
Dorothy K. Grange, M.D.
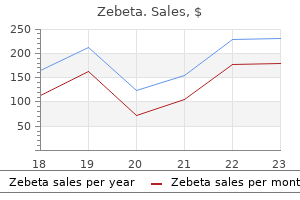
Zebeta dosages: 10 mg, 5 mg
Zebeta packs: 60 pills, 90 pills, 120 pills, 180 pills, 270 pills, 360 pills

The polyps in these syndromes are usually bland in appearance blood pressure chart log excel cheap 5 mg zebeta fast delivery, often somewhat resembling large hyperplastic polyps. Their true nature is established by identifying other features of the respective syndrome. There is sharp demarcation between the glandular epithelium with enlarged, hyperchromatic pencil-shaped nuclei (left) and adjacent normal foveolar epithelium (right). Gastric adenocarcinoma has declined markedly in incidence in Western countries over the past century. There are a number of factors involved, but the most important appears to Gastric Adenomas Are Relatively Uncommon True adenomas of the stomach occur far less often than adenomas of the colon. Intestinal-type adenomas are far more common and usually arise in stomachs with intestinal metaplasia. Nuclei tend to be enlarged, elongated and hyperchromatic, like their intestinal counterparts. While the colon is the main target organ in this syndrome, the stomach can be involved and carpeted by polyps. With improved recognition and treatment of Helicobacter infections, gaps between the West and East are narrowing. Diets high in smoked or pickled foods are associated with a higher cancer rate, while consumption of fresh vegetables and leafy greens has the opposite effect. Genetic factors also play a significant role, particularly with some types of gastric cancer. Most carcinomas form large polypoid masses or growths with significant ulceration. The latter differ from benign peptic ulcers by their large size, raised firm irregular borders and ragged ulcer surfaces. A minority of cancers infiltrate the gastric wall deeply, beneath a surface that may seem deceptively intact. This results in a rigid thick-walled stomach, an appearance that has been classically described as linitis plastica. Gastric carcinoma has traditionally been separated into two categories, intestinal and diffuse, with some cases showing overlap; this is the Lauren classification. The term "intestinal" in this context mainly describes the architecture, rather than the cell type. These tumors form glands or papillae, as well as some solid areas; mucin production may occur. Diffuse-type carcinoma contains poorly cohesive cells, widely infiltrating the gastric wall, often with striking desmoplasia. Although the diffusely infiltrating cells may have a signet ring appearance, other cells may more mimic histiocytes or even lymphocytes. These patients may develop cancer at an early age and often have multiple small foci of signet ring carcinoma in situ detectable only by thorough microscopic examination.
In men heart attack sam tsui chrissy costanza of atc buy zebeta 5 mg online, lung and gastrointestinal cancers are most often associated with dermatomyositis, whereas in women, the most common association is with breast cancer. Sweet syndrome is a combination of elevated neutrophil count, acute fever and painful red plaques in the anus, neck and face. About 1/5 of cases occur with malignancies, particularly those of the hematopoietic system (see Chapter 26). Its boundaries are: the anterior two thirds of the tongue to the line of the circumvallate papillae (inferior) the buccal mucosa of the cheeks (lateral) the vermilion border of the lips (anterior) A line from the junction of the hard and soft palate to the circumvallate papillae of the tongue (posterior) the hard palate until its junction with the soft palate (superior) the oral mucosa consists of keratinized epithelia of the attached gingiva, hard palate mucosa and specialized keratinized gustatory mucosa of the dorsum of the tongue. It also includes nonkeratinized mucosal surfaces of the inner lip and inner cheek, the nonattached, movable gingiva that continues into the maxillary and mandibular sulci, ventral tongue, floor of the mouth, soft palate and tonsillar pillars. Under the epithelium is a lamina propria of fibrous tissue and blood vessels, beneath which is the densely fibrous periosteum of the hard palate or the alveolus of the maxilla and mandible. The term submucosa is sometimes loosely applied to the deep connective tissue just above the muscle layer, in which the minor salivary glands are often embedded. Minor salivary glands are scattered throughout the oral cavity as unencapsulated small lobules within the mucosa and submucosa. There are mucous glands in the lamina propria, particularly in the posterior hard palatal mucosa. Minor salivary glands of pure mucous type exist in the anterior ventral portion of the tongue (called Blandin, or Nunn, glands). Serous salivary glands lie near circumvallate papillae on the posterior and lateral tongue (von Ebner glands). Mixed mucoserous and mainly mucous glands predominate in the rest of the oral cavity. There are minor salivary glands in the retromolar mandibular ridge, but not the anterior hard palate or gingiva. The anterior two thirds of the dorsum of the tongue is covered by keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that is specialized to form filiform papillae (pointed projections of keratin). Between these are fungiform papillae, mushroom-shaped mucosal elevations containing taste buds. Circumvallate papillae separate the anterior 2/3 of the tongue from the posterior 1/3 and contain taste buds at their base. The final group is the foliate papillae, in the posterior lateral tongue in a series of ridges. Each taste bud is a barrel-shaped collection of modified epithelial cells that extend vertically from the basal lamina to the epithelial surface, opening via a taste pore. It may be unilateral or bilateral and often occurs in association with cleft palate (see Chapter 6).
Diseases
These cells still synthesize hemoglobin blood pressure ranges child discount 5 mg zebeta visa, and the ribosomes needed for this process impart the polychromatophilia. Transmembrane receptors, channels and anchors for other membrane components insert into the lipid bilayer, as does the underlying cytoskeleton. Carbohydrate groups added to some membrane proteins lead to formation of different red cell antigen groups. The erythrocyte cytoskeleton contains interconnected spectrin dimers and other stabilizing proteins (ankyrin, actin, band 4. Each hemoglobin molecule has 4 heme groups and 4 globin chains and, when fully saturated, transports 4 molecules of oxygen. The most abundant normal form, hemoglobin A, has two alpha ()- and two beta ()-globin chains. In addition, hemoglobin F has two gamma ()- and hemoglobin A2 has two delta ()-globin chains, instead of -globin chains. Synthesis and assembly of each hemoglobin molecule requires multiple biochemical steps that require distinct enzymes. Each heme group interacts with a hydrophobic pocket of one globin chain, and the entire molecule has a globular tertiary structure. After this initial interaction, hemoglobin molecules undergo conformational change, which facilitates subsequent oxygen binding to the remaining heme groups. Progressive increase in oxygen affinity is reflected in the sigmoid shape of the oxygen dissociation curve. Normal red blood cells are approximately the same size as the nucleus of a small lymphocyte (approximately 7 m). With decreasing pH (acidosis), the oxygen affinity declines (shifts right); with increasing pH (alkalosis), the affinity increases (shifts left). Using this stain, storage and sideroblastic iron granules can be found within the cytoplasm of macrophages and nucleated red blood cell precursors, respectively. Finally, marrow infiltration by abnormal cells, such as metastatic tumor cells, malignant hematopoietic cells or infectious granulomas, can be identified. Reticulocytes can be accurately quantitated using supravital dyes that stain their cytoplasmic ribosome aggregates.
The mitotic rate among the malignant cells is characteristically high (arrowheads) blood pressure medication harmful order 10 mg zebeta with visa. A diffuse infiltrate of neoplastic lymphocytes is present in the upper dermis and may occasionally invade the epidermis, as small Pautrier microabscesses (arrows). A higher magnification of a Pautrier microabscess is shown in the inset (arrowhead). Partially effaced lymph node with accumulation of malignant cells in the subcapsular sinus. Higher magnification showing the blood vessels (representative vessels are highlighted by arrows) and their prominent endothelial cells. Over 90% of cases have T-cell receptor rearrangements, even if the tumor cells do not express T-cell antigens. Some cases contain lymphoma cells with abundant clear cytoplasm and minimal atypia, and others show a population of atypical large lymphoid cells. Peripheral and central lymphadenopathy are common, as are extranodal and bone marrow involvement. Patients present with generalized adenopathy and symptoms consistent with a systemic disease process. Neoplastic T-cell infiltrates expand the paracortical regions of lymph nodes and are associated with a striking proliferation of high endothelial venules. At the outset, most patients have high-stage disease, generalized lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, bone marrow involvement, hypergammaglobulinemia and body cavity effusions. Other laboratory findings include cold agglutinins, hemolytic anemia, circulating immune complexes and rheumatoid factor. Some 8000 cases occur annually in the United States, an incidence of 3 per 100,000 people. But these clusters are beguiling: such apparent case grouping is predictable on statistical grounds. Fibroblasts are variably prominent, with or without distinct bands of collagen fibrosis. These are (1) nodular sclerosis, (2) mixed cellularity, (3) lymphocyte rich and (4) lymphocyte depleted. Prototypical Reed-Sternberg cells are large with at least two nuclear lobes or nuclei and abundant light blue cytoplasm. Gross photograph showing an enlarged lymph node with a thickened capsule and broad bands of fibrosis dividing the parenchyma into distinct nodules. It was only with advanced molecular diagnostic techniques in the late 1990s that their relationship to clonal B cells of germinal center cell origin became clear. Lacunar cells are helpful in diagnosis but result from a retraction artifact in formaldehyde-fixed tissue.
In place of the cortex is a series of large nodular structures with nuclear architecture blood pressure medication viagra effective 10 mg zebeta. In the nucleus that corresponds to the striate (visual) cortex of mammals, the total number of synapses between the retina and the visual forebrain is exactly the same in reptiles, birds, and mammals, and visual function is equally good or better than many mammals in birds, such as eagles, with nuclear organization of its visual forebrain. Cortical architecture is found in many parts of the brain and not only in the cerebral and cerebellar cortices, At times they may persist into adult life as a congenital vascular anomaly, usually resulting in posterior fossa circulation coming mainly from the internal carotids rather than from the vertebral and basilar arteries. Such a condition may be asymptomatic, but leaves such a patient at risk for a more extensive infarct that involves the cerebellum and brainstem if the internal carotid artery becomes occluded. The microcirculation of the cerebral parenchyma begins as radial small vessels that then branch and form the capillary network. Arterioles in the cortex do not acquire their muscular coat (tunica media) until relatively late in gestation, near term. This explains why preterm neonates do not have autoregulation of cerebral blood flow: not only is the neurogenic autonomic mechanism for its regulation not mature but also the end organ is unable to respond to innervations because the tunica media is incompletely formed around the vessels that must dilate or contract. Watershed zones Watershed zones are territories between the circulations of major cerebral arteries. The term was first used in agriculture in the nineteenth century to describe the strip of land between two parallel creeks or rivers, protected from drought if one of the rivers was dammed because it had two sources of water, but vulnerable to general drought because it was the last to receive water from both rivers and the first strip of land to become parched with loss of vegetation. Extrapolated to the brain, the major arteries are the rivers and the strip between their territories are the watershed zones, which become selectively infarcted with prolonged systemic hypotension (shock), hypovolemia due to blood loss, or other conditions of hypoperfusion. The best-known watershed zones are between the middle and anterior cerebral arterial and the middle and posterior cerebral arterial perfusion zones. The mesencephalic colliculi are other watershed territories that can be selectively involved with basilar artery insufficiency. Vascular Development Major arteries of the brain form as independent segments and join only later. The middle cerebral artery, for example, is a well formed vessel that finally forms a connection with the also previously formed internal carotid artery. The basilar artery begins in the embryo as a pair of longitudinal neural arteries ventral to the neural tube in the zone of the future brainstem. This pair of vessels undergoes true fusion to form a single midline basilar artery. It later connects with the preformed posterior cerebral arteries, and indeed the circle of Willis forms from the formation of connections of arterial segments as well. The vertebral arteries initially are a plexus of primitive small vessels that coalesce and then join the basilar artery soon after their formation from the longitudinal neural arteries. The internal carotid and rostral end of the basilar artery initially are connected, so that the blood flow in the early basilar artery is rostrocaudal, from the internal carotids.
If conception does not occur arteria publicidad buy zebeta 5 mg otc, the endometrium is shed, and then regenerated to support a fertilized ovum in the next cycle. The endometrium becomes desiccated, spiral arteries collapse and stroma disintegrates. The denuded surface is regenerated by extension of the residual glandular epithelium. The lining cells develop abundant and prominent, glycogen-rich, subnuclear vacuoles (day 17). Over the next several days, these cells produce copious secretions that support the zygote as it develops early chorionic villi capable of invading the endometrium. Glands have homogenous cytoplasm with a few discrete vacuoles and are dilated and more tortuous. Day 23 (postovulatory day 9): Stromal cells surrounding spiral arterioles enlarge and exhibit large, round, vesicular nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm ("vascular cuffing"). With time, these cells become more extensively distributed until they fill the functionalis. They are precursors of the decidual cells of pregnancy and are referred to as "predecidua. Scanty mitoses Loose stroma Stromal edema Focal Extensive predecidua Predecidua predecidua. Dilated tortuous glands with serrated borders are situated in a predecidual stroma. Remaining glands have a thin epithelium and the stroma contains abundant collagen. Glands of the atrophic endometrium are often quite dilated, and this condition is called senile cystic atrophy of the endometrium. In the hypersecretory endometrium of pregnancy, highly dilated glands are lined by cells with abundant glycogen. The hypersecretory response may be exaggerated with intrauterine pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy or trophoblastic disease. These nuclei protrude beyond the apparent cellular cytoplasmic limits into the gland lumen, an appearance referred to as the Arias-Stella phenomenon. Enlarged nuclei are polyploid rather than aneuploid, a condition sometimes seen in adenocarcinoma.
Cassia acutifolia (Senna). Zebeta.
Source: http://www.rxlist.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=96642
Nodules of regenerative mucosa and inflammation surrounded by denuded areas provide a diffuse polypoid appearance of the mucosa blood pressure yahoo health purchase zebeta 5 mg without prescription. Blood and fluid loss rapidly lead to anemia, dehydration and electrolyte depletion. Toxic megacolon-extreme dilation of the colon that carries a high risk for perforation-is particularly dangerous. It requires immediate, intensive medical therapy and, sometimes, prompt colectomy. The medical treatment of ulcerative colitis depends on the sites involved and the severity of the inflammation. There may be some benefit of fecal transplant in patients with refractory disease. In advanced ulcerative colitis, mucosal atrophy and chronic inflammation are present in the mucosa and superficial submucosa. Differential Diagnosis the most important conditions to be distinguished from ulcerative colitis are other forms of chronic colitis due to specifically treatable causes, and Crohn disease. Other conditions in the differential diagnosis of ulcerative colitis are bacterial infections and amebic colitis, especially in areas where it is endemic. If inflammation is limited to the rectum, other infectious agents, including viruses, chlamydia, fungi and other parasites, merit consideration. Other conditions that may mimic ulcerative colitis are ischemic colitis, antibiotic-associated colitis, radiation injury and solitary rectal ulcer syndrome. The distinction between ulcerative colitis and Crohn colitis is based on different anatomic localization and histopathology (Table 19-3). Ulcerative colitis is a diffuse process, usually more severe distally, while Crohn colitis is patchy or segmental and often spares the rectum. If disease stops at the ileocecal valve or is limited to the distal colon, ulcerative colitis is more likely. Involvement of the terminal ileum suggests Crohn colitis, unless there is pancolitis with backwash ileitis. In 10% of cases, definitive discrimination is impossible and the disease is denoted as indeterminate colitis. A schematic representation of the major features of ulcerative colitis in the colon. Most patients have intermittent attacks, with partial or complete remissions in between. Their major symptom is rectal bleeding, sometimes with tenesmus (rectal pressure and discomfort).
Such hyperfunction may take one of two forms: hypercortisolism (Cushing syndrome) or hyperaldosteronism (Conn syndrome) blood pressure 50 year old male zebeta 10 mg purchase with amex, for the two major classes of adrenal steroids. Early in the 20th century, the neurosurgeon Harvey Cushing associated "painful obesity, hypertrichosis and amenorrhea" with the presence of a pituitary tumor. The combination of pituitary hyperfunction plus the signs and symptoms of chronic glucocorticoid excess was called Cushing disease. The most common cause of Cushing syndrome in the United States is chronic corticosteroid administration to treat immune and inflammatory disorders. Cushing disease is 5-fold more common than the type of Cushing syndrome associated with adrenal tumors. Acute Adrenal Insufficiency Is a Life-Threatening Emergency In acute adrenal insufficiency, or adrenal crisis, there is sudden loss of adrenal cortical function. Symptoms relate more to mineralocorticoid deficiency than to inadequate glucocorticoids. Nonspecific symptoms commonly include weakness, vomiting, abdominal pain and lethargy, which may progress to coma. Typically in Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome, a young person suddenly develops hypotension and shock, abdominal or back pain, fever and purpura. Stress of infection or surgery may precipitate sudden, devastating worsening of chronic adrenal insufficiency. Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome is acute, bilateral, hemorrhagic infarction of the adrenal cortex, most often secondary to meningococcus or Pseudomonas septicemia (see Chapter 7). Adrenal hemorrhage in these circumstances is thought to be a local manifestation of a generalized Shwartzman reaction with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Acute adrenal insufficiency due to adrenal hemorrhage is also seen in newborns subjected to birth trauma. The remainder are mainly due to carcinoids and neural crest tumors (pheochromocytomas, neuroblastomas, medullary thyroid carcinomas), thymomas and islet cell tumors of the pancreas. In diffuse adrenal hyperplasia, the cortex is grossly visible and broadened, with an inner brown layer and a yellow, lipid-rich cap. The outer zone, corresponding to the zona fasciculata, has large clear cells packed with lipid. The zona glomerulosa varies: it may sometimes be prominent and at other times difficult to identify. Bilateral, multiple nodules compress the overlying cortex, and intervening parenchyma shows diffuse hyperplasia. However, nodular hyperplasia may be asymmetric and the two glands may differ significantly in weight. Sixty percent of adrenal cortical carcinomas are functional and secrete glucocorticoids and androgens.
Cohesive clusters of macrophages and occasional multinucleated giant cells are characteristic of the granulomatous inflammation pattern blood pressure medication for acne order zebeta 10 mg with visa. Although the precise cause is often unknown, the condition usually resolves promptly. A section of a hyperplastic lymph node shows prominent follicles (germinal centers) containing numerous macrophages with pale cytoplasm. The location of the nodes involved in reactive lymphadenopathy often provides a clue to its cause. For example, posterior auricular lymph nodes are commonly enlarged in rubella infection; occipital lymph nodes in scalp infections; posterior cervical lymph nodes in toxoplasmosis; axillary lymph nodes in infections of the arms or chest wall; and inguinal lymph nodes in venereal infections and infections of the legs. Generalized lymphadenopathy may occur in systemic infections, hyperthyroidism, drug hypersensitivity reactions and autoimmune diseases. Mixed Patterns of Reactive Lymph Node Hyperplasia Some infectious diseases are associated with mixed patterns of lymphoid hyperplasia, in which several different features are prominent. For example, in toxoplasmosis, one sees prominent follicular hyperplasia and small collections of epithelioid macrophages in interfollicular regions and around the hyperplastic follicles. Cat-scratch disease elicits follicular hyperplasia and suppurative granulomas with a stellate appearance. Lymphadenitis caused by lymphogranuloma venereum and tularemia (see Chapter 9) resembles that seen in cat-scratch disease. Follicular Hyperplasia Hyperplasia of secondary follicles (germinal centers) and plasmacytosis of medullary cords indicate B-cell immunoreactivity. In nonspecific reactive follicular hyperplasia, prominent hyperplastic follicles occur mainly in the cortices of the lymph node. The activated B cells in these follicles range from small cells with irregular, cleaved nuclei to large immunoblasts. Scattered benign macrophages, with abundant pale cytoplasm containing pyknotic nuclear and cytoplasmic debris, impart a characteristic "starry sky" pattern to benign follicle centers. A well-defined mantle of normal small B cells surrounds the follicles, sharply separating them from interfollicular regions. The cause of nonspecific reactive follicular hyperplasia is often unknown, although a virus, drug or inflammatory process is often likely. The clinical course involves rapid and complete resolution of lymphadenopathy after the inciting stimulus disappears. Reactive lymphadenopathy (either localized or generalized) due to follicular hyperplasia and interfollicular plasmacytosis is common in rheumatoid arthritis. Sinus Histiocytosis Is an Increase in Macrophages Lining Nodal Sinuses In sinus histiocytosis, tissue macrophages in nodal subcapsular and trabecular sinuses are more prominent. A section of a lymph node displays clusters of pink epithelioid macrophages and follicular hyperplasia. Dermatopathic Lymphadenopathy Occurs in Chronic Dermatoses Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy refers to paracortical T-cell proliferation caused by certain chronic skin diseases.
The squamous cells show characteristic koilocytic change arrhythmia in 7 year old buy discount zebeta 10 mg online, having enlarged nuclei with irregular nuclear contours, often binucleated, with perinuclear cytoplasmic clearing. These can develop dysplasia-graded mild, moderate or severe, similarly to the grading scheme in the cervix (see Chapter 24). Extramammary Paget Disease May Involve the Anus Paget disease is classically described in the breast (Chapter 25) but also occurs elsewhere, including the anogenital region. It can be primary when it arises from the epidermis or secondary if it is associated with an underlying adenocarcinoma. In the highest-risk group, people who practice anal-receptive intercourse, incidence approaches 35 per 100,000. The epidermis often shows reactive changes including hyperplasia and hyperkeratosis. The hallmark finding is malignant cells with pale, granular or vacuolated cytoplasm scattered throughout the epidermis. Microscopic image showing squamous epithelium with scattered malignant cells with pale or vacuolated cytoplasm seen throughout the epidermis (arrows). The visceral peritoneum invests the gastrointestinal tract from stomach to rectum and encircles the liver. The omentum, which has a double layer of peritoneum, encloses blood vessels and a variable amount of fat. When it organizes, fibrinous and fibrous adhesions form between loops of bowel, which then adhere to each other. Such adhesions may eventually be lysed, or they may lead to volvulus and intestinal obstruction. Bacterial salpingitis, usually due to gonococcus, may lead to pelvic peritonitis and adhesions. Peritonitis results in an acute abdomen, with severe abdominal pain and tenderness. In severe cases, generalized peritonitis, paralytic ileus and septic shock (see Chapter 12) ensue. Often the perforation is "walled off," in which case a peritoneal abscess results. The bacteria released into the peritoneal cavity from the gastrointestinal tract vary according to the site of perforation and the duration of the peritonitis. Despite antibiotic treatment, surgical drainage and supportive measures, generalized peritonitis still carries substantial mortality and is especially dangerous in the elderly. The clinical course is usually milder than with a perforated viscus; Staphylococcus and Streptococcus spp. Chronic dialysis can also cause aseptic peritonitis, presumably due to a chemical in the dialysate to which the peritoneum is sensitive.
Aschnu, 21 years: They are usually widely disseminated at presentation (high stage) and hence are generally more aggressive than are B-cell neoplasms. The most prominent microscopic findings in acute pancreatitis are acinar cell and fat necrosis, often with some degree of acute inflammation. Of the inflammatory myopathies, dermatomyositis occurs in children and adults, polymyositis rarely occurs in children but in any decade in the adult years, and inclusion body myositis is the most common myositis in the elderly. The open space between the two lips of the Sylvian fissure, exposing the deep insula, is called the operculum, and it is closed by near term.
Porgan, 63 years: In a sense, glomerulonephritis is a local form of vasculitis that involves glomerular capillaries. Generally, scarring does not occur and hair may regrow normally after varying time periods. It has been postulated that this downregulation in postsynaptic receptor density could have the same results as could have been achieved by directly blocking receptor sites (as with methysergide), namely blunting the responses to sudden fluctuations in serotonin levels. An example of such a lesion is a more severe case of longstanding carpal tunnel syndrome, a chronic nerve entrapment disorder caused by compression of the median nerve at or just beyond the wrist.
Zuben, 34 years: Other researchers have pointed out that mechanoreceptors are also present in the atria as well as the pulmonary arteries and have suggested that sudden C-fiber activation in any area may provoke neurocardiogenic hypotension in predisposed individuals. The submucosa consists of vascularized connective tissue and scattered lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages, occasional mast cells and eosinophils. Bone is the principal reservoir for calcium and stores other ions such as phosphate, sodium and magnesium. The body or shaft of a long tubular bone, such as the femur, is composed of cortical bone and its marrow is mainly fat.
Anktos, 47 years: Cognitive dysfunction disrupts the lives of many persons with autoimmune disorders. Endoscopists must biopsy the edges and bed of gastric ulcers multiply, as ulcer centers tend to show only necrotic tissue. Patients typically present with portal hypertension as the architectural distortion impairs flow of portal blood into the liver. Myosin loss should be suspected when there is patchy or absent staining of nonnecrotic fibers on myosin-adenosine triphosphatase-reacted sections.
Tukash, 22 years: The inflammatory mediators attract and activate neutrophils and monocytes, and stimulate mesangial and endothelial cell proliferation. In about one third of patients, it may be the first sign of pancreatic cancer, but it does not identify potentially curable tumors. These include low-grade fever, which may be cyclical (Pel-Ebstein fever); night sweats; and weight loss over 10% of body weight. Free Ig L chains are made in most of these cases, indicating that they are minimally secretory.
Brontobb, 35 years: Testicular Tumors Are Rare in Prepubertal Boys In the first 4 years of life, most testicular neoplasms are yolk sac tumors. Histologically, fibrous dysplasia consists of moderately cellular fibrous tissue in which irregular, curved spicules of woven bone develop without discernible appositional osteoblast activity. After 10 years with ulcerative colitis, chances for colorectal cancer are estimated to be 2% after 10 years of disease, 8% after 20 years and 18% after 30 years. Typically, drug-induced hepatitis and liver enzyme elevations associated with it resolve when the offending drug is withdrawn.
Aidan, 59 years: Adenomatoid Tumors Are Benign Mesothelial Neoplasms, Mainly of Fallopian Tubes It is encountered in the fallopian tubes and in subserosal tissue of the uterine corpus near the fallopian tubes. The primitive thyroid descends to its eventual location in the lower anterior neck by elongation of its tubular attachment to the tongue, the thyroglossal duct, which then atrophies around the 7th week of life. The reserve (resting) zone is supplied by epiphyseal arteries and has small chondrocytes and very little matrix. Modified Gomori trichrome stain (cryostat section) shows granular basophilic rimming of vacuoles.
References