
Liza D. L?e, MD
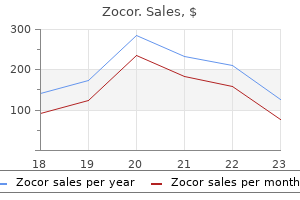
Zocor dosages: 40 mg, 20 mg, 10 mg
Zocor packs: 30 pills, 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

Surgical Conversion from Endovascular Repair Conversion from endovascular to open repair may be required for a number of reasons (Table 104-1) cholesterol lowering diet plan menu generic 10mg zocor overnight delivery. In one study, the mortality rate of patients who underwent emergency conversion operations was 40%. Erectile dysfunction may occur because of poor flow through the internal pudendal artery as a result of narrowing or occlusion, ligation of the internal iliac artery, an embolus or emboli in the distal pudendal arteries, or injury to the sympathetic nerves in the fascia surrounding the aorta. Other late complications include pseudoaneurysm formation, graft thrombosis, infection, aortoenteric fistula, aneurysm rupture, colonic ischemia, and peripheral embolism. Flank ecchymosis (the Grey-Turner sign) may be apparent, and reflects retroperitoneal hemorrhage. It does not contain all the layers normally present in an arterial wall and are at risk for rupture. Anastomotic pseudoaneurysms most commonly result from arterial degeneration or infection. Pseudoaneurysms may also manifest with symptoms caused by compression of adjacent structures or acute limb ischemia, or as an asymptomatic pulsatile mass. Some patients present with a herald bleed followed by temporary stoppage and then severe hemorrhage. These patients may present with a herald upper gastrointestinal bleed followed by severe hemorrhage. Ultrasound is an operator-dependent modality and is often suboptimal in patients who are obese or of large body habitus and in patients with excessive overlying bowel gas may obscure proper visualization of the abdominal aorta. Associated septicemia, wound infection, and graft dysfunction from thrombosis or hemorrhage from the anastomotic site may occur. Infections that occur more than 4 months postoperatively may present with more subtle signs and symptoms, and a fever may be absent. Such patients have a higher likelihood of presenting with signs of complications from their aortic graft infection, such as pseudoaneurysm, aortoenteric fistula, hydronephrosis, or osteomyelitis. Patients with an aortocaval fistula most commonly present with abdominal pain, back pain, and dyspnea. On physical examination, a machinery-type abdominal bruit may be auscultated, and an abdominal thrill may be palpated. Occasionally, color and Duplex scanning are useful, such as in the identification of an aortocaval fistula. Oral water-soluble contrast, however, is helpful for the evaluation of a suspected aortoenteric fistula in a patient who is not actively bleeding. A delayed-phase acquisition (90 to 120 seconds postcontrast, 2- to 3 mmreconstructions) is also carried out to evaluate the abdomen and pelvis.
Diseases
Heterotaxy There are a number of synonyms for heterotaxy17 including asplenia/polysplenia syndrome and atrial isomerism cholesterol zocor purchase 20 mg zocor amex. The fundamental lesion in these patients is that there is poor differentiation into right and left side. This can result in bilateral right sidedness (asplenia syndrome) which may be associated with bilateral right lungs. Mitral Atresia Including Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome Absence of the mitral valve as with marked absence of the tricuspid valve excludes the possibility of a biventricular repair. If the mitral valve is the only underdeveloped structure in the left heart an assessment must be made of the Z scores for both the diameters and cross-sectional area of the mitral valve. This may be long and narrow and therefore cause significant obstruction to outflow into the systemic circulation. In contrast, the unoperated patient who has a single ventricle has parallel pulmonary and systemic circulations. Blood leaving the single ventricle has a choice of either passing to the pulmonary circulation or the systemic circulation. Therefore, the relative resistances of the pulmonary and systemic vascular beds will determine the amount of flow which passes to each unless there is anatomical obstruction to pulmonary outflow or obstruction to systemic outflow. In the absence of either pulmonary or systemic outflow obstruction or pulmonary vascular disease there will be very much more pulmonary than systemic blood flow. This will result in an arterial oxygen saturation of approximately 80% and is consistent with surprisingly good long-term survival with a satisfactory quality of life. The single ventricle under these circumstances is being asked to pump only double the normal cardiac output and generally this can be achieved for many years. Most amphibians such as frogs have exactly this type of circulation (see Chapter 34, Vascular Rings, Slings, and Tracheal Anomalies). In time, the patient will suffer the usual consequences of severe cyanosis including polycythemia, stroke, brain abscess, hemoptysis, and ultimately death. At the other end of the spectrum the patient who has inadequate obstruction to pulmonary outflow will likely develop excessive pulmonary blood flow in the first weeks and months of life as pulmonary resistance falls and symptoms of congestive heart failure will develop. If the heart is able to cope with the massive volume load with which it is likely to be confronted there will subsequently be progressive development of pulmonary vascular disease. The ultimate result is similar to the patient who has a severe fixed degree of obstruction to pulmonary outflow.
Hydration will also help decrease radiation dose to the bladder wall5 and to the surrounding reproductive organs by diluting the radioactivity in the bladder cholesterol levels results safe zocor 20 mg. Patients can receive oral or intravenous hydration, although intravenous hydration is generally preferred with enalaprilat. A baseline blood pressure reading should be taken and recorded prior to administration of the medication. At the culmination of the study, a final blood pressure reading should be taken prior to discharge home. Patients receiving enalaprilat should have blood pressure measured every 5 minutes during the examination. The patient should void when the waiting period comes to an end, prior to imaging, because a full bladder may affect emptying of the upper tract6 and could also lead to premature termination of the study if the patient needs to void during imaging. The patient is then brought into the scan room and positioned supine on the imaging table with the camera located posteriorly to ensure that the kidneys are lying at the same depth, which could be affected with the patient semirecumbent or sitting. The study should be dynamic, with the first series generally consisting of 1 sec/ frame for 1 minute to assess early perfusion, the second series consisting of 5 sec/frame for 24 frames, and the final functional sequence, 30 sec/frame for 60 frames, for a total imaging time of approximately 30 minutes. The patient should void at the end of the study to reduce radiation dose to the kidneys, bladder, and pelvic organs. A postvoid bladder residual can also be calculated with a postvoid image consisting of a single 60-sec/frame image. Correction for infiltration can be done by imaging the injection site and qualitatively or quantitatively assessing the injection dose. A quantitative evaluation is performed by determining the ratio of infiltrated counts to the original counts in the injected dose; with this method, syringe counts should be calculated prior to injection. Assessment of a region of interest over the abdominal aorta during the immediate postinjection perfusion phase can also provide information about the quality of the injection bolus. The 1-day protocol requires the patient to visit the imaging department only once, but the length of time spent may be longer than with the 2-day protocol. It is helpful to obtain a single static postvoid image of the kidneys and bladder prior to the second injection of the radiopharmaceutical to assess how much, if any, residual activity remains, because residual activity could interfere with interpretation of the second imaging sequence. Following radiotracer injection, the loop diuretic furosemide may also be administered intravenously to clear radiotracer activity from the collecting system, reducing retention which could otherwise confound quantitative assessment. These patients generally are found to have ischemic nephropathy, often with a small shrunken kidney. Bilateral cortical retention is more often caused by dehydration or a hypotension artifact rather than bilateral renal artery stenosis. An increase in the 20/peak (ratio of cortical activity at 20 minutes to the amount of peak activity) or 20/3 ratio (count activity at 20 minutes divided by the activity at 3 minutes). Grades 1 through 3 reflect progressive worsening from baseline, with increasing grade indicating more corresponding profound changes. An increase in time to maximum parenchymal uptake (Tmax) of at least 2 to 3 minutes. Chronic administration of certain antihypertensives can reduce specificity of the examination and these medications may need to be held prior to the study.
This stage ends with full dilatation of the cervix cholesterol levels chart in uk cheap zocor 10 mg line, and is further divided into the latent and active stage. Malpresentations and malpositions increase the maternal risks of prolonged labour, infection, obstructed labour, tissue necrosis resulting in vesico/rectovaginal fistulas, and deep venous thrombosis. Fetal risks of malpresentation and malposition are cord prolapse, traumatic delivery and hypoxia. Occipito-posterior position the fetal head usually engages in the lateral position, and in 80% of cases it rotates anteriorly. About 20% of fetuses are in the occipito-posterior position in early labour (usually occiput to the right). With increasing flexion in labour, there is a tendency for the fetal head to rotate when it reaches the pelvic floor. When the diamond-shaped anterior fontanelle can be palpated on vaginal examination, this indicates deflexion of the fetal head. The maternal abdomen appears flat below the umbilicus, and fetal limbs can be palpated anteriorly on the maternal abdomen. Occasionally, the fetus will spontaneously deliver in the occipito-posterior position. Vacuum extraction, using the posterior cup position, will encourage flexion and rotation of the fetal head to correct the relative disproportion. Management Aim for a vaginal delivery, especially if the baby is in the mento-anterior position. However, if the baby is in the mento-posterior position and there is failure to rotate, the baby cannot be delivered vaginally and caesarean section is required. If the unstable lie persists after 38 weeks or labour commences, caesarean section is indicated. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Chapter 40 Operative delivery Michael Flynn Caesarean section Caesarean section births constitute approximately one-quarter of births in many countries. Although now a relatively safe procedure, emergency caesarean section carries an increased risk of maternal mortality and morbidity.
Hydrolyzed Chicken Collagen Type II (Chicken Collagen). Zocor.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96699

Generally cholesterol machine purchase zocor 10mg overnight delivery, the decision does not need to be finalized in the newborn period because palliative procedures such as a shunt or a band do not exclude a subsequent biventricular repair. If there is associated ciliary dyskinesia the child must be carefully managed by the immunology and pulmonary medicine teams. The neonate may be prostaglandin dependent because of pulmonary atresia or require urgent surgery because of obstructed total anomalous pulmonary venous connection. There may be a balanced single-ventricle circulation so that the child needs little treatment until the time of the bidirectional Glenn shunt at 4 or 5 months of age. If there is little pulmonary stenosis treatment for congestive heart failure may be needed as pulmonary resistance falls. A pulmonary artery band may be required if the child is to be managed with the singleventricle track. There is usually no place for interventional catheter therapy initially though situations can certainly arise where it will be helpful, for example if the child has required anastomosis tHe siNgle VeNtricle track for tHe NeoNate witH Heterotaxy the neonate with heterotaxy who will pursue a singleventricle track must follow the general principles of single-ventricle management. Thus the goals should be excellent diastolic function, large pulmonary arteries, and low pulmonary vascular resistance. The cephalic end of the vein is opened longitudinally avoiding extending the incision into the individual lobar pulmonary veins. A wide anastomosis is fashioned to the posterior wall of what is usually a common atrium. This vicious circle must be avoided by avoiding volume loading of the single ventricle. Thus a pulmonary artery band should be applied if there is excessive pulmonary blood flow which will result in an arterial oxygen saturation of greater than approximately 80%. Assuming complete mixing, an oxygen saturation of greater than 80% suggests a Qp:Qs of greater than 2:1 and this should be avoided. Although a tight band will result in the child outgrowing the band within a few months, this is also desirable. More commonly, a thickened regurgitant commissure can be completely closed in conjunction with placement of a commisuroplasty suture. Thickening of the valve leaflet margins along the commissure responsible for regurgitation is helpful to the surgeon. Not only does it indicate the likely site of regurgitation but it also means that sutures used to close this commissure will be secure.
In situations in which other approaches to assess the proximal and middle segments of renal arteries fail because of bowel gas cholesterol in a shrimp 10mg zocor sale, morbid obesity, or inability to hold the breath, the lateral approaches in decubitus positions are used to assess the proximal two thirds of both renal arteries. An additional approach that yields a banana or banana peel view is also popular with renal sonographers. A, Spectral waveform pattern in main renal artery is of low impedance with continuous forward diastolic flow and a characteristic early systolic peak (arrow) at the end of the systolic rise. The spectral waveforms of the proximal segments of the right (A) and left (B) renal arteries show a lowresistance waveform, with an early sytolic peak and flow throughout the diastole. Before sampling intrarenal vessels, a perfusion scan of the kidney should be obtained. Sampling of the intrarenal arteries is done in the upper, middle, and lower poles of the kidney by color Doppler guidance. By taking a Doppler angle of insonation of 0 degree, using the lowest velocity scale and lowest wall filter setting, and adjusting the smallest Doppler gate width, a good spectral waveform is typically obtained. Peak systolic and end-diastolic velocities are recorded for the intrarenal arteries. The software installed in almost all modern ultrasound machines automatically performs these calculations. The blood flow in the right renal artery (short arrow) is toward it and hence is shown in red, whereas flow in the left renal artery (long arrow) is away from the transducer and is shown in blue. The transducer is adjusted slightly in an anterior or posterior direction so that both renal arteries are seen arising from the aorta and coming toward the transducer. The banana peel view is especially useful in older patients, in whom stenosis caused by atherosclerosis is expected in the ostium of the renal arteries. In case of failure of all approaches for optimum visualization of the renal arteries, the patient can be asked to lie prone and the examination can be attempted by using the kidneys as acoustic windows on both sides. Peak systolic and end-diastolic velocities (see Table 109-1) are obtained at the origin, proximal segment, and middle segment of both renal arteries with a Doppler angle of insonation of 60 degrees or less. After taking these samples, the distal part of the renal arteries is sampled for peak systolic and end-diastolic velocities in a lateral decubitus position with the use of a 0-degree angle of insonation. Renal Morphology No evaluation of renal vessels is complete without assessment of kidney size, shape, and echo texture. Longitudinal measurement of the kidney in the cephalocaudal plane should always be performed. In case of a normal-sized kidney, and a very small diameter main renal artery (less than 5 mm), there is every likelihood that an accessory, supernumerary, or polar renal artery supplies the kidney. Therefore, to see any accessory renal arteries, longitudinal and transverse sweeps of the transducer are done in the decubitus position. A, Waveform of a segmental artery recorded in the lateral decubitus position after placing the sampling gate (=) at the segmental artery. The normal waveform shows a sharp systolic upstroke (short arrow) and forward flow throughout the cardiac cycle (long arrows).

The spectrum of pathology that one is likely to encounter is also somewhat different livalo cholesterol medication side effects cheap 40mg zocor otc. Whereas almost all lower extremity occlusive disease is the result of long-standing atherosclerosis, nonatherosclerotic disease and uncommon causes make up a substantial part of the case mix of clinicians dealing with patients suffering from upper extremity arterial disease. Furthermore, apart from intrinsic vascular disease, there are other well-recognized extrinsic entities that may compromise the arterial supply of the upper extremity. There are several main reasons why examinations of the upper extremity arterial tree account for a minority of all vascular examinations in the average radiologic practice. The abundant collateral supply in the lower neck, shoulder, and upper arm regions provide a robust means for the reconstitution of distal perfusion, thus delaying symptoms. Also, a large fraction of patients suffer from small vessel disease, which is primarily managed medically instead of with percutaneous or surgical techniques. When the clinical history and laboratory information suggest small vessel disease, many patients are not even referred for vascular imaging because the information obtained does not necessarily influence treatment. In this chapter, different vascular diseases affecting the upper extremity are discussed, as well as the relative merits and shortcomings of different techniques for imaging the upper extremity vasculature in the context of the most frequent diseases one is likely to encounter. Other entities one is likely to encounter are thoracic outlet syndrome, autoimmune vasculitis, thromboembolism, and vascular damage caused by trauma, sports injuries, and radiation therapy. Patients with atherosclerotic occlusive disease typically present with upper extremity claudication or steal phenomenon. The most common locations for upper extremity large vessel involvement include the brachiocephalic and subclavian arteries. However, atherosclerosis can also cause small vessel obstruction by atheromatous embolization or thromboembolism. A particularly helpful clinical clue in establishing the correct cause is the age of the patient. Atherosclerotic disease of the upper extremity tends to affect older adult patients, whereas nonatherosclerotic upper extremity arterial occlusive disease affects younger patients. In polymyalgia rheumatica, the vasculitis is located more distally in the cervicocranial arteries. Symptoms are caused by compression at the interscalene triangle, costoclavicular space, or retropectoralis minor space. A large majority of cases (70% to 90%) is caused by involvement of the brachial plexus. Blunt and penetrating trauma to the chest and upper extremity may compromise the vascular supply as well.
This common pathway of hepatic injury leading to portal inflow resistance causes predictable morphologic changes in the portal and mesenteric vasculature that are diagnostic of portal hypertension cholesterol levels definition zocor 10mg mastercard. Flow in the portal vein, normally directed into the liver (hepatopetal) eventually reverses direction away from the liver (hepatofugal). Shunted blood pools at these sites of portosystemic anastomosis, causing the formation of varices. The contrast is then injected at a rate of 2 mL/s, followed by at least 20 mL of saline flush using a dual-chamber injector, which allows for a continuous influx of gadolinium during imaging. This soft tissue detail, together with vascular evaluation, provides a comprehensive analysis of the etiology and subsequent effects of various pathologic processes affecting the abdominal vasculature. Manifestations of Disease Clinical Presentation Patients often have a history of predisposing factors, such as alcohol abuse or viral (hepatitis B and/or C) infection. Clinical symptoms usually manifest with the development of portal hypertension, and include edema, ascites, and bleeding from varices and decreased production of clotting factors by the liver. This reticular parenchymal enhancement can identify fibrotic liver disease before morphologic changes of cirrhosis and portal hypertension develop. This is a powerful tool in that it allows for an earlier, more aggressive treatment plan in patients at high risk for chronic liver disease. Conventional catheter angiography assesses strictly vascular morphology, which only typically becomes abnormal with more advanced disease and cannot evaluate parenchymal changes of fibrosis. Varices may be identified within the esophageal wall (termed esophageal varices) or surrounding the esophagus (termed paraesophageal varices), although both drain the portal system via the left gastric (cardinal) vein. Additional common sites of variceal formation within the abdomen due to portosystemic shunting include gastric and retroperitoneal varices, spontaneous splenorenal shunts, and recanalized paraumbilical veins. Recanalized paraumbilical veins drain into the epigastric veins along the undersurface of the abdominal wall, often forming a mesh of dilated varices surrounding the umbilicus termed caput medusa. Identification of paraumbilical varices are important in that the draining meshwork of superficial veins along the anterior abdominal wall must be avoided during diagnostic and therapeutic paracenteses that are often performed in patients with chronic liver disease. Other etiologies of intrahepatic portosystemic shunting include congenital malformations and rupture of a portal vein aneurysm into a hepatic vein, whereas posttraumatic shunts are most often associated with surgical interventions such as transhepatic catheter placement. In addition to portosystemic shunting, chronic liver injury and fibrosis also causes arterioportal shunting, either secondary to underlying tumor (hepatocellular carcinoma) or cased by the parenchymal changes of fibrosis itself. Arterioportal shunts may also occur in settings other than chronic liver disease, such as trauma, iatrogenic (postbiopsy or surgery), congenital anomalies, or aneurysm rupture. Imaging also serves to grade disease and provide a pathway for tumor surveillance. Etiology and Pathophysiology Thrombosis of the portal vein may be idiopathic, iatrogenic, or secondary to adjacent infection and/or inflammation, and is a cause of prehepatic portal hypertension. Portal thrombosis is also common in the setting of portal hypertension due to intrinsic liver disease, likely caused by altered flow dynamics in the setting of sinusoidal obstruction.

Autoimmune hypothyroidism may also result in isolated breast development cholesterol test after exercise order zocor 10 mg with mastercard, although this is rarely seen before 5 years of age. Androgen-secreting tumours are usually associated with severe virilization in young girls (<6 years old). The diagnosis is made by the finding of excessively raised circulating plasma sex hormone levels. A 24-h urine collection for steroid profile often demonstrates excess levels of sex Thelarchevariants There appears to be a whole spectrum of presentations between premature thelarche and true precocious puberty. These tumours are often palpable and an abdominal ultrasound scan will confirm the diagnosis. Androgen receptor blockade Androgen receptor blocking agents, such as cyproterone acetate, finasteride or flutamide, may be used for symptomatic treatment of excess androgen production in girls with premature adrenarche. Delayed Puberty Delayed puberty is defined as the absence of onset of puberty by more than 2 standard deviations later than the average age, i. Delayed puberty may be idiopathic/familial or due to a number of general conditions resulting in undernutrition. Absence of puberty may also be due to gonadal failure (elevated gonadotrophin levels) or impairment of gonadotrophin secretion. All cells descended from the mutated embryonic cell line are affected, while cells descended from non-mutated cells develop into normal tissues. The diagnosis is made by clinical assessment, based on the presence of skin, bone and other lesions. Although constitutional delay presents more commonly in males, this may merely reflect their higher level of concern. It can be very difficult to distinguish hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism from constitutional delay in puberty, and therefore it is better to provide treatment and revisit the diagnosis at a later date. Appropriate investigations, after physical examination and measurement of weight Managementofprecociouspuberty It is important to exclude severe diseases. Premature thelarche and thelarche variant need no treatment as there are no long-term consequences and, furthermore, treatment appears to be without effect.
Hanson, 55 years: Conception Conception requires: � sperm* � adequate (quantity, quality) � deposition (in vicinity of cervix, prior to/at ovulation, permeable cervical mucus) � ovulation* � at least one patent fallopian tube to allow fertilisation* � transport to endometrial cavity � implantation the probability of conception is time dependent: � after 3 months: 60% � after 6 months: 75% � after 12 months: 85% � after 24 months: 95% Therefore, the majority of couples who have not conceived after 1 year are likely to conceive in the subsequent year.
Derek, 24 years: Advances in the management of uterine myomas have resulted in a need to provide accurate pretreatment information concerning their size, quantity and location.
Kippler, 53 years: Grafts from living donors, who cannot sacrifice an aortic patch, are typically anastomosed end to end to the internal iliac artery.
Quadir, 61 years: However, diabetic women with high glycosylated haemoglobin A1c levels in the first trimester are at significantly higher risk of both miscarriage and fetal mal- Recurrent miscarriage formation (Hanson et al 1990).
Jens, 23 years: A stitch of 6/0 Prolene between both ends of the mesosalpinx should be applied as a stay suture.
Folleck, 27 years: This will allow both appropriate sizing and optimal placement of the endoprosthesis.
References