dictate the management approach. Tears that involve only the serosa can typically be managed with simple interrupted sutures or imbrication using a Lembert-style repair. Intramural hematomas will usually heal spontaneously and do not typically require intervention. Full-thickness defects will require either a primary repair or resection and primary anastomosis depending on the nature and extent of the injury. A mesenteric vascular injury will require careful inspection of the bowel to assess for viability. All bowels with compromised vasculature will require wide resection with primary anastomosis of the viable bowel. When a bowel injury occurs because of trocar injury, whether laparoscopic or from a sling or prolapse mesh device, it is prudent to leave the trocar in position until the full nature of the injury is known as it is much easier If one is in doubt about the appropriate approach or one does not feel comfortable repairing a small bowel injury, then the next step is to obtain an intraoperative surgical consult. Primary Repair of Enterotomy Lacerations of less than half the circumference of the small bowel without associated vascular or thermal injury may be repaired primarily without bowel resection. The small bowel should be inspected throughout its entirety to ensure that all injuries are located (eg, "run the bowel"). Isolate the site of injury with noncrushing bowel clamps or Babcock clamps to prevent further spillage of bowel contents. Repair of enterotomy-Although single-layer closure has been described, we prefer a two-layered closure. It is essential that the edges of the repair be viable; any devascularized or nonviable tissue should be debrided. The first layer of closure can be performed with simple interrupted sutures or a running suture of 3-0 or 4-0 absorbable suture material incorporating all layers. Also, if multiple enterotomies occur within a localized segment of small bowel, it is often prudent to resect the entire damaged segment rather than perform multiple primary enterotomy repairs regardless of their size. Similarly, if primary repair will result in significant narrowing of the small bowel lumen, then resection and primary anastomosis should be performed.
Ajuga (Bugle). Imitrex.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96215
Combined behavioral and individualized drug therapy versus individualized drug therapy alone for urge urinary incontinence in women spasms leg 25 mg imitrex for sale. Behavior therapy to enable drug discontinuation in the treatment of urgency incontinence: a randomized controlled trial. Combined effects of behavioral intervention and tolterodine in subjects dissatisfied with their overactive bladder medication. A randomized controlled trial of duloxetine alone, pelvic floor muscle training alone, combined treatment, and no active treatment in women with stress urinary incontinence. Evaluation of neuromuscular electrical stimulation in the treatment of genuine stress incontinence. Pelvic floor stimulation in the treatment of genuine stress incontinence: a multicenter placebo-controlled trial. Pelvic floor electrical stimulation in the treatment of stress incontinence: an investigational study and a placebo controlled double-blind trial. Long-term effect of pelvic floor muscle exercise 5 years after cessation of organized training. Adherence to behavioral interventions for urgency incontinence when combined with drug therapy: adherence rates, barriers, and predictors. In a population of ambulatory women presenting for routine gynecologic care, 35% and 2% of patients had stage two and stage three prolapse, respectively. Obliterative procedures such as a colpocleisis or LeFort partial colpocleisis close off the vaginal canal either completely or partially and elevates the pelvic viscera back into the pelvis; these procedures are usually reserved only for elderly women who are no longer sexually active and who are often medically compromised. An obvious disadvantage to these procedures is the elimination of the future possibility of vaginal intercourse. These reconstructive surgical procedures may be approached vaginally, abdominally, or laparoscopically, and all may utilize graft materials to replace or augment native tissue. National or insurance databases suggest that the preferred route for primary prolapse repair is vaginal, with approximately 80% to 90% of operations performed vaginally. On the other hand, traditional vaginal approaches to prolapse repair often have higher rates of recurrent prolapse than an abdominal sacral colpopexy, a mesh repair with an abdominal approach. This article will review the indications for grafted repairs of prolapse and stress urinary incontinence and will characterize the various types of graft materials used in reconstructive pelvic surgeries. While the efficacy and potential complications related to graft use will be summarized for stress urinary incontinence procedures and abdominal sacral colpopexies, more attention will be focused on the more controversial transvaginal placement of graft materials for prolapse repair. Typically, autologous skin grafts or biologic grafts are used for neovagina procedures. The use of biologic grafts for vesicovaginal and rectovaginal fistula repairs has also been described when repairing fistulas that are recurrent, related to previous radiotherapy or ischemic injury, large, and/or associated with difficult closure, or when the surgeon suspects there is poor tissue quality or vascularization, although most of the data are limited to case series and case reports. Finally, biologic and autologous graft use has also been described in reconstructive cases for bladder exstrophy to allow a tension-free reconstructive closure. Efficacy of synthetic material in the abdominal repair of vaginal vault prolapse (sacral colpopexy) and anti-incontinence procedures such as full length midurethral slings is robust. Less evidence exists to guide when and in whom biologic or synthetic grafts should be used for transvaginal prolapse repairs.
Syndromes
Bicipital Myotatic Reflex the biceps reflex is one of several deep tendon reflexes that are routinely tested during physical examination muscle relaxant medicines discount 25 mg imitrex visa. A normal (positive) response is an involuntary contraction of the biceps, felt as a momentarily tensed tendon, usually with a brief jerk-like flexion of the elbow. A positive response confirms the integrity of the musculocutaneous nerve and the C5 and C6 spinal cord segments. Excessive, diminished, or prolonged (hung) responses may indicate central or peripheral nervous system disease. Rupture of Tendon of Long Head of Biceps Rupture of the tendon of the long head of the biceps usually results from wear and tear of an inflamed tendon (biceps tendinitis). Normally, the tendon is torn from its attachment to the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. Distally displaced belly of long head of biceps brachii Injury to Musculocutaneous Nerve Injury to the musculocutaneous nerve in the axilla is usually inflicted by a weapon such as a knife. A musculocutaneous nerve injury results in paralysis of the coracobrachialis, biceps, and brachialis; consequently, flexion of the elbow and supination of the forearm are greatly weakened. Loss of sensation may occur on the lateral surface of the forearm supplied by the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm. When the radial nerve is injured in the radial groove, the triceps is usually not completely paralyzed but only weakened because only the medial head is affected; however, the muscles in the posterior compartment of the forearm that are supplied by more distal branches of the radial nerve are paralyzed. Instead, the wrist is flexed because of unopposed tonus of the flexor muscles and gravity. Measuring Blood Pressure A sphygmomanometer is used to measure arterial blood pressure. A cuff is placed around the arm and inflated with air until it compresses the brachial artery against the humerus and occludes it. A stethoscope is placed over the artery in the cubital fossa, the pressure in the cuff is gradually released, and the examiner detects the sound of blood beginning to spurt through the artery. As the pressure is completely released, the point at which the pulse can no longer be heard indicates diastolic blood pressure. Compression of Brachial Artery the best place to compress the brachial artery to control hemorrhage is near the middle of the arm. Because the arterial anastomoses around the elbow provide a functionally and surgically important collateral circulation, the brachial artery may be clamped distal to the inferior ulnar collateral artery without producing tissue damage. The anatomical basis for this is that the ulnar and radial arteries still receive sufficient blood through the anastomoses. Ischemia of the elbow and forearm results from clamping the brachial artery proximal to the deep artery of the arm for an extended period. Occlusion or Laceration of Brachial Artery Although collateral pathways confer some protection against gradual, temporary, and partial occlusion, sudden complete occlusion or laceration of the brachial artery creates a surgical emergency because paralysis of muscles results from ischemia within a few hours. After this, fibrous scar tissue develops and causes the involved muscles to shorten permanently, producing a flexion deformity-ischemic compartment syndrome (Volkmann ischemic contracture).

When prolapse is symptomatic muscle relaxant definition imitrex 100 mg order mastercard, options include observation, pessary use, and surgery. Surgical therapy for prolapse can be broadly categorized into reconstructive and obliterative techniques. Reconstructive techniques may be performed using an abdominal or vaginal approach. Although no effective strategy to prevent prolapse recurrence has been identified, weight loss, minimizing heavy lifting, treating constipation, modifying or reducing obstetrical risk factors, and maintaining or improving pelvic floor muscle strength through pelvic floor physical therapy can be considered. Prolapse development is multifactorial, with vaginal childbirth and increasing body mass index as the most consistent risk factors (Table 14-1). Patients at a young age are at higher risk for prolapse recurrence following surgery and a lower overall risk from surgery compared with older women (Table 14-2). The normal intervening endopelvic fascia is absent, and small bowel fills the hernia sac. Normally, posthysterectomy enterocele is precluded by the apposition of pubocervical and rectovaginal fascia (collectively termed endopelvic fascia) at the apex. Posterior vaginal wall prolapse usually involves the rectum (rectocele) but may also include the small or large bowel. Table 14-1 Established and Potential Risk Factors for Pelvic Organ Prolapse Established Risk Factors Vaginal delivery Advancing age Obesity Other Potential Risk Factors Obstetrical factors: Pregnancy (regardless of mode of delivery) Forceps delivery Young age at first delivery Prolonged second stage of labor Infant birthweight >4,500 g Shape/orientation of bony pelvis Family history of pelvic organ prolapse Race/ethnicity Occupations involving heavy lifting Constipation Connective tissue disorders Previous hysterectomy Selective estrogen receptor modulators Generally, enteroceles have been divided into four types: congenital, traction, pulsion, and iatrogenic. Factors that may predispose to the development of congenital enterocele include neurologic disorders, such as spina bifida, and connective tissue disorders. Traction enterocele occurs secondary to uterovaginal descent, and pulsion enterocele results from prolonged increases in intra-abdominal pressure. Iatrogenic enterocele occurs after surgical procedures that elevate the normally horizontal vaginal axis toward a vertical direction; examples include colposuspension and needle urethropexy operations for stress incontinence, or hysterectomy, with or without repair, when the vaginal cuff and cul-de-sac are not managed effectively. Apical enteroceles herniate through the apex of the vagina, posterior enteroceles herniate posterior to the vaginal apex, and anterior enteroceles herniate anterior to the vaginal apex. Color codes include purple (bladder), orange (vagina), brown (colon and rectum), and green (peritoneum). The levator ani muscle complex consists of the pubococcygeus, the puborectalis, and iliococcygeus muscles. This muscle complex is tonically contracted at rest and acts to close the genital hiatus and provide a stable platform to support the pelvic viscera. Loss of normal levator ani tone, through denervation or direct muscle trauma, results in a more open urogenital hiatus, loss of the horizontal orientation of the levator plate, and a more bowl-like configuration.
A window has been cut in the wall of the cecum to expose the ileocecal orifice and the orifice of the appendix spasms meaning in english generic imitrex 50 mg overnight delivery. The mesentery of the transverse colon, the transverse mesocolon, loops down, so that the central transverse colon is inferior to the level of the iliac crests and is adherent to the posterior wall of the omental bursa. Some nerves derived from the inferior mesenteric plexus may follow anastomoses from the left colic artery. Peritoneum covers the colon anteriorly and laterally and binds it to the posterior abdominal wall. Although retroperitoneal, the inferior descending colon, especially in the iliac fossa, has a short mesentery in approximately 33% of people. As with the ascending colon, a left paracolic gutter lies on the lateral side of the descending colon. The sigmoid colon extends from the iliac fossa to the third sacral segment, where it joins the rectum. The sigmoid colon usually has a relatively long mesentery (sigmoid mesocolon) and, therefore, has considerable freedom of movement, especially its middle part. The left ureter and the division of the left common iliac artery lie retroperitoneally posterior to the apex of the root of the sigmoid mesocolon. The second important transition in the blood supply to the abdominal portion of the alimentary tract occurs approximately at the left colic flexure. The left colic and sigmoid arteries pass to the left, where they divide into ascending and descending branches. The parasympathetic nerve supply is from the pelvic splanchnic nerves via the inferior hypogastric (pelvic) plexus and nerves, which ascend retroperitoneally from the plexus, independent of the arterial supply. Proximal to the middle of the sigmoid colon, the visceral afferents conveying pain pass retrogradely with sympathetic fibers to thoracolumbar spinal sensory ganglia, whereas those carrying reflex information travel with the parasympathetic fibers to vagal sensory ganglia. Clinical Box Hiatal Hernia A hiatal (hiatus) hernia is a protrusion of part of the stomach into the mediastinum through the esophageal hiatus of the diaphragm. The hernias occur most often in people after middle age, possibly because of weakening of the muscular part of the diaphragm and widening of the esophageal hiatus. Although clinically there are several types of hiatal hernias, the two main types are para-esophageal hiatal hernia and sliding hiatal hernia (Skandalakis et al. However, a pouch of peritoneum, often containing part of the fundus, extends through the esophageal hiatus anterior to the esophagus. In these cases, usually no regurgitation of gastric contents occurs because the cardial orifice is in its normal position. As stomach cancer becomes more advanced, the lymphogenous dissemination of malignant cells involves the celiac lymph nodes to which all gastric nodes drain.
Fadi, 54 years: Impregnation of catheters with antimicrobial agents such as silver has been shown to delay or reduce the onset of bacteriuria; however, there is the possibility of future resistance to silver. Fistula surgery can also be responsible for damage to the anal sphincters and up to 60% of patients can become incontinent following treatment of complex, high fistulas or after multiple operations for a recurrent or persistent fistula. Examples of signs are stress or urgency urinary incontinence, extraurethral incontinence (fistula), or stress incontinence with prolapse reduction (occult or latent incontinence). The detrusor, the main structural element of the urinary bladder, is composed primarily of smooth muscle under autonomic control and connective tissue.
Iomar, 59 years: Inhalation of Carbon Particles Lymph from the lungs carries phagocytes, cells possessing the property of ingesting carbon particles from inspired air. Transobturator tape: using a helical needle, the sling material is passed through one obturator foramen, under the midurethra, and pulled through the contralateral obturator foramen. Proximally, the graft can be attached to the apical support sutures if the patient is concurrently undergoing an apical suspension procedure. Once the mesh has been appropriately sized and secured, the mesh arms are retrieved by using the retrieval sutures previously introduced.
References